
grammar reference
82
•
Eighty-two
CZAS
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
FORMY TWIERDZÑCE (PEŁNE)
FORMY TWIERDZÑCE (SKRÓCONE)
I am working.
I’m working.
You are working.
You’re working.
He is working.
He’s working.
She is working.
She’s working.
It is working.
It’s working.
We are working.
We’re working.
You are working.
You’re working.
They are working.
They’re working.
FORMY PRZECZÑCE (PEŁNE)
FORMY PRZECZÑCE (SKRÓCONE)
I am not working.
I’m not working.
You are not working.
You aren’t working.
He is not working.
He isn’t working.
She is not working.
She isn’t working.
It is not working.
It isn’t working.
We are not working.
We aren’t working.
You are not working.
You aren’t working.
They are not working.
They aren’t working.
FORMY PYTAJÑCE
KRÓTKIE ODPOWIEDZI
Am I working?
Yes, I am. / No, I’m not.
Are you working?
Yes, you are. / No, you aren’t.
Is he working?
Yes, he is. / No, he isn’t.
Is she working?
Yes, she is. / No, she isn’t.
Is it working?
Yes, it is. / No, it isn’t.
Are we working?
Yes, we are. / No, we aren’t.
Are you working?
Yes, you are. / No, you aren’t.
Are they working?
Yes, they are. / No, they aren’t.
WHAT’S + PODMIOT + LIKE?
JeÊli chcemy zapytaç o czyjÊ wyglàd lub o wyra˝enie opinii na czyjÊ temat, u˝ywamy
konstrukcji What’s + podmiot + like?, np.:
What’s your teacher like?
82-85_Grammar_reference.indd 82
12/27/12 11:40:25 AM
Eighty-three
•
83
