STERILIZATION PROGRAMS,
AIR REMOVAL AND
STEAM PENETRATION
Peter Hooper
CEng MIMechE FIHEEM, United Kingdom
WFHSS Conference, Crete, October 2009

Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
Agenda:
How steam sterilization works
Why air is a problem
How is air removed
What are the effects of poor air removal
Different cycle types
Monitoring air removal

Steam sterilization works by:
Using steam to transfer energy from the boiler/generator to
the load in the sterilizer
The steam contains two packets of energy
1.
that to raise its temperature from cold to boiling point
2.
t
hat to turn boiling water into steam at the same
temperature
For each kilogram of steam energy 2 is approximately 4-5
times that of energy 1
When steam condenses energy 2 is given to the surface it
condenses on
– this condensation is vital
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam
Penetration

Why is air a problem?
It inhibits the access of steam (and hence energy transfer) to
ALL surfaces –
ie inhibits steam penetration
It acts as an insulator to inhibit energy transfer
It mixes with the steam to destroy the fixed
pressure/temperature relationship used to control the
sterilizer
It is non-condensible and contains little energy to transfer
Thus AIR MUST BE REMOVED FROM THE ENTIRE CHAMBER
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration

A steam sterilizer cycle consists of:
Air removal –
the stage without which sterilization will not occur
Heat-up
Sterilization –
the central 3 minutes of a 45-minute cycle
Steam removal
Drying
Air inlet
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
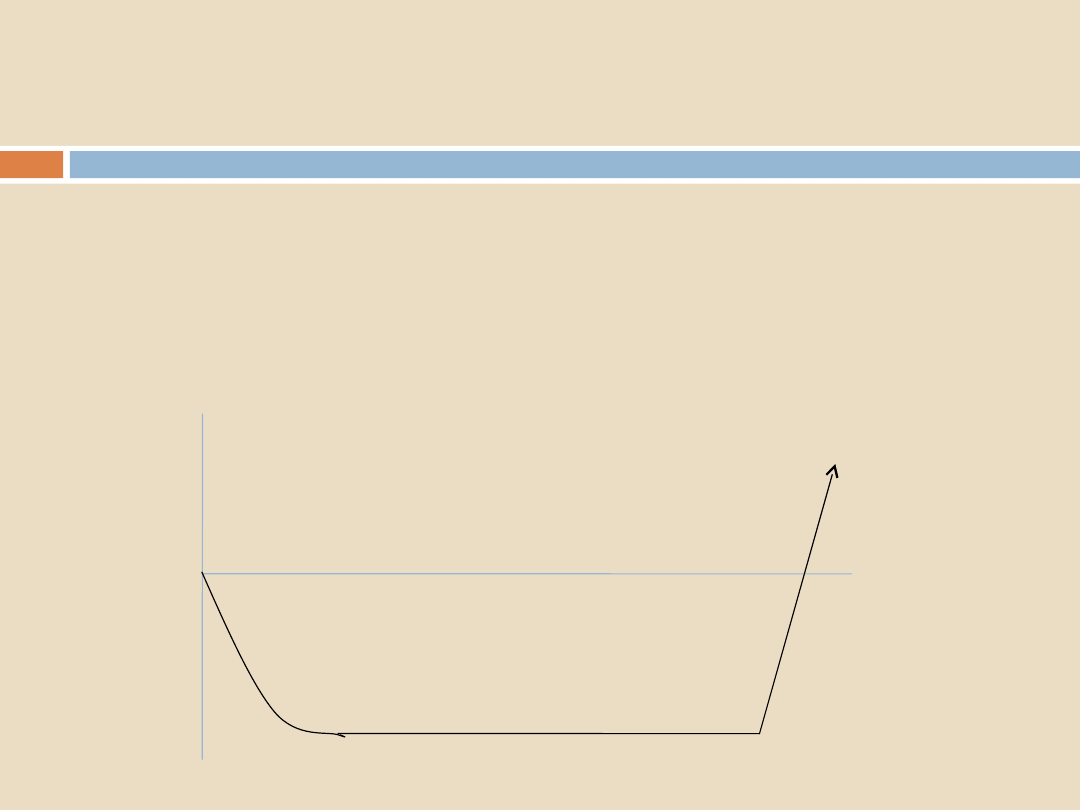
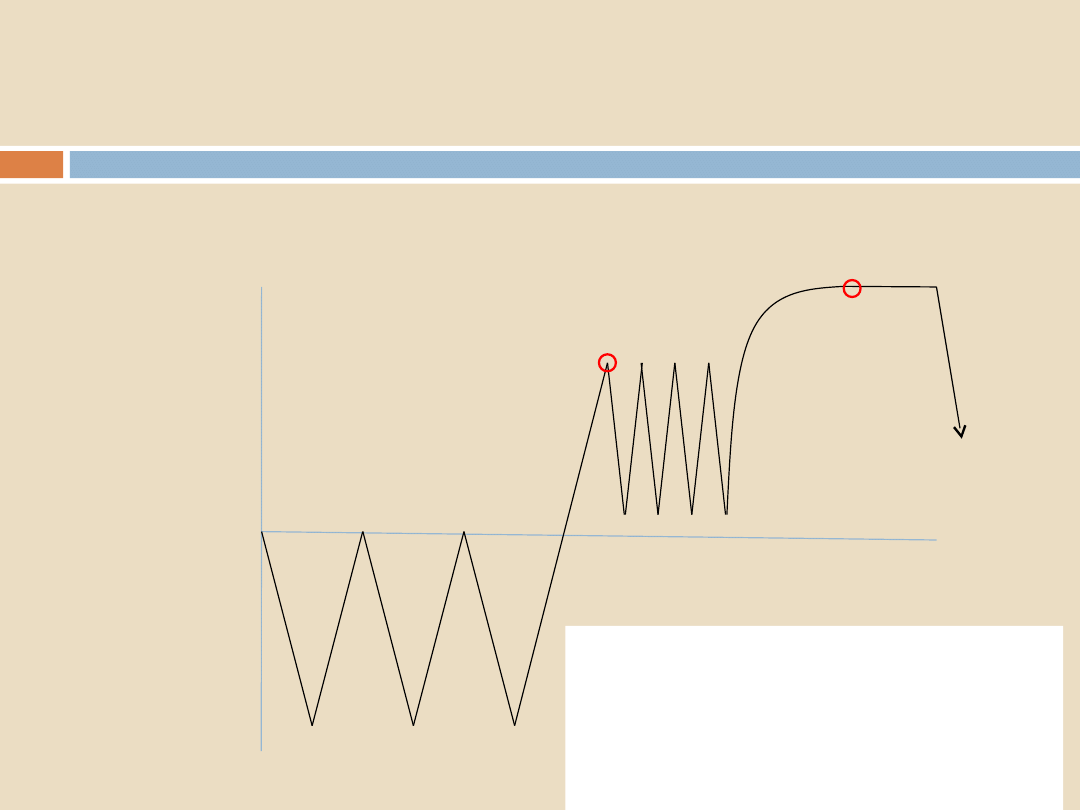
How is air removed?
