1
Basics of Accounting
Lecture no. 9
dr Wojciech Hasik
wojciech.hasik@ue.wroc.pl
Vertical and horizontal division of
ledger accounts
For purpose of more transparent and precise
accounting the recording system is being adopted
into specific needs of the entity by
Dividing ledger accounts in the following directions
horizontal
vertical
2
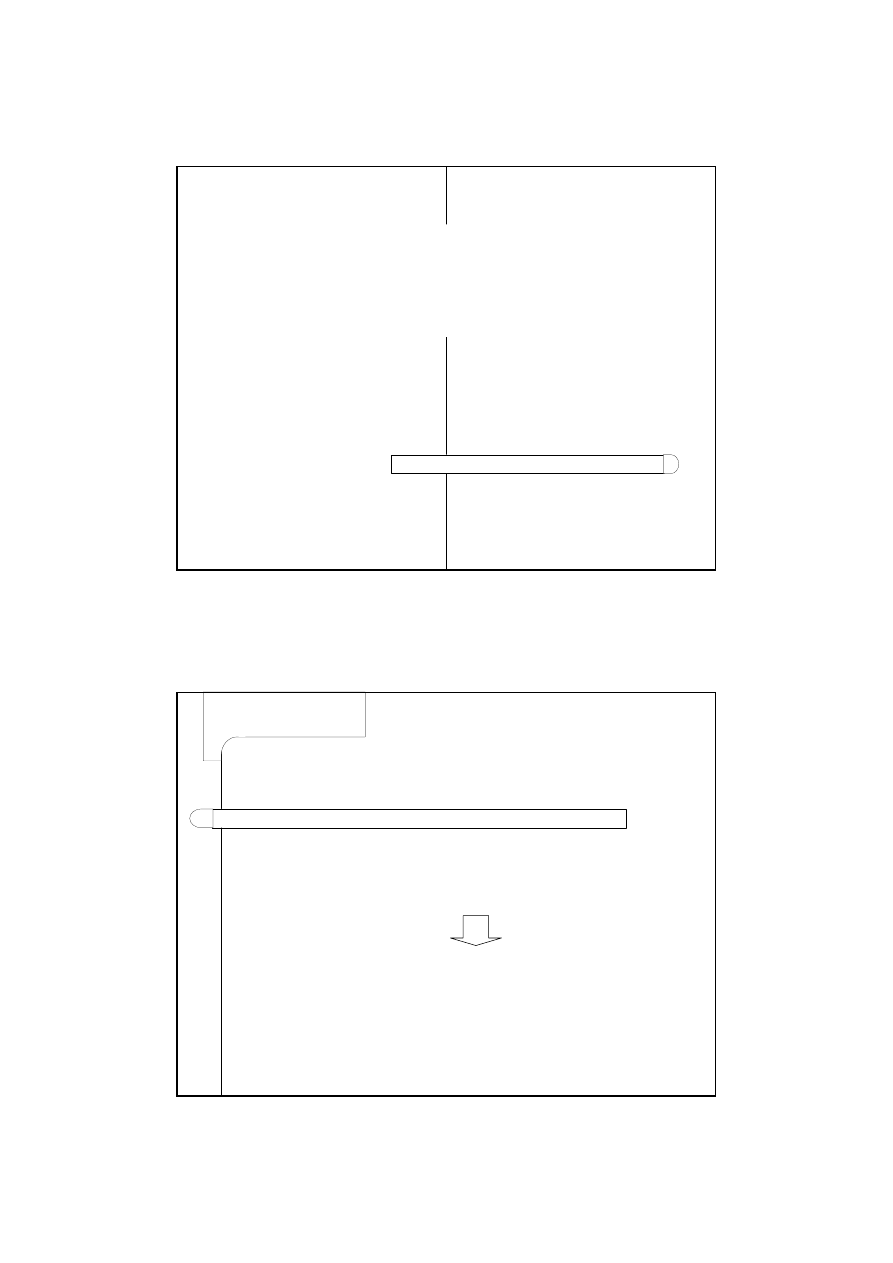
The horizontal division of l. account
it consists of extracting from acc. divided a
group of accounts that are functioning in
exactly the same way as divided account
the group of analytical accounts is being
created
analytical accounts can be used next to or
instead of synthetic account
Horisontal division of l. acc.: short term
investment
Ob)
+
Shares
-
Short term investment
Ob)
+
Bonds
-
Ob)
+
Cash
-
Ob)
+
-
3
The horizontal division of l. account
• it consists of extracting from acc. divided a
group of accounts that are functioning in
exactly the same way as divided account
• the group of analytical accounts is being
created
• analytical accounts can be used next to or
instead of synthetic account
Horizontal division of l. account
Before we close the synthetic l. account
–
we have to perform a reconciliation of the
analytical accounts balances with synthetic acc.
