
Cloud Integration:
4 Key Recommendations
White Paper

Talend White Paper
4 Key Recommendations for Cloud Integration
Page 2 of 14
Table of Contents
Introduction .................................................................... 3
Cloud Computing Adoption on the Rise ................................... 4
Cloud Especially Attractive for SMBs .................................. 4
What Does Cloud Computing Mean to You? ............................... 5
Private Cloud ............................................................. 5
Public Cloud .............................................................. 6
Hybrid Cloud .............................................................. 6
Integration Required, Yet Concerns Block Cloud Adoption ........... 7
Main Characteristics of Integration for Cloud ............................ 8
Elasticity .................................................................. 9
Ubiquity ................................................................... 9
Extensibility ............................................................. 10
Security and Reliability ................................................ 11
A Unified Approach to Cloud Integration ................................ 11
What to Look for in a Cloud Integration Solution ..................... 12
Conclusion – Five Questions to Ask ....................................... 12

Talend White Paper
4 Key Recommendations for Cloud Integration
Page 3 of 14
Introduction
Cloud computing is changing how businesses manage their IT assets
and automate their business processes. In this new environment, IT
resources are no longer housed solely on-premise and boundaries of
business-to-business applications have become blurred.
As business solutions evolve to embrace cloud computing, it is only
natural that integration solutions must change as well. The old
approaches to integration based on centralized hubs no longer suffice.
The elasticity, ubiquity and extensibility of the cloud demand a new
class of integration solutions that must traverse corporate and
geographic boundaries and must be able to adapt to changing business
needs. Forward-thinking organizations choose integration solutions
that can not only address the needs that cloud computing presents
today but also adapt to future challenges.
Open source integration solutions that are lightweight, easily
embedded and modular are the best option for integrating today’s
hybrid cloud deployments. And with enterprise features such as
security and reliability, such integration solutions can help address the
perceived weakness of cloud-based applications for mission-critical
business functions.
This white paper presents the key characteristics of cloud computing,
the integration challenges this deployment model introduces, four
recommendations for what to look for in a solution and five key
questions you should ask when considering cloud integration solutions.

Talend White Paper
4 Key Recommendations for Cloud Integration
Page 4 of 14
Cloud Computing Adoption on the Rise
Business users were first attracted to cloud-based applications and
software-as-a-service (SaaS) from vendors like Salesforce.com,
NetSuite and WorkDay because they are easy to use, manage and
provision, and they offer a ―pay as you go‖ pricing model. According to
a recent eWeek survey, 64 percent of companies have implemented at
least one SaaS application in the past two years. By 2013, that number
is expected to increase to 77 percent, and nearly half of these
organizations plan to roll out at least four SaaS applications.
i
Gartner defines cloud computing as ―a style of computing where
scalable and elastic IT-related capabilities are provided as a service to
customers using Internet technologies.‖ As companies continue to look
for ways to reduce costs and gain flexibility in their IT infrastructures,
cloud computing applications and platforms offer substantial benefits.
These include:
Rapid time-to-value. With no hardware or software to deploy
and manage, cloud-based applications minimize the demand on
IT resources and speed time to production.
Cost efficiency. Subscription-based pricing models make cloud-
based applications and platforms more affordable upfront.
Organizations pay only for the resources they use and can
monitor their usage to ensure a greater return on investment
(ROI).
Ease-of-use. Setting up and maintaining SaaS applications is
achieved through configuration, not coding—an approach that
organizations often can handle with minimal training.
Cloud is Especially Attractive for SMBs
Small- to mid-sized businesses (SMBs) are embracing SaaS and cloud-
based solutions even more rapidly than larger enterprises. According
to IDC, ―small and medium-sized business cloud adoption will surge.

Talend White Paper
4 Key Recommendations for Cloud Integration
Page 5 of 14
Adoption of some cloud resources will top 33% among U.S. midsize
firms by the end of 2011.‖
ii
Yet Gartner estimates that 10% of SMBs
with less than 100 physical servers will move their data centers
entirely to the Cloud by 2015. The majority of SMBs will need to
integrate on-premise infrastructure with cloud-based applications.
Gartner Dataquest Market Trends – We estimate by 2015
that 10% of SMBs with fewer than the equivalent of
100 physical servers will move their data centers
entirely to external clouds.
iii
Cloud application platforms have stepped up their offerings to go
beyond mere productivity applications, such as email, spreadsheets
and word processors, to offer real business applications like CRM and
ERP. These emerging offerings make cloud computing especially
attractive to SMBs, as they have access to the robust functionality that
was previously only available to large enterprises, and at significant
expense.