1.
A long, deep vacuum at the start of the cycle?
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
TIME
PRESSUR
E
VACUU
M
ATMOSPH
ERIC
PRESSURE
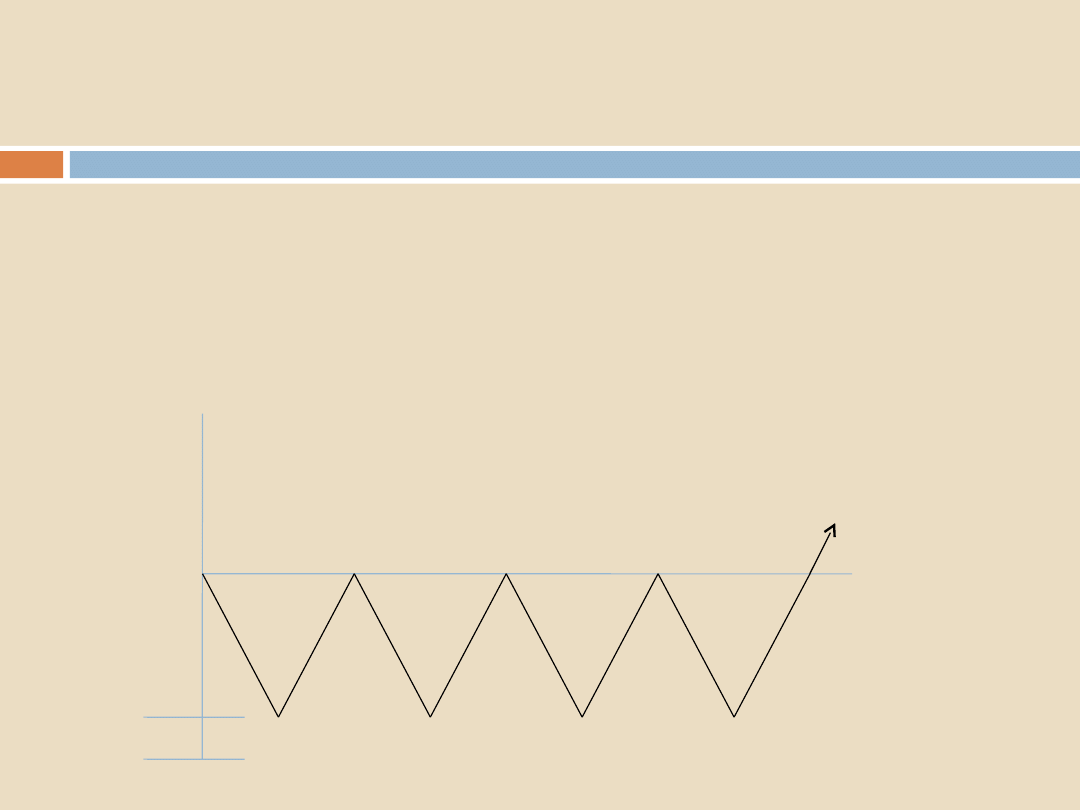
How is air removed?
2.
Pulsing
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
TIME
100% 10% 1% 0.1% 0.01%
AIR
0% 90% 99% 99.9%
99.99%
STEAM
10% 1% 0.1% 0.01%
AIR
0% 9% 9.9% 9.99%
STEAM
0 mbar
-900 mbar
-1000
mbar

Conclusion:
Pulsing is the most efficient method
The efficiency depends upon:
1.
The number of pulses
2.
The depth of each pulse
So which is the best pulsing system design?
