
Fiber Optic Sensors
Properties, which can be sensed:
Displacement
Force
Liquid Level
Magnetic Fields
Motion
Temperature
Vibration
Position (linear, angular)
Pressure (fluid, gas, etc.)
Sound
Radiation
Speed
Weight
Pressure
How does a Fiber Optic Sensor work?
In a fiber optic sensor, one of the following characteristics of a propagating
lightwave is altered under an externally induced physical parameter:
Intensity
of light
Frequency
of light
Phase
of light
Polarization state
of light
Why are fiber optic sensors becoming so popular?
Small/lightweight
Allow access into normally inaccessible areas (often embedded)
Passive (non-electrical)
Highly sensitive
Easy to install
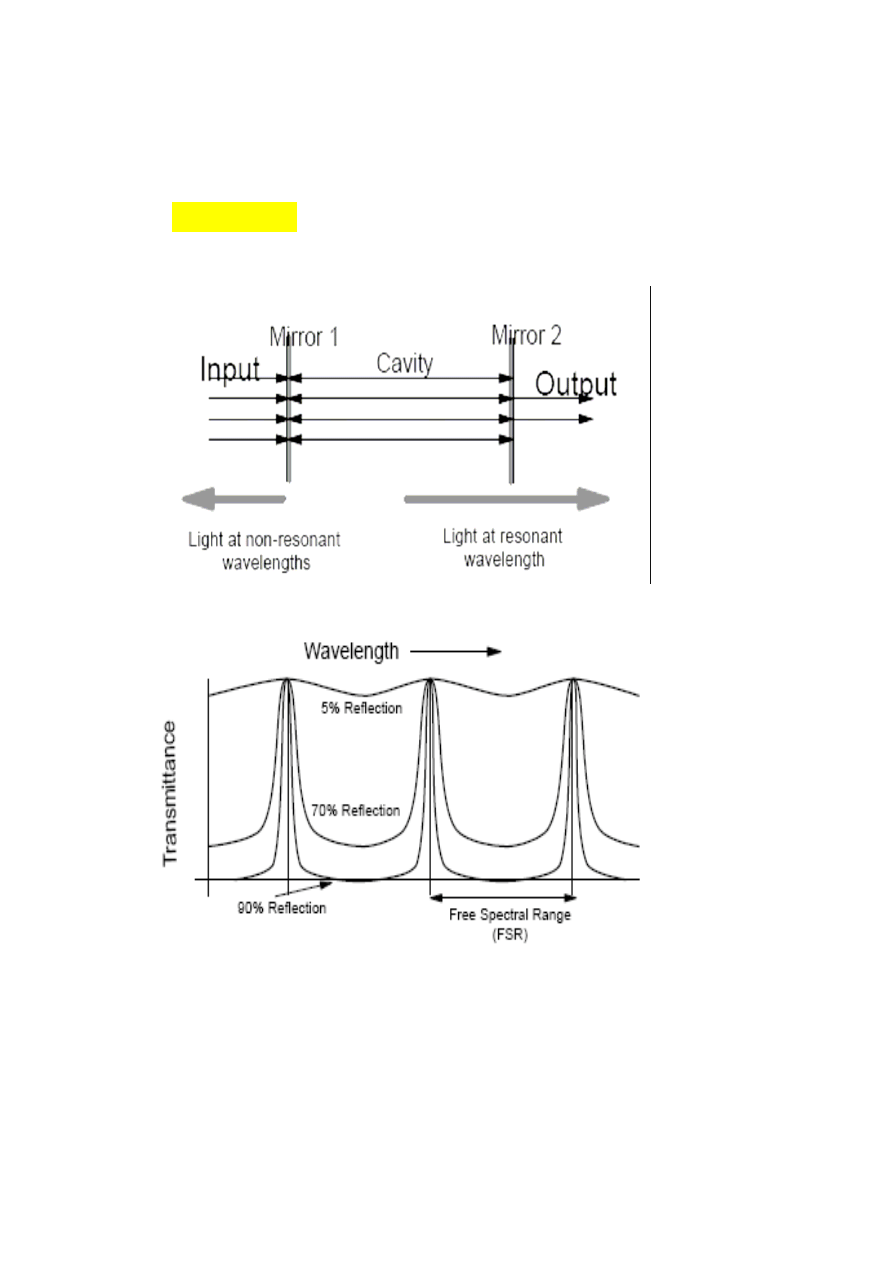
The Fabry-Perot fiber optic sensor.