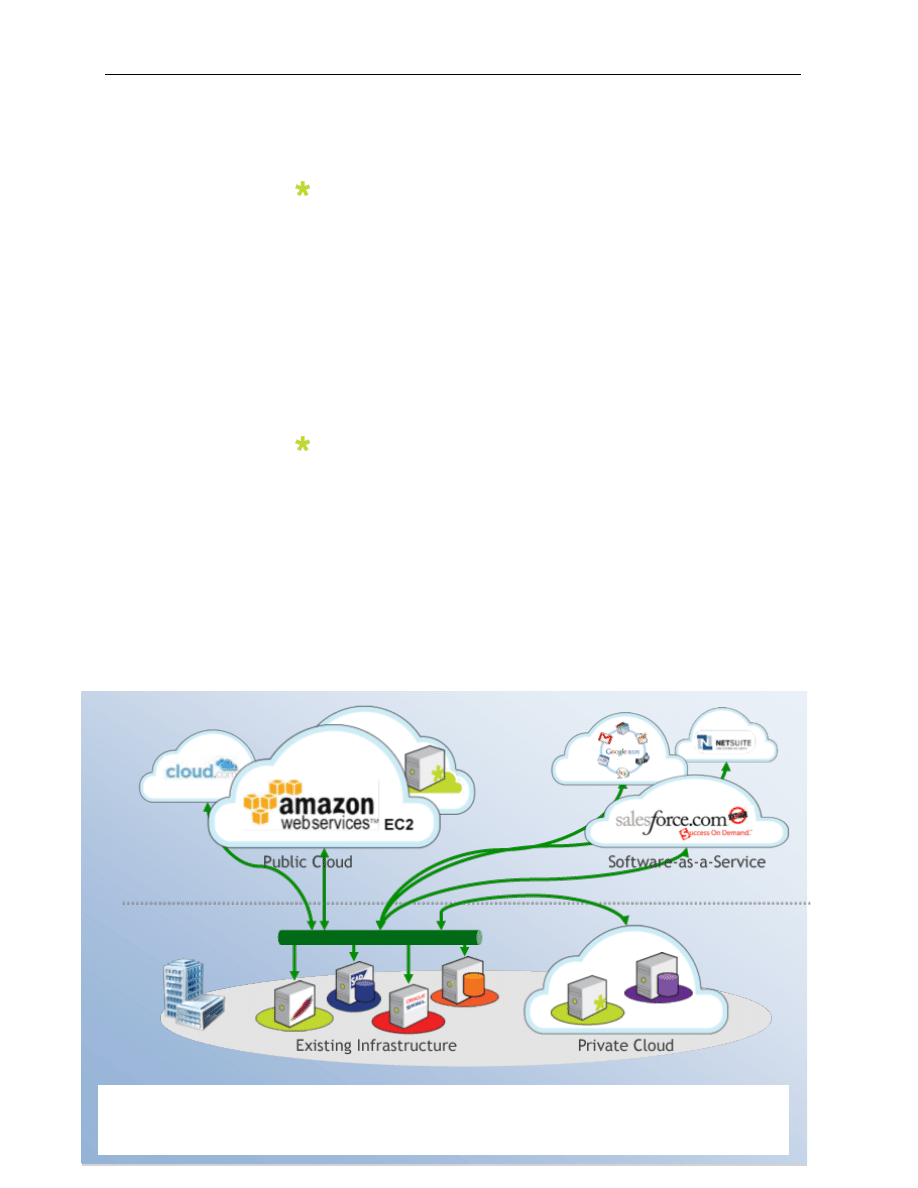
What Does Cloud Computing Mean to You?
As organizations evolve to embrace cloud computing, it is only natural
that integration solutions must change as well. In addition to SaaS,
many businesses are supported by a complex ecosystem consisting of a
combination of on-premise, platform-as-a-service (PaaS), e-
commerce, and cloud-based applications. There are three models of
deployment for cloud – private, public and hybrid cloud.
Private Cloud
With a private cloud, the cloud infrastructure (e.g., mission,
security requirements, policy, and compliance considerations) is
operated solely for an organization. It might exist on- or off-
Talend White Paper
4 Key Recommendations for Cloud Integration
Page 6 of 14
premise and could be managed by the organization or a third
party.
Public Cloud
A public cloud infrastructure is typically made available to the
general public or a large industry group and can be owned by an
organization selling cloud services or shared by several
organizations to support a specific community that has shared
concerns. It may be managed by an organization(s) or by a third
party. As with a private cloud, it could exist on-premise or off-
premise.