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
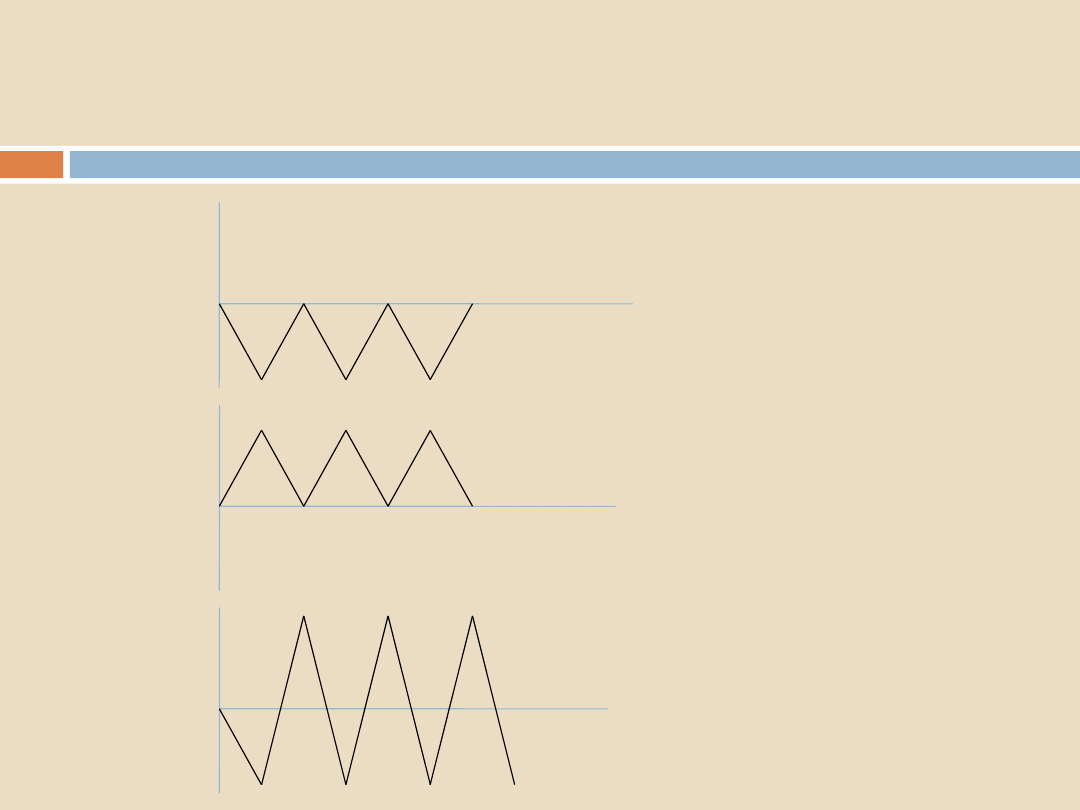
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
NEGATIVE
POSITIVE
TRANS_ATMOSPH
ERIC
1
2
3

Advantages & disadvantages:
Negative pulses
Can induce air through leaks
Positive pulses
Less efficient but no air ingress
Trans-atmospheric pulses
Most efficient but has negative sections
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
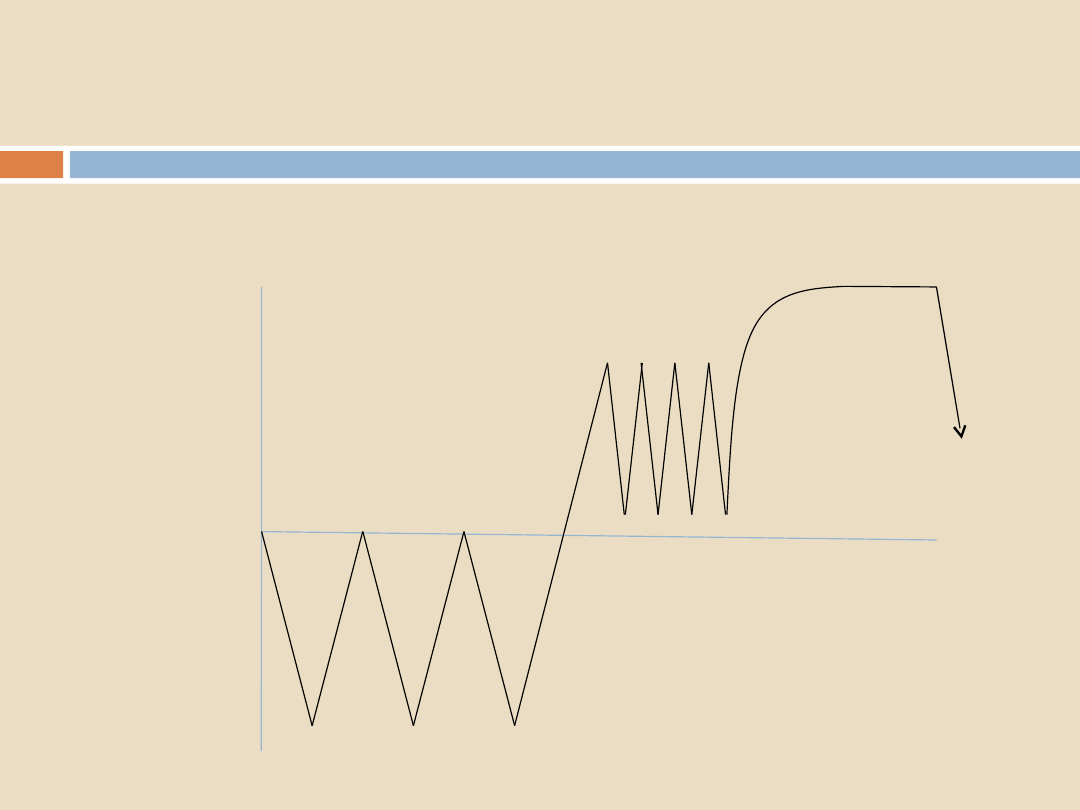
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
A possible final cycle – a compromise:
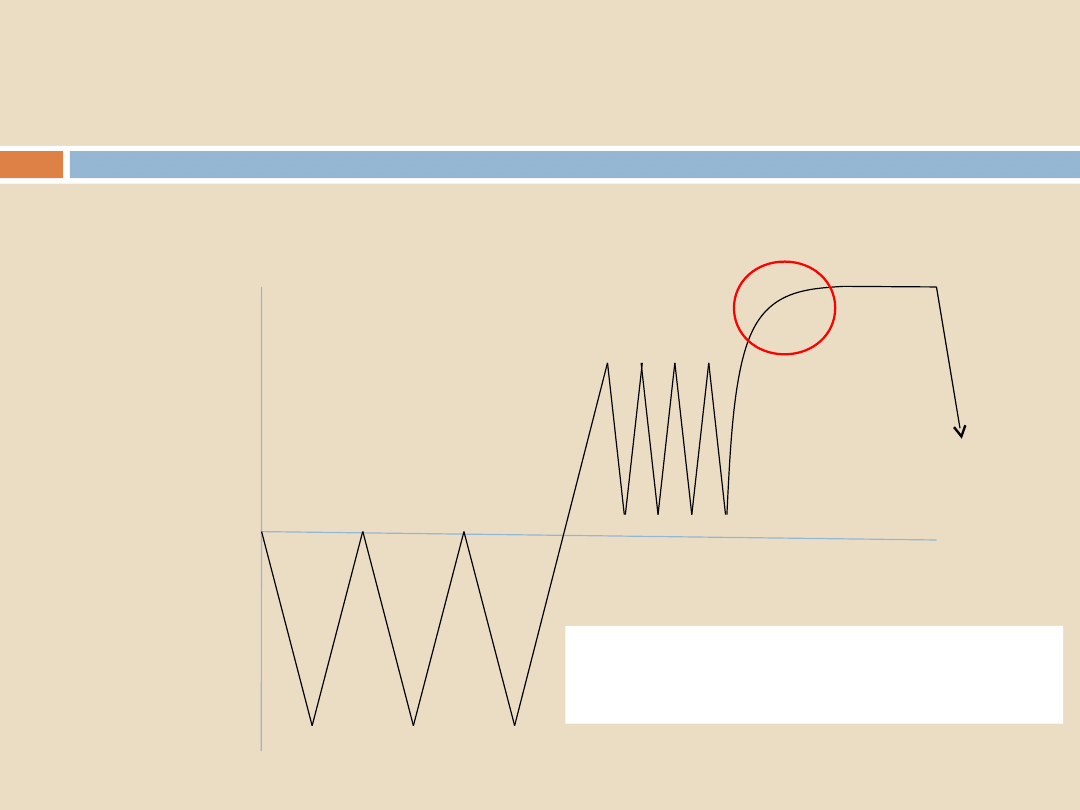
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
Important points for air removal:
1
1. Poor air-removal can be
identified here
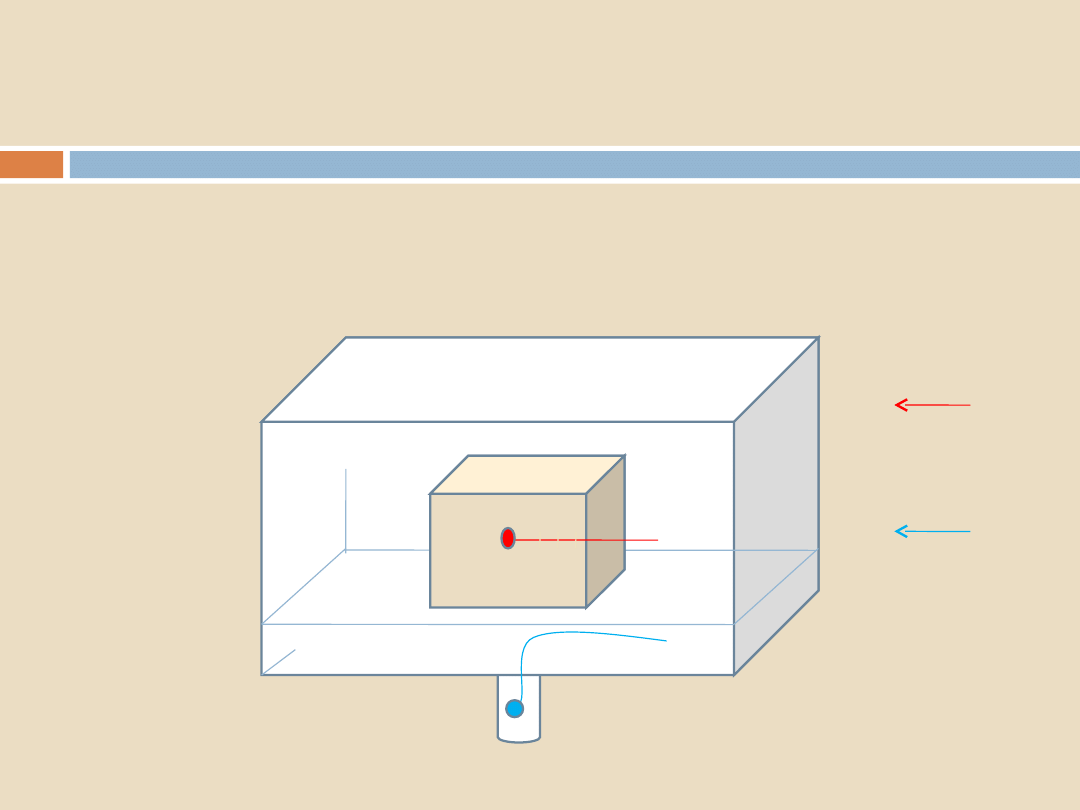
Measuring air-removal:
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
LOAD
CENTRE
DRAIN/
REFERE
NCE

Thermocouple traces: perfection
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