Fabry-Perot Filter (interferometer)
The Fabry-Perot fiber optic sensor:
Principal applications:
Pressure, Strain, Temperature sensing etc.
Design of Fabry-Perot strain sensor:
Fiso, Inc. sensor: see www.fiso.com

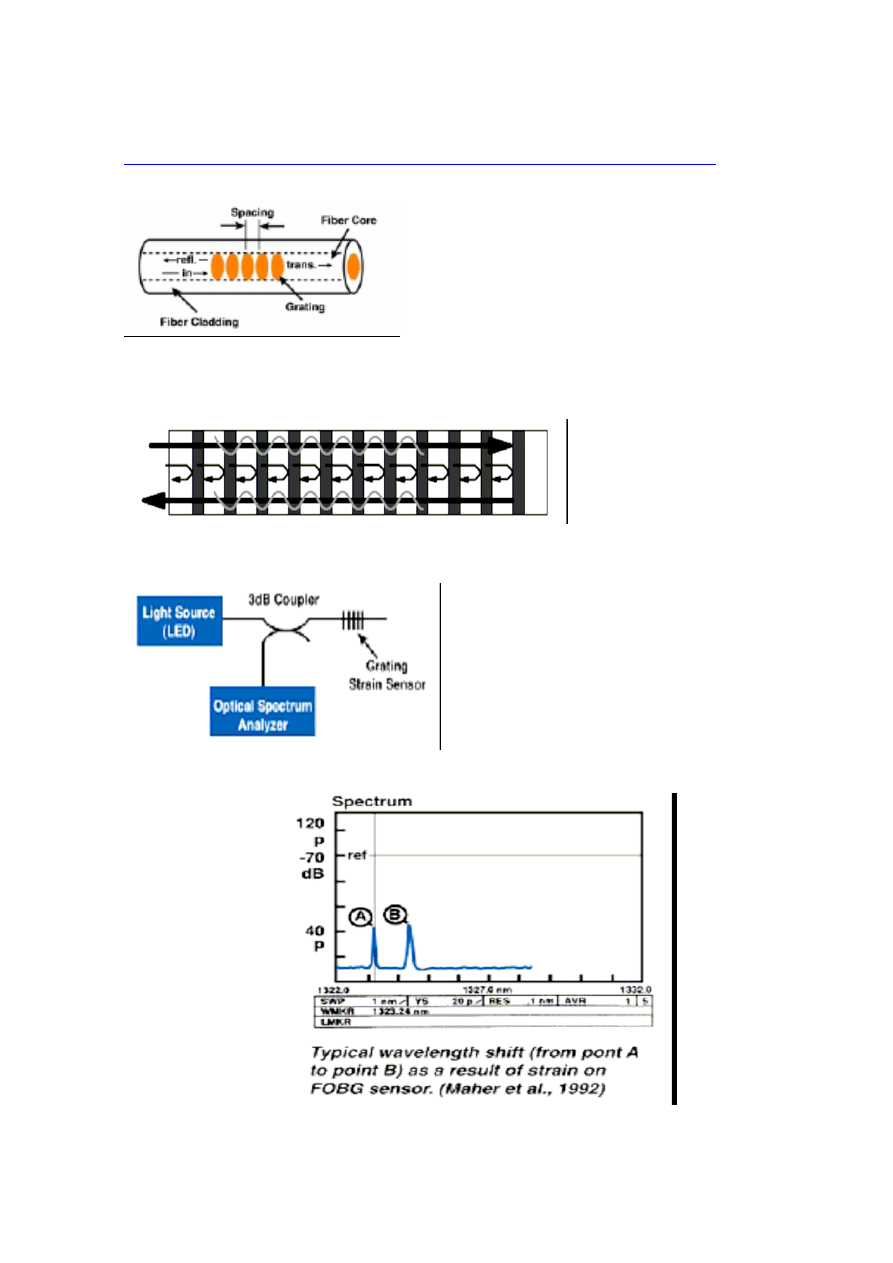