Hybrid Cloud
In a hybrid cloud, the infrastructure is a composition of two or
more deployment types that remain unique entities but are
bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that
enables data and application portability (e.g., cloud bursting
for load balancing between clouds). Hybrid clouds often
incorporate on-premise infrastructure.
Figure 1: Organizations might implement any combination of the three deployment models of cloud –
private, public and hybrid.
.
Talend White Paper
4 Key Recommendations for Cloud Integration
Page 7 of 14
What the cloud means to your organization – including which
deployment models you choose to implement – will help to guide your
requirements for an integration solution.
Integration Required, Yet Concerns Block Cloud Adoption
Just as cloud infrastructure is not particularly useful without software
applications that run on it, cloud applications and platforms are not
very valuable unless they can reuse the critical corporate data that is
typically locked away in various on-premise systems.
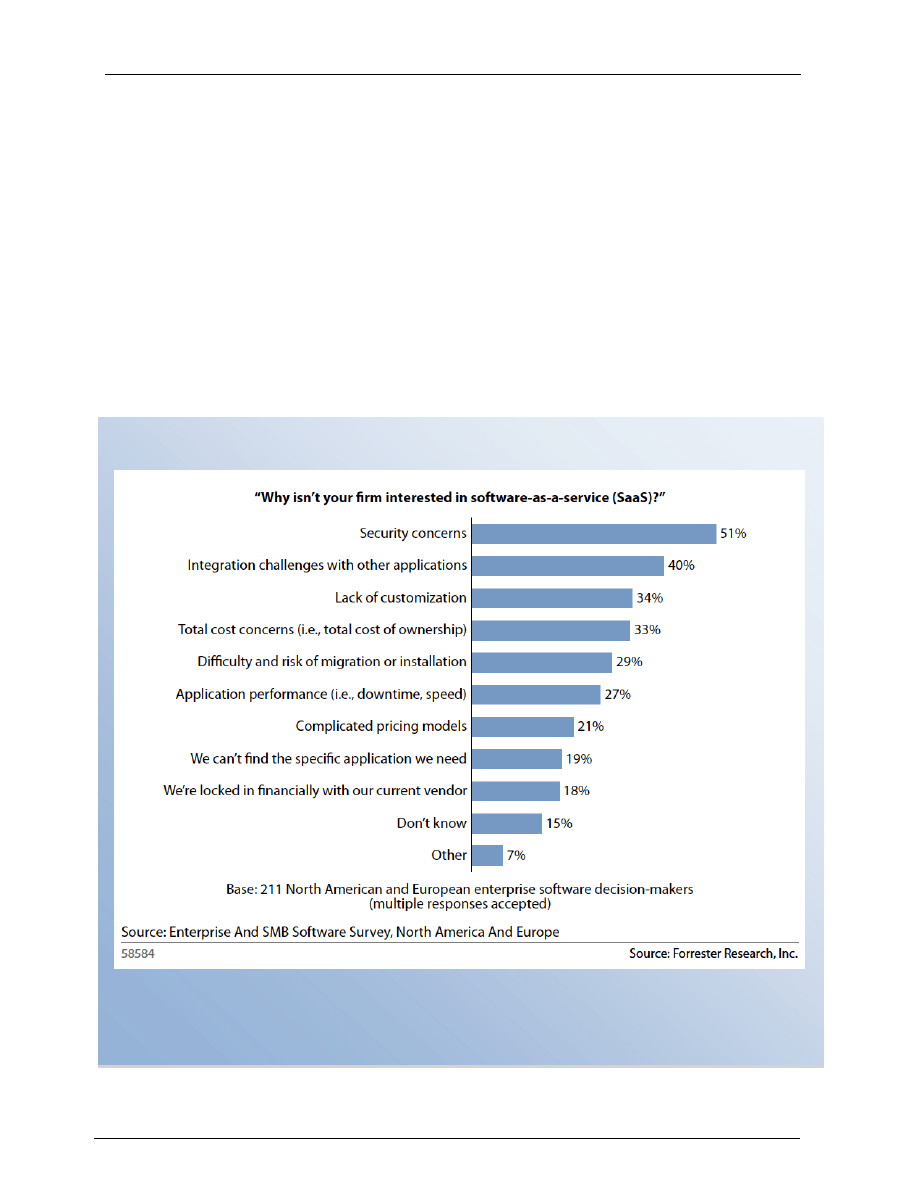
Figure 2: In a recent study conducted by Forrester Research, “integration challenges with other
applications” is cited as the second highest barrier to cloud adoption.