137 C
134 C
LOAD CENTRE
DRAIN/REFERENC
E
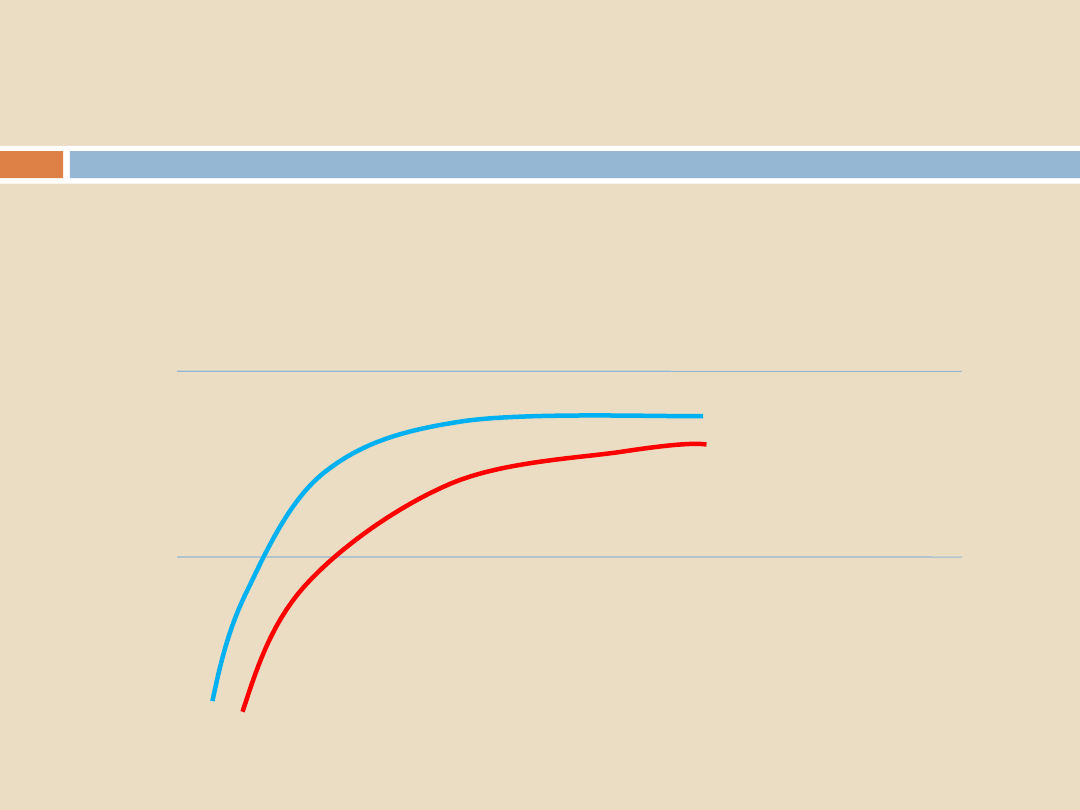
Thermocouple traces: reality
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
137 C
134 C
LOAD CENTRE
DRAIN/REFERENC
E
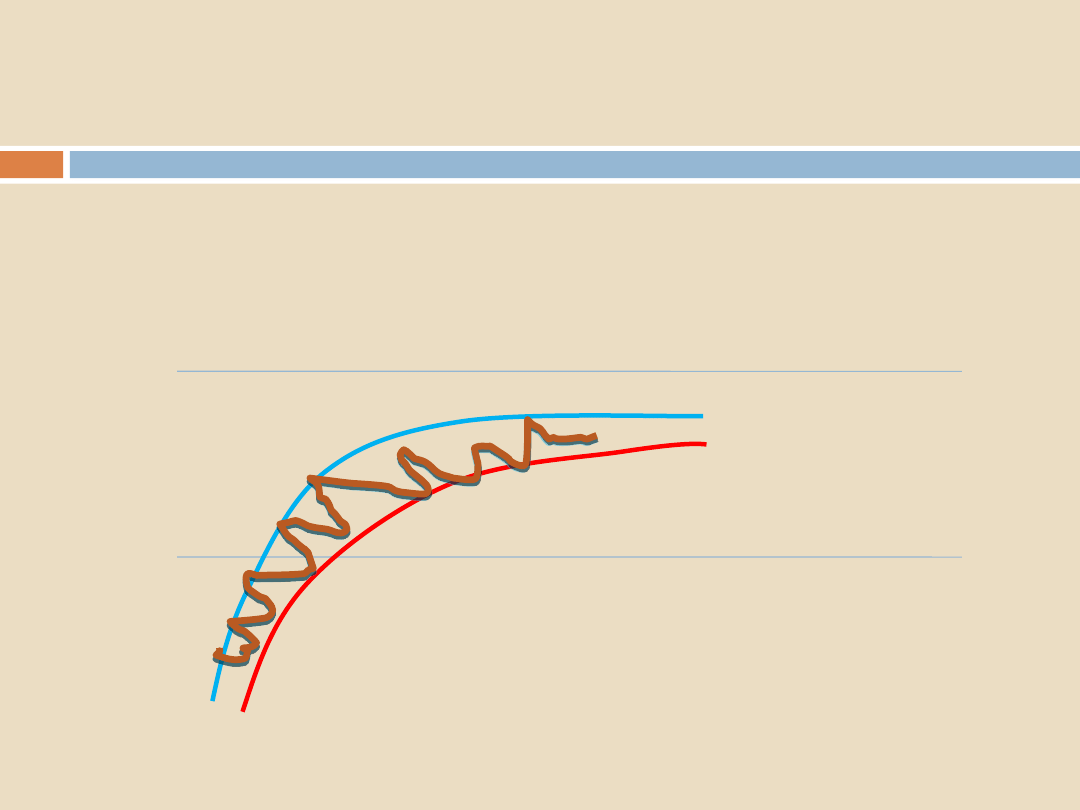
Thermocouple traces:
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
137 C
134 C
INDICATION OF POOR
AIR REMOVAL – the
greater the area the worse
the air removal
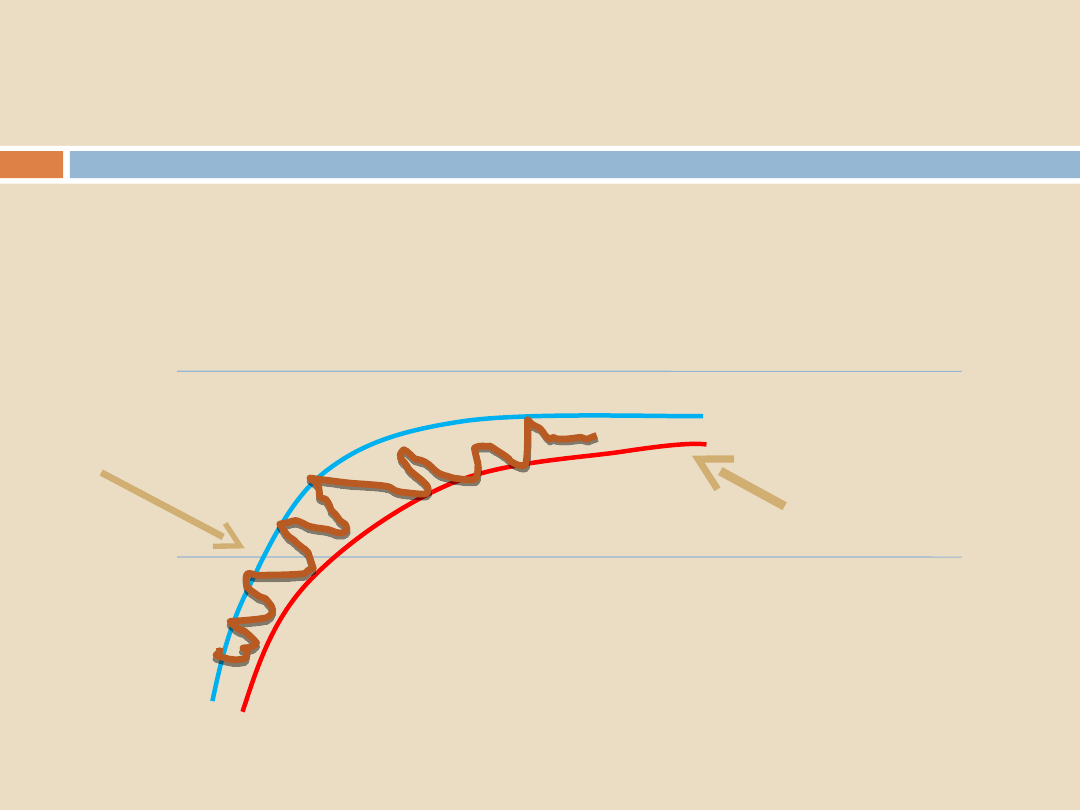
Thermocouple traces:
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
137 C
134 C
*
= points at which
measurement can be done
*
*
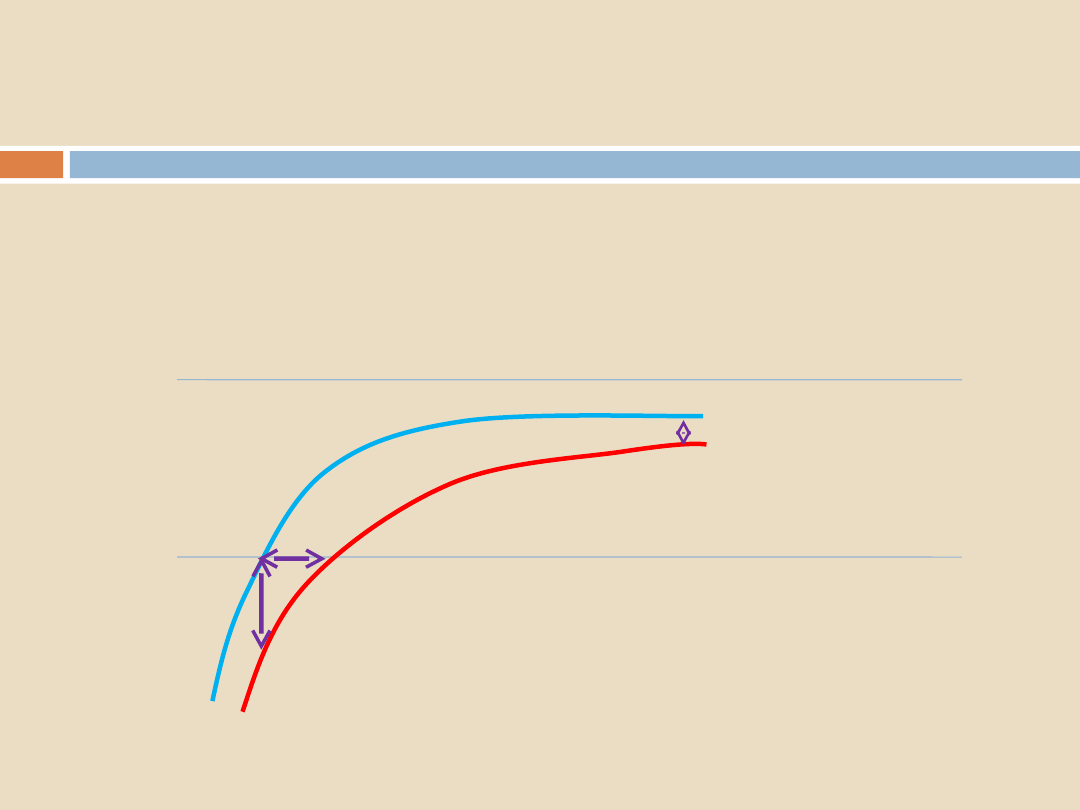
Quantification of thermocouple traces:
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
137 C
134 C
1: EQUILIBRATION
2: DEPRESSION
3: DIFFERENCE IN LAST 2 MINUTES
2
1
3
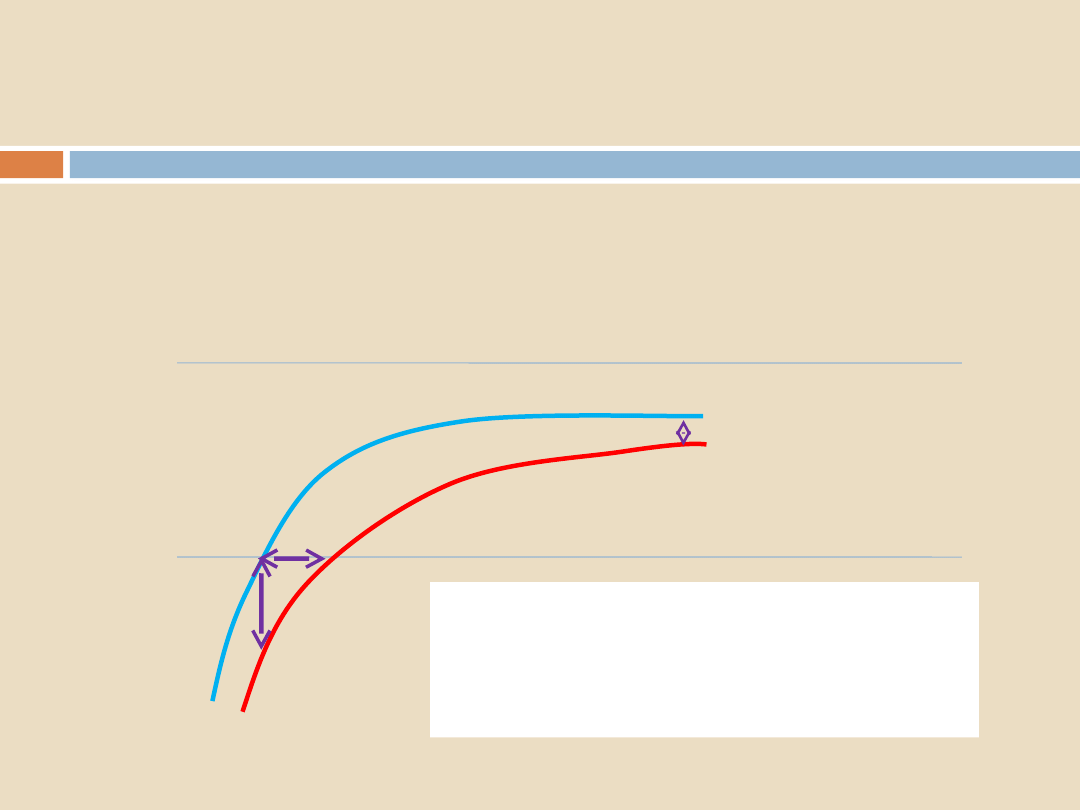
Quantification of thermocouple traces:
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