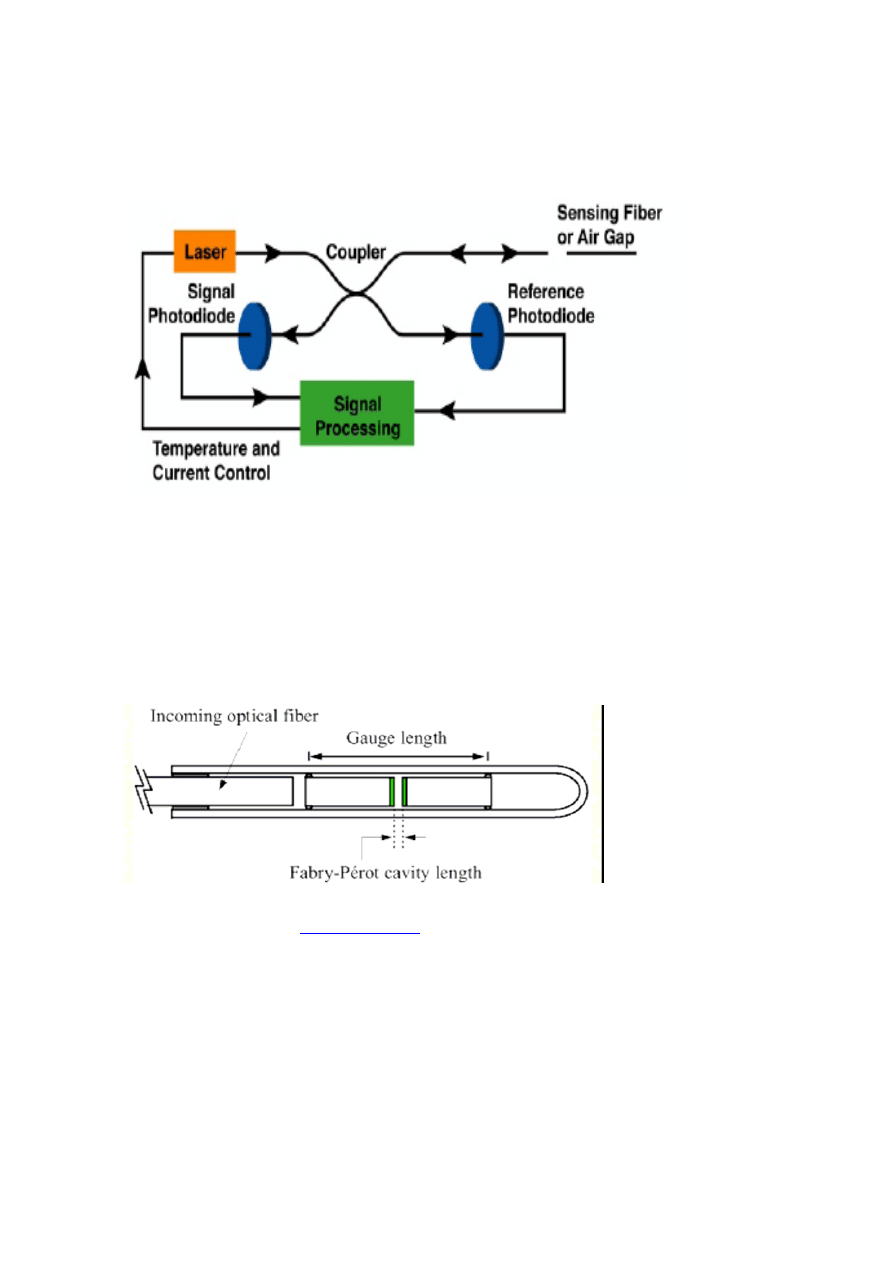
Fiber optic Bragg grating temperature and strain sensors
Schematic diagram of fiber Bragg grating
Principle of operation of fiber Bragg grating:
Schematic of instrumentation for fiber optic Bragg
sensor.