Integration Challenges Are Impeding Cloud Adoption

Talend White Paper
4 Key Recommendations for Cloud Integration
Page 8 of 14
For cloud applications and platforms to provide maximum value, they
need to seamlessly integrate and stay synchronized with both on-
premise and other cloud-based applications and data sources. Yet
―integration challenges with other applications‖ is cited as the second
highest barrier to cloud adoption. This should come as no surprise.
In this new environment, IT resources are no longer contained in
private data centers, blurring the integration boundaries for many
cross-functional applications. Choosing the appropriate integration
solution can mean the difference between success and failure to your
cloud initiative. Forty-two percent of organizations are looking to
implement solutions to address on-premise to cloud integration in the
next two years, and integration vendors need to step up to address
this underserved market.
Main Characteristics of Integration for Cloud
As business solutions evolve to embrace cloud computing, it is only
natural that integration solutions must change as well. The added
complexity of these hybrid environments requires significant
integration and coordination between the on-premise and off-premise
applications and data sources. The old approaches to integration
solutions, based on centralized hubs, no longer suffice.
Today’s integration solutions must traverse corporate and geographic
boundaries and be able to adapt to changing business needs. Solutions
that cannot integrate numerous platforms, data sources and
applications will fail. Integration solutions in the cloud must maintain
accurate information and process business transactions across hybrid
environments. Rather than look at each integration project in a silo,
companies must select an integration strategy that will support this
dynamic and varied environment.
Talend White Paper
4 Key Recommendations for Cloud Integration
Page 9 of 14
Elasticity
Some basic tenets of the cloud help to inform how integration
solutions must change. First, the cloud is elastic. If demand for IT
resources increases, the cloud must expand to meet this need. Just as
importantly, when demand wanes, resources should contract in turn.
Elasticity demands an integration solution that can expand and
contract in kind. IT organizations rely on enterprise services buses
(ESBs) for on-premise integration projects for their flexibility and
reliability. ESBs that are lightweight and easily embedded into
applications are best suited to meet these varying demands. For
example, if a retailer’s order management and inventory system needs
to expand to accommodate year-end demand and then contract to a
normal load after the New Year, a traditional centralized application
server cannot easily add capacity and then have it removed. On the
other hand, IT organizations can deploy a lightweight, distributed ESB
to meet the short-term demand and just as easily retire it when
demand levels return to normal.
Recommendation #1: An integration solution that is lightweight
and easily embedded into applications supports the ability to
expand and contract deployments as required.
Ubiquity
Another trait of the cloud is that it is ubiquitous. Access to resources
cannot be restricted by platform or by access device. In the past,
ubiquity meant choosing the most popular industry standard and
complying with it. However, beyond standardization, the cloud puts a
new emphasis on accessibility and availability of infrastructure
resources. Integration solutions used in the cloud must not only
support standard Web services and REST approaches to integration,
but also be freely available as open source. Easily downloaded and
#
1
Talend White Paper
4 Key Recommendations for Cloud Integration
Page 10 of 14
transparent to users and developers alike, open source integration
solutions ensure that cloud resources are accessible to a wide variety
of existing and new applications and devices through standard and
available interfaces.
Recommendation #2: Support for standard Web services and
REST integration approaches and an open source model makes
resources easily accessible by myriad platforms and devices.
Extensibility
The cloud is extensible as well. Never static, the application and
service offerings of the cloud change and grow over time. Integration
solutions based on a modular architecture that can add, modify or
remove functionality work best in cloud environments. For instance,
some users of solutions in the cloud will require greater access
control, while others need to ensure business continuity.
The ability to meet the divergent needs of different users of cloud
solutions demands an extensible integration infrastructure. Today,
ESBs that are built on the OSGi standard support a modular approach
to integration that is ideal for cloud applications. ESBs built on
standards also can interoperate with future applications and services
as the infrastructure evolves to support the business.
Recommendation #3: Employing a modular architecture allows
organizations to add, modify or remove functionality as
integration requirements and cloud topologies change over time.
#
2
#
3
Talend White Paper
4 Key Recommendations for Cloud Integration
Page 11 of 14
Security and Reliability
Finally, the cloud must be secure and reliable for businesses to trust
using it for their most critical applications. Today, many businesses
hedge against perceived risk in the cloud by building ―private clouds‖.
These cloud implementations are dedicated to a specific business thus
limiting their exposure to the outside world. Over time, private cloud
applications will link to public clouds, eventually fully migrating once
corporations have confidence that the business gain of interacting with
other companies in the cloud outweighs the risk of participating in this
public forum. The integration solutions that link these cloud
environments will need to maintain security and reliability down to
the individual message level. ESBs based on Web services standards
for security and reliability are an excellent solution for maintaining
mission-critical quality of service.