137 C
134 C
AIR REMOVAL CAN NOW BE
QUANTIFIED BY PUTTING VALUES
TO THESE THREE PARAMETERS
2
1
3
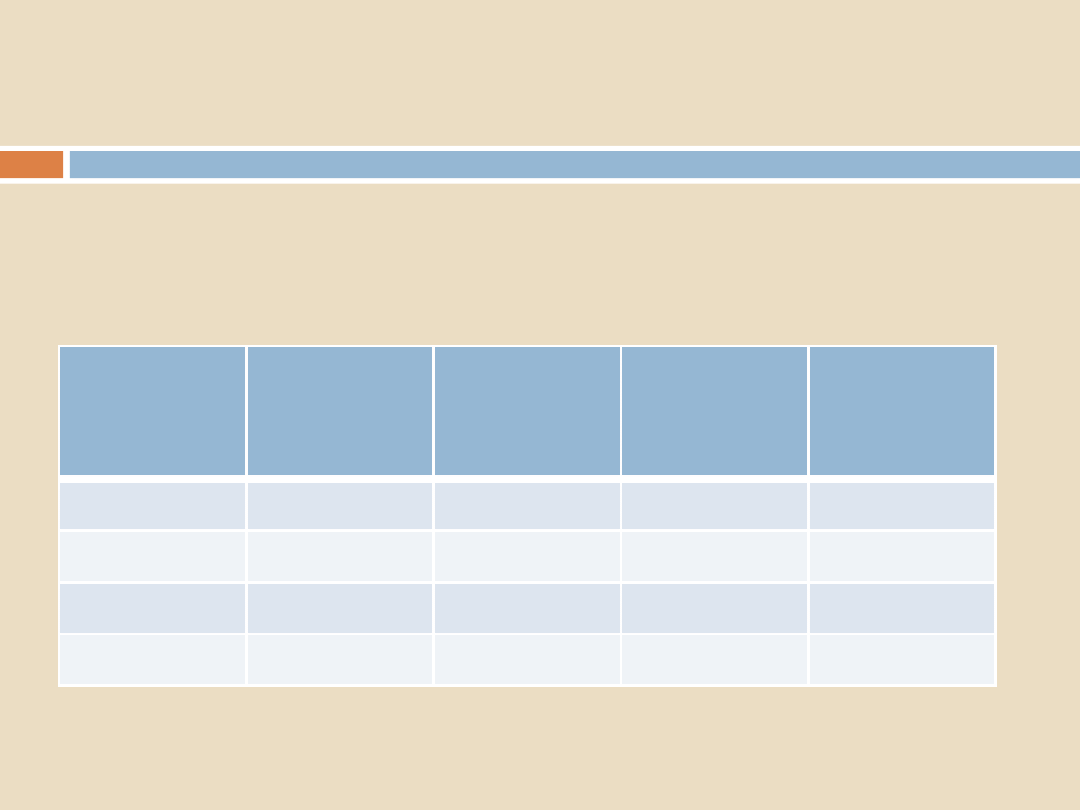
Comparison of parameter values in the UK:
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
DOCUME
NT
YEAR
1
equilibratio
n
2
depression
3
difference
HTM 10
1968
-
-
-
HTM 10
1980
-
-
0
HTM 2010
1994
15
2*
2
EN 285 >>
1994 >>
15
2*
2
* = for air detectors

Air removal monitoring:
Internal sensors and timers (control)
Bowie & Dick test (daily test
Process Challenge devices (in-chamber in-cycle
when used)
Air detector (external in-cycle every cycle)
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration

Bowie & Dick test:
Initially defined with Standard Test Pack (textile)
Later quantified via Standards
Parameter definitions used to define failure chemistry
NOTE: parameter values and test pack details may
differ in different parts of the World
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration