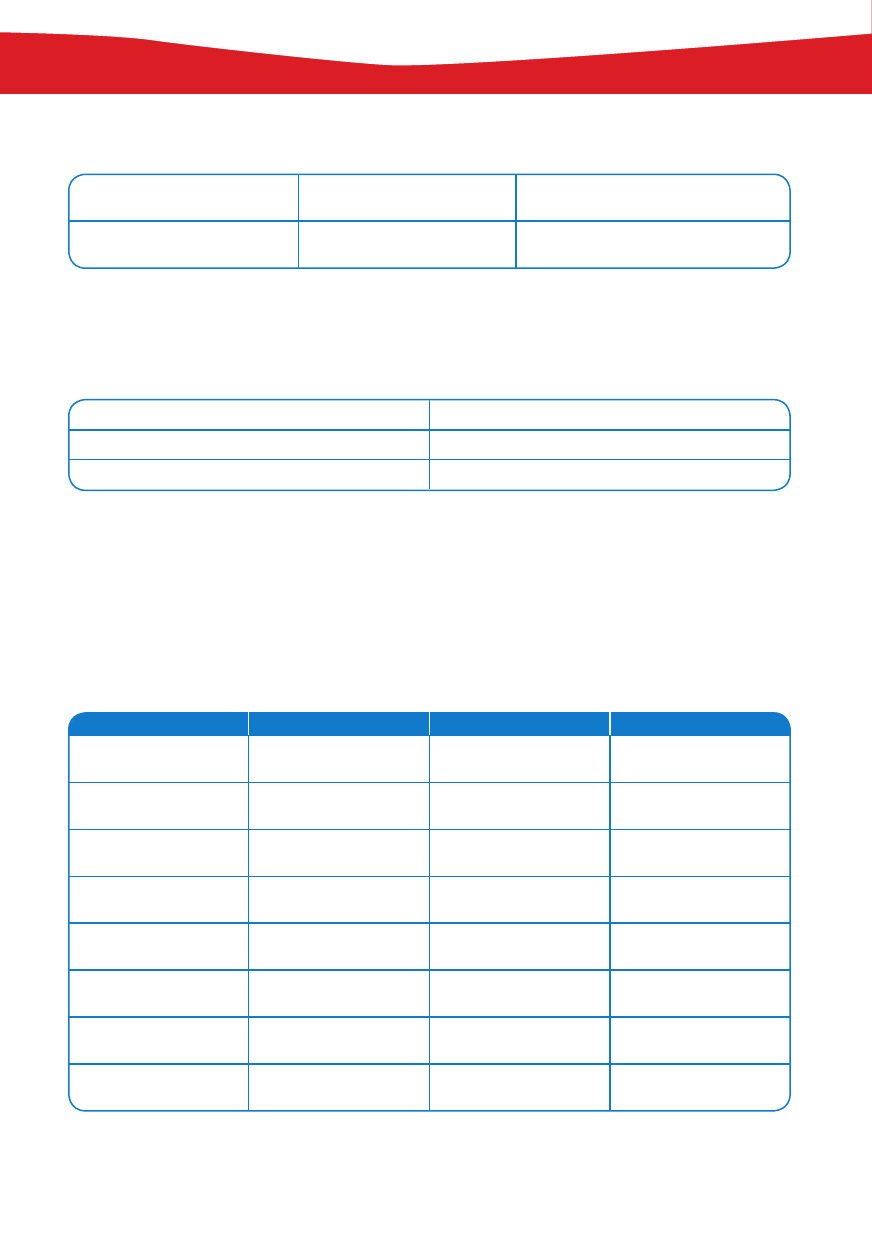
PRESENT SIMPLE
vs
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
Present Simple
It often rains in wet
season.
CzynnoÊç powtarzajàca si∂,
wyst∂pujàca regularnie.
Present Continuous
It is raining now.
CzynnoÊç, która dzieje si∂
w momencie, gdy o niej mówimy.
Czasowniki live, like, hate, want wyst∂pujà tylko w czasie Present Simple.
CZASOWNIK
MUST
FORMA TWIERDZÑCA
I/You/He/She/It/We/You/They must go.
FORMA PRZECZÑCA
I/You/He/She/It/We/You/They mustn’t go.
PYTANIE
Must I/you/he/she/it/we/you/they go?
SHALL
Shall stosujemy tylko z I lub We. Zazwyczaj shall u˝ywamy, kiedy coÊ planujemy lub proponujemy, np.:
Shall I call you tomorrow?
CZASOWNIK
HAVE TO
FORMA TWIERDZÑCA
FORMA PRZECZÑCA
PYTANIE
KRÓTKA ODPOWIEDè
I have to go.
I don’t have to go.
Do I have to go?
Yes, I do.
No, I don’t.
You have to go.
You don’t have to
go.
Do you have to go?
Yes, you do.
No, you don’t.
He has to go.
He doesn’t have to
go.
Does he have to
go?
Yes, he does.
No, he doesn’t.
She has to go.
She doesn’t have to
go.
Does she have to
go?
Yes, she does.
No, she doesn’t.
It has to go.
It doesn’t have to
go.
Does it have to go?
Yes, it does.
No, it doesn’t.
We have to go.
We don’t have to
go.
Do we have to go?
Yes, we do.
No, we don’t.
You have to go.
You don’t have to
go.
Do you have to go?
Yes, you do.
No, you don’t.
They have to go.
They don’t have to
go.
Do they have to
go?
Yes, they do.
No, they don’t.