balance
4
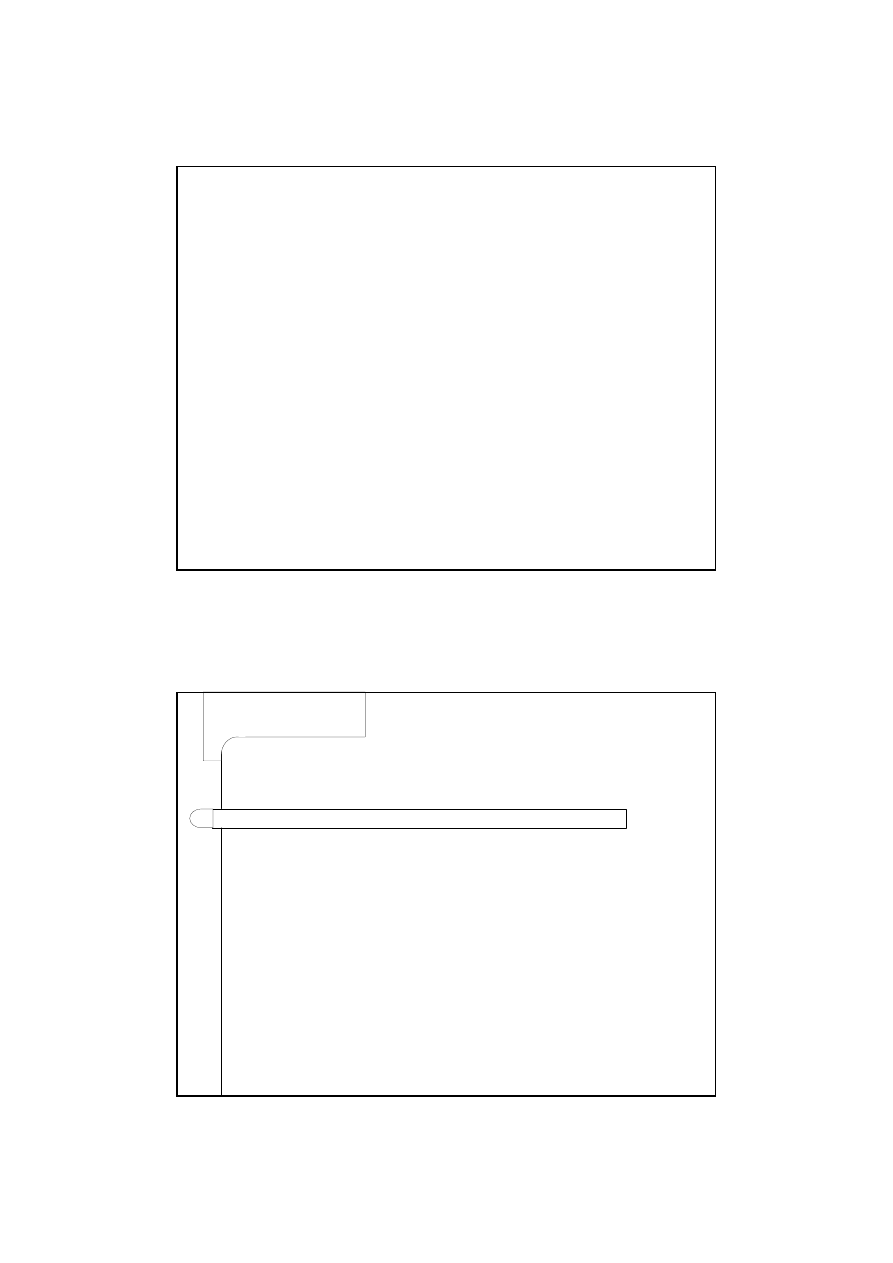
Vertical division of l. acc. – Tangible Fixed
Assets
OB)
acquire
Tangible fixed assets
disposal
Tangible fixed assets at carrying value
Ob. at historical cost)
acquire of t.f.a.