Air detector:
A device to automatically monitor the efficacy of the
air-removal process – it can automatically fail the cycle
if it measures unacceptable air removal
It can function each cycle
It is part of the control system, not an accessory
It can abort cycles at an early stage of air-removal
– ie it can be predictive
It must be validated and periodically tested with care
and skill
It is extremely accurate and precise
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration

Air detector:
It works by sealing a sample of chamber contents and, by
condensation caused by heat loss, separates residual
air
The amount of air can be measured by either its partial
pressure or temperature depression
It is part of the chamber but external to it to enable the
heat loss to occur
A temperature-operated air detector can be predictive
and can be used to monitor hold-time conditions
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
Important points for air detector:
1
1. A decision can be made here
to minimise lost productivity
2. It can also monitor NCG
levels
2

Summary:
Complete air-removal is essential to good sterilization
Pulsing is the most efficient method of air removal
A variety of pulsing systems may be used – they each have
benefits and disadvantages
Poor air-removal can be shown by thermometric testing
Thermometric data can be used to quantify air-removal and
thus define performance of air-removal monitors
Bowie & Dick test parameters can be thus defined but may
differ from place to place
An air-detector is an accurate and repeatable method of
monitoring every process cycle
Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration

Thank you
σε ευχαριστώ
Document Outline
- Sterilization Programs, Air Removal AND Steam Penetration
- Sterilization Programs, Air Removal and Steam Penetration
- Slide 3
- Slide 4
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- Slide 7
- Slide 8
- Slide 9
- Slide 10
- Slide 11
- Slide 12
- Slide 13
- Slide 14
- Slide 15
- Slide 16
- Slide 17
- Slide 18
- Slide 19
- Slide 20
- Slide 21
- Slide 22
- Slide 23
- Slide 24
- Slide 25
- Slide 26
- Slide 27
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
wfhss conf20091007 lecture sp op03 en
wfhss conf20091007 lecture sp s401 en
wfhss conf20100730 lecture sp s502 en
wfhss conf20091007 lecture sp s501 en
wfhss conf20091007 lecture sp s301 en
wfhss conf20091007 lecture sp s401 training programme en
wfhss conf20100730 lecture sp oc01 pt
wfhss conf20100730 lecture sp s901 pt
wfhss conf20100730 lecture sp s303 pt
wfhss conf20070503 lecture10 en
wfhss conf20070503 lecture03 en
wfhss conf20070503 lecture09 en
wfhss conf20070503 lecture05 en
wfhss conf20070503 lecture15 en
wfhss conf20080604 lecture1 02 it
wfhss conf20080604 lecture4 03 it
co acpce conf20070927 lecture c04 en
fr cefh conf20080409 lecture00 en
więcej podobnych podstron