82-85_Grammar_reference.indd 83
12/27/12 11:40:25 AM
grammar reference
84
•
Eighty-four
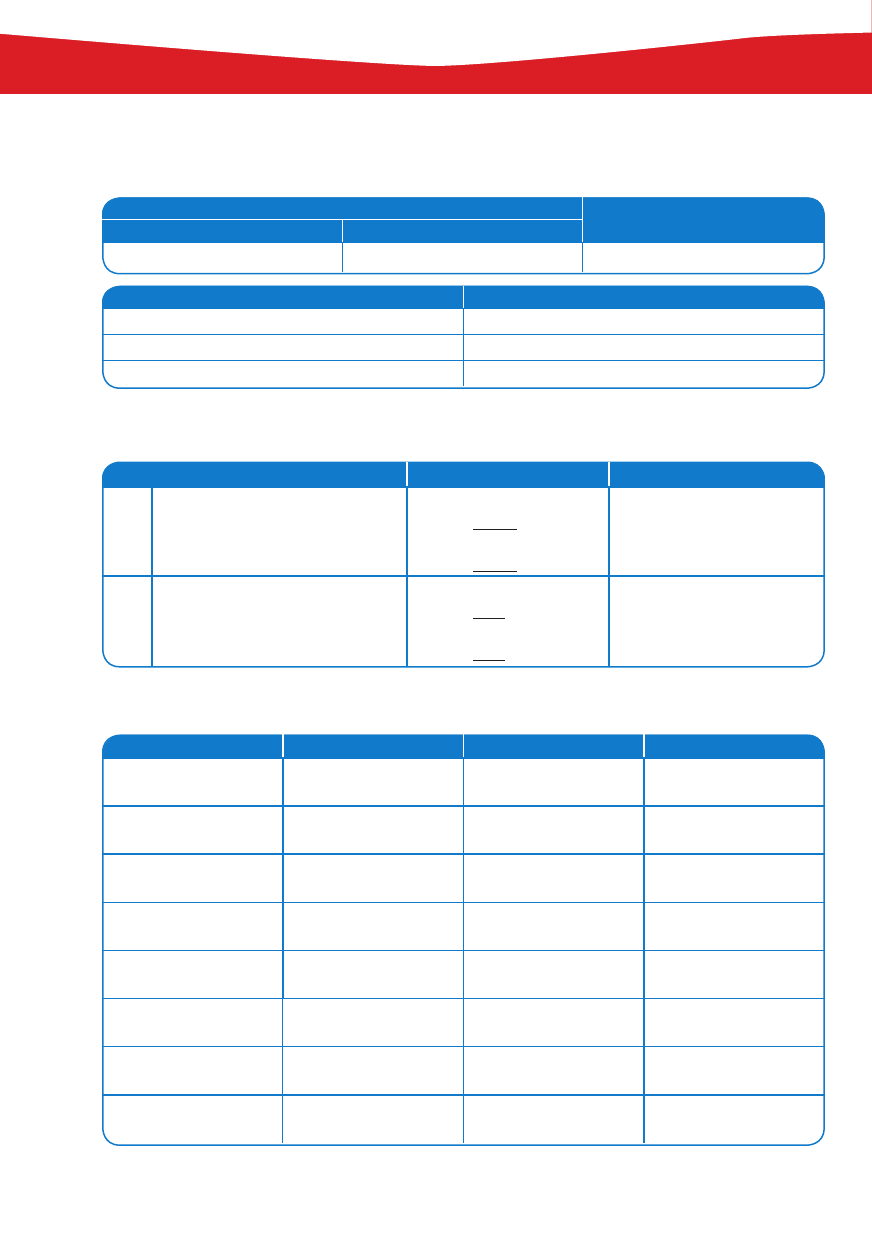
RZECZOWNIKI POLICZALNE I NIEPOLICZALNE:
A, SOME, ANY
POLICZALNE (COUNTABLE)
NIEPOLICZALNE (UNCOUNTABLE)
LICZBA POJEDYNCZA (SINGULAR)
LICZBA MNOGA (PLURAL)
a sausage
sausages
sugar
POLICZALNE W LICZBIE MNOGIEJ
NIEPOLICZALNE
Have you got any mushrooms?
Have you got any water?
Yes, we’ve got some mushrooms.
Yes, we’ve got some water.
No, we haven’t got any mushrooms.
No, we haven’t got any water.
MUCH, MANY, A LOT OF, A FEW, A LITTLE, SOME, ANY
CZAS
PAST SIMPLE
–
TO BE
FORMA TWIERDZÑCA
FORMA PRZECZÑCA
PYTANIE
KRÓTKA ODPOWIEDè
I was at home.
I wasn’t at home.
Was I at home?
Yes, I was.
No, I wasn’t.
You were at home.
You weren’t at
home.
Were you at home?
Yes, you were.
No, you weren’t.
He was at home.
He wasn’t at home.
Was he at home?
Yes, he was.
No, he wasn’t.