Fiber optic Bragg sensors advantages:
High sensitivity
Low –cost sensors
Small/lightweight
Linear response
Drawbacks
Sensitive to more than one parameter
Require relatively expensive processing equipment
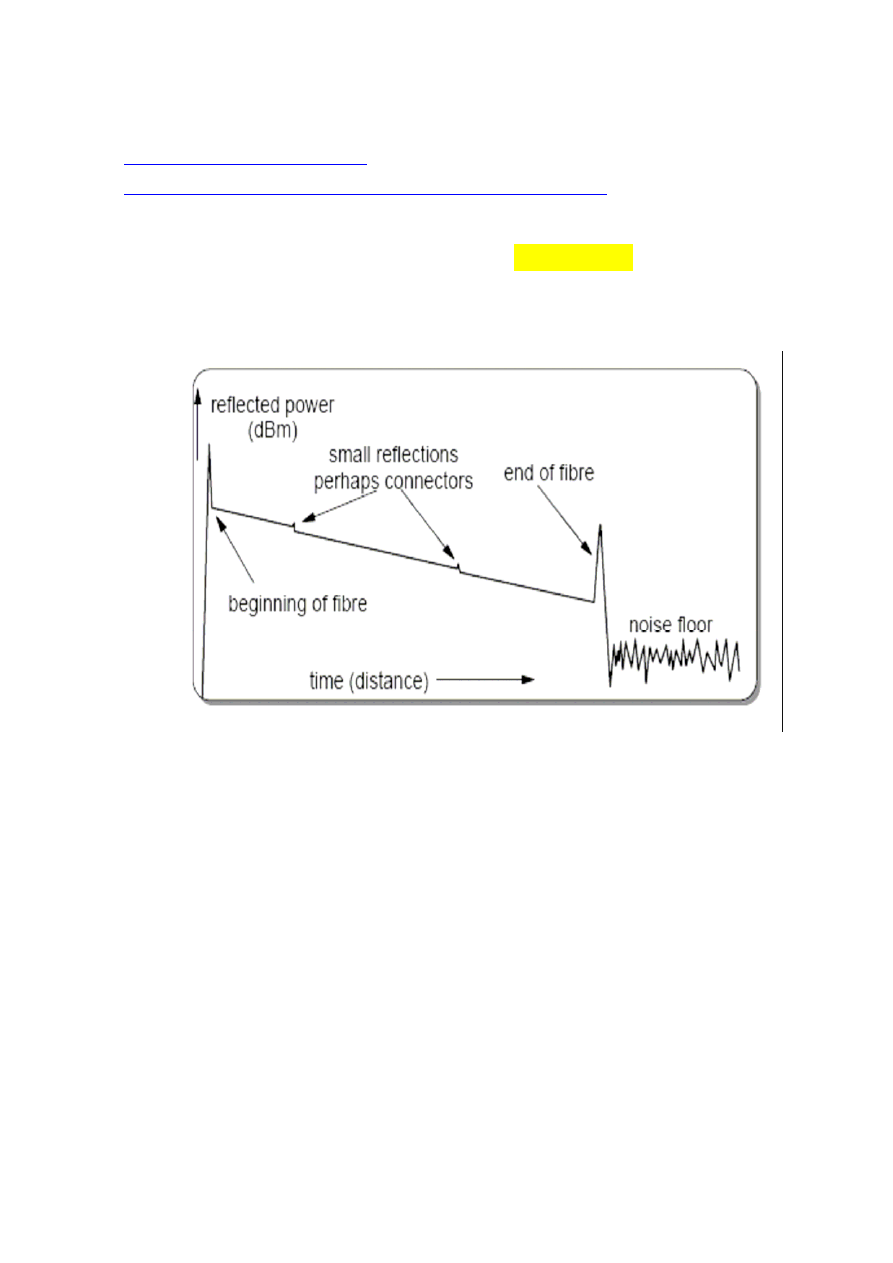
Fiber Optic Sensing by
Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (OTDR)
The Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer enables us to look at a fiber link
from inside the fiber. In reality it is just a radar system for looking at fiber.
High intensity pulses are sent into the fiber from a specialised laser and
when the pulse returns its strength is displayed on an oscilloscope screen in
the form of a trace. A schematic of such a display is shown in Figure
In the trace you see reflections coming from all along the fiber itself. This
is the result of Rayleigh scattering. Rayleigh scattering was mentioned in
the chapter on optical fiber as the major limiting factor in fiber attenuation.
This scattering occurs backwards towards the transmitter and we can
receive it and display the result.