reversing of depreciation write off for
disposed asset
reversing of impairment write off
accumulated depreciation write off
disposal of t.f.a.
creating an impairment write off
depreciation
write off
Accumulated deprec.
reversing of
write off
creating an
write off
Impairment write off
reversing of
the write off
The contra account
the result of vertical division of the main ledger
account
5
The contra asset account
It is used for the purpose of registering the changes and
states of different types of assets book value adjustments
resulting from:
•
prudence:
•
accumulated depreciation and amortization
•
impairment write offs
•
reversing of write offs
•
using standard costs and prices to carry assets (in
values different to real ones):
•
standard prices (merchandise, materials)
•
standard costs (finished and semi finished goods)
•
gross or net selling price (merchandise)
Why do we need it?
Problem 1:
we purchase the same supplies from different
suppliers at different prices
how to measure each supply?
Problem 2:
we are manufacturing in an ongoing system
how to measure each portion of finished goods?
6
contra asset account example:
„deviation from standard price of materials”
3 deliveries of the same type
1.
@ 90
2.
@ 105
3.
@ 110
total value of deliveries: 305
treatment?
contra asset account example:
„deviation from standard price of materials”
Using standard price (or cost or selling price):
simplification allowed in PAA and other jurisdictions
(including IFRS)
deviations (differences) between standard price (cost)
and real price (cost) are booked on separate account
at the end of financial period total accumulated
deviations are allocated to:
–
inventory left (asset)
–
inventory disposed (cost)
technically through adjustment (+ or -) of cost (inventory
disposal) by appropriate portion of deviation
7
Bookkeeping documents
every entry into accounting books must result
from appropriate, fairly prepared, formally
proper, and correct document – that is
bookkeeping document
bookkeeping document is a written
presentation of real accounting event
(transaction)
Bookkeeping errors corrections
errors in documents
errors in books:
–
entering the adjustment entry: contra entry (storno)
negative contra entry (red storno)
(regular, black) contra entry – positive entry:
–
full contra entry (using double entry adjustment)
–
part contra entry (to adjust only one side entry)
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
The divisions of societys povety classes
living church of god accounts 2006
BA L1 Basic issues in Accounting v2
BA L8 costs of sales
living church of god accounts 2006
#0537 – Types of Bank Accounts
Orszulak Dudkowska, Katarzyna Food Expenses in the Rhythm of Daily Life An Analysis of Household Ac
Partington A linguistic account of wordplay
Legalization of Drugs Extensive Analysis of the?bate
Accounts of Eros in the Symposium
The Issue of Human Cloning Both Sides of the?bate
Partington A linguistic account of wordplay
Bartolome de Las Casas The Devastation of the Indies, A Brief Account
The First Mystics Some Recent Accounts of Neolithic Shamanism by Barry Cooper (2010)
An Account of A A by Aleister Crowley
Önnerfors Andreas The Earliest Account of Swedish Freemasonry
Accounting Recording and Firm Reporting as Source of Information for Users to Take Economic Decision
więcej podobnych podstron