She was at home.
She wasn’t at home.
Was she at home?
Yes, she was.
No, she wasn’t.
It was at home.
It wasn’t at home.
Was it at home?
Yes, it was.
No, it wasn’t.
We were at home.
We weren’t at
home.
Were we at home?
Yes, we were.
No, we weren’t.
You were at home.
You weren’t at
home.
Were you at home?
Yes, you were.
No, you weren’t.
They were at home.
They weren’t at
home.
Were they at
home?
Yes, they were.
No, they weren’t.
ZDANIE TWIERDZÑCE
ZDANIE PRZECZÑCE
PYTANIE
Rzeczowniki
policzalne
a lot of/lots of/some/a few
There are a lot of/lots of cars.
There are some cars.
There are a few cars.
many/any
There aren’t many
eggs.
There aren’t any eggs.
many/any
How many eggs are
there?
Are there any eggs?
Rzeczowniki
niepoliczalne
a lot of/lots of/some/a little
There’s a lot of/lots of sugar.
There’s some sugar.
There’s a little sugar.
much/any
There isn’t much
sugar.
There isn’t any sugar.
much/any
How much sugar is
there?
Is there any sugar?
82-85_Grammar_reference.indd 84
12/27/12 11:40:25 AM
Eighty-fi ve
•
85
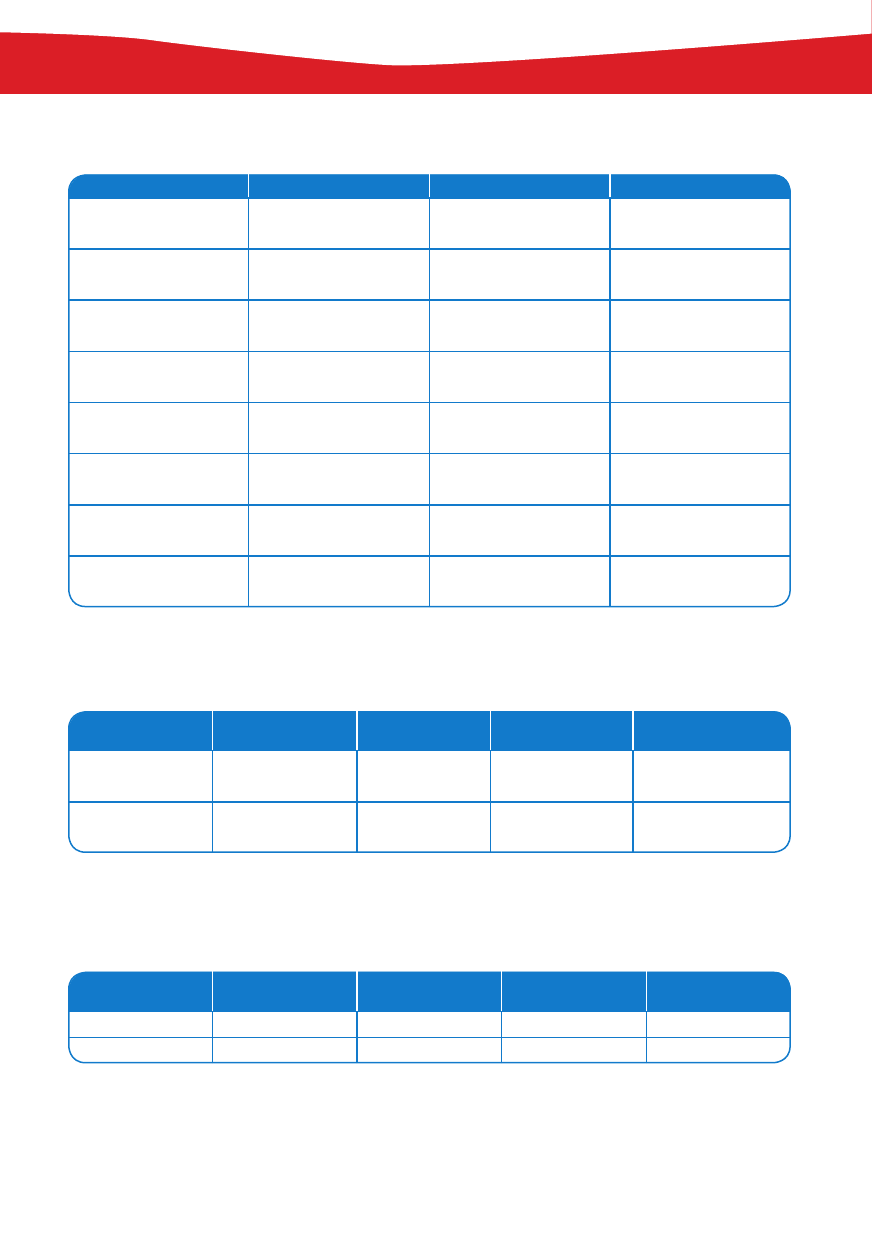
CZAS
PAST SIMPLE
FORMA TWIERDZÑCA
FORMA PRZECZÑCA
PYTANIE
KRÓTKA ODPOWIEDè
I worked/swam
yesterday.