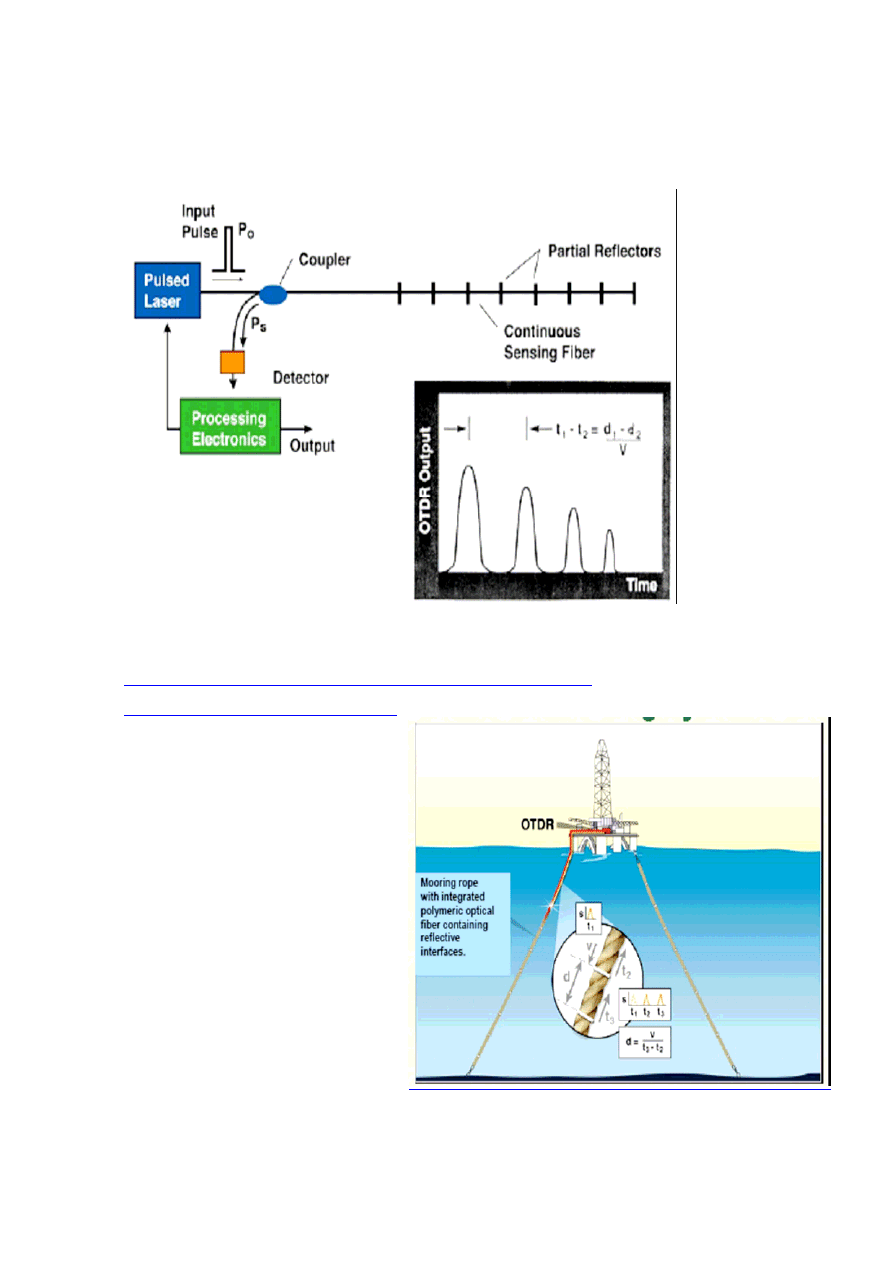
Fiber optic sensing by OTDR.
Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer- Based
Strain Monitoring System

Fiber optics is emerging as a mainstream sensor technology capable of
measuring numerous physical parameters;
New low-cost sources, detectors, and processing hardware and industry
maturity are making FO sensors more cost effective.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Glomb Architecture for Fiber Optic Sensors and Actuators in Aircraft Propulsion Systems
9 Guidelines for Fiber Optic Design and Installation
19 Appendix A Glossary of Fiber Optic Terms
5 Specifying Fiber Optic Cable
20 Appendix B Fiber Optic Standards
6 Fiber Optic Connectors, Splices, and Tools
7 Fiber Optic Hardware
17 Fiber Optic Testing
13 Fiber Optic Cable Plant Documentation
3 Fiber Optic Networks
1 The Origins of Fiber Optic Communications
14 Estimating and Bidding Fiber Optic InstallationX
11 Fiber Optic Installation Safety
16 Fiber Optic Restoration
15 Fiber Optic Cable Pulling
więcej podobnych podstron