Recommendation #4: Choosing a solution that supports the
ability to maintain security and reliability of cloud-based
applications down to the individual message level is critical for
organizations to meet customer service level agreements (SLAs).
A Unified Approach to Cloud Integration
Talend Cloud, consisting of rich data management and an ESB designed
for deployment in hybrid environments, delivers an excellent solution
for cloud integration. With greater usage of cloud computing in IT
organizations, there is an increasing demand to integrate applications
and data while preserving the benefits of the cloud, namely elasticity
and affordability ― all while maintaining performance, reliability and
security. Talend Cloud enables enterprises large and small to achieve
these benefits.
#
4

Talend White Paper
4 Key Recommendations for Cloud Integration
Page 12 of 14
Talend Cloud provides a unified platform to integrate the data and
applications that support critical business processes spanning hybrid
computing environments. By offering over 450 connectors and
components ― many designed specifically for popular cloud-based and
SaaS applications ― Talend Cloud simplifies the integration of these
business processes.
The unified platform provides a consistent development, deployment,
runtime and monitoring environment allowing application integration
and data management to work in concert. The offering of a common
toolset shortens the time to deployment for integration by eliminating
the need to learn multiple tools and environments. By offering the
products as open source, Talend makes integration more affordable
and accessible to a broad set of users.
Businesses benefit from the greater affordability, accessibility and
ease-of-use of our open source version of Talend Cloud, which reduces
cost and speeds time-to-market for new business solutions. Further,
businesses benefit from the greater productivity and efficiency that
Talend provides through the inclusion of richer tools for development
and operations teams.
What to Look for in a Cloud Integration Solution
Integration projects ― especially those that incorporate a combination
of on-premise, public cloud and private cloud deployments ― come in
all shapes and sizes. The integration platform that you choose needs
to be flexible to accommodate a variety of use cases. If the business
processes and applications you are looking to integrate are mission-
critical to your business, your integration solution also must be
reliable, secure and high performing.
The future of a business is hard to predict. Choose an integration
solution that is extensible to easily adapt to these changes. Integration
solutions should be open, modular and easy-to-use to provide the
greatest return on investment to the organization.

Talend White Paper
4 Key Recommendations for Cloud Integration
Page 13 of 14
1. What does the Cloud mean to my organization?
2. Can my integration solution expand and contract
deployments as required?
3. Can I easily make resources accessible by myriad
platforms and devices in hybrid environments?
4. Can I easily add, modify or remove functionality
as integration requirements and cloud topologies
change over time?
5. Can I maintain security and reliability of cloud-
based applications down to the individual
message level?
And finally, integration projects can be complex. Make sure that your
solution doesn’t require an army of expensive consultants or the
purchase of a stack of technology that you don’t intend to use.
Conclusion – Five Questions to Ask
Forward-thinking organizations select integration solutions that will
support their cloud computing adoption strategy both short and long-
term. How can you do the same? Start by asking yourself these five
questions:
Talend provides the industry’s first open source unified platform for
application integration and data management to address integration of
on-premise, public cloud and private cloud IT infrastructure.
To learn more about integrating hybrid cloud environments with
Talend, please visit talend.com.

Talend White Paper
4 Key Recommendations for Cloud Integration
Page 14 of 14
i
Cloud Application Integration: 10 Key Trends to Follow, eWeek, 14
September 2011
ii
IDC Predictions 2011: Welcome to the New Mainstream, IDC,
December 2010
iii
Gartner Dataquest Market Trends: Application Infrastructure and
Middleware in Small and Midsize Businesses, 2009-2014, Gartner, Inc.,
February 16 2011
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
100108 nmea 0183 sentences not recommended for new designs
M000549 B Eng Oil recommendation for SP14 35
Modeling Of The Wind Turbine With A Doubly Fed Induction Generator For Grid Integration Studies
Outer membrane proteins key players for bacterial adaptation
Cd key Need for Speed
100108 nmea 0183 sentences not recommended for new designs
Recommendations for the Design of Bridges [Benson]
NIST Cloud Computing Synopsis and Recommendations sp800 146
10 Integracja NT i NetWare File and Print Services for NetWare
key pro m8 supported models for vw
Oxford Excellence for matura, Vocabulary Expander Key
Check Your Vocabulary For Ielts Answer Key
Presentation for Strategy Recommendation ppt
Test for Renault Key
Integrated Plant for the Municipal Solid Waste of Madrit 01bm 196 1991
więcej podobnych podstron