I didn’t work/swim
yesterday.
Did I work/swim
yesterday?
Yes, I did.
No, I didn’t.
You worked/swam
yesterday.
You didn’t work/
swim yesterday.
Did you work/swim
yesterday?
Yes, you did.
No, you didn’t.
He worked/swam
yesterday.
He didn’t work/
swim yesterday.
Did he work/swim
yesterday?
Yes, he did.
No, he didn’t.
She worked/swam
yesterday.
She didn’t work/
swim yesterday.
Did she work/swim
yesterday?
Yes, she did.
No, she didn’t.
It worked/swam
yesterday.
It didn’t work/swim
yesterday.
Did it work/swim
yesterday?
Yes, it did.
No, it didn’t.
We worked/swam
yesterday.
We didn’t work/
swim yesterday.
Did we work/swim
yesterday?
Yes, we did.
No, we didn’t.
You worked/swam
yesterday.
You didn’t work/
swim yesterday.
Did you work/swim
yesterday?
Yes, you did.
No, you didn’t.
They worked/swam
yesterday.
They didn’t work/
swim yesterday.
Did they work/swim
yesterday?
Yes, they did.
No, they didn’t.
THERE WAS/WERE
FORMA
TWIERDZÑCA
FORMA
PRZECZÑCA
PYTANIE
KRÓTKA
ODPOWIEDè
LICZBA
POJEDYNCZA
There was
There wasn’t
Was there …?
Yes, there was.
No, there wasn’t.
LICZBA
MNOGA
There were
There weren’t
Were there …?
Yes, there were.
No, there weren’t.
CZAS
PAST SIMPLE
Z
WHEN, WHAT, WHERE, HOW,
WHO, WHY
SŁOWO
PYTAJÑCE
DID
PODMIOT
CZASOWNIK
When
did
the train
leave?
What
did
she
do
yesterday?
82-85_Grammar_reference.indd 85
12/27/12 11:40:25 AM
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Rules of the Present Simple, Present Continuous, Past Simple, Past Continuous tenses
35 Strona bierna Present Continuous Past Continuous czesc 2
Present Simple vs Present Continuous ćwiczenia4
Present Simple vs Present Continuous ćwiczenia8
Present Simple vs Present Continuous, szkolne, 2015 2016
Present Simple vs Present Continuous ćwiczenia2
Present Simple vs Present Continuous ćwiczenia3
present simple vs present continuous zebrane z internetu
Present Simple vs Present Continuous ćwiczenia6
Present Simple vs Present Continuous ćwiczenia
Simple Present, the Present Continuous, the Simple Past, the Past Continuous or the Present Perfect
PRESENT SIMPLE vs PRESENT CONTINUOUS
D present simple vs present continuous PL
Present Simple vs Present Continuous
Present simple vs Present continuous ccc
present simple vs present continuous
Sobczak, Witold Jak wykorzystać znajomość czasów Present Perfect, Past Simple i Past Continuous w n
present simple vs present continuous redux
więcej podobnych podstron