Dydaktyka 3

It was called Classical Method sińce it was first used in the teaching of the classical languages, Latin and Greek
Ss should leam to think in the target Ig.
Ss need to associate meaning and the target lg. directly.
This method was used for the purpose of helping students read and appreciate foreign language literaturę
It was thought that foreign language leaming would help Ss grow intellectually;
When the teacher introduces a new target lg. or phrase, he demonstrates its meaning through the use of realia, pictures, or pantomimę; he never translates it into the Ss’ native lg.
The syllabus is based upon situations or topics
It was hoped that, through the study of the grammar of the target language, Ss would become morę familiar with the grammar of their native language and that this familiarity would help them speak and write their native lg. better.
Grammar is thought inductively (Ss are presented with examples and they figurę out the rule or generalization from the examples)
An explicit grammar rule may never be given
It was recognized that Ss would probably never use the target language, but the mental exercise of leaming it would be beneficial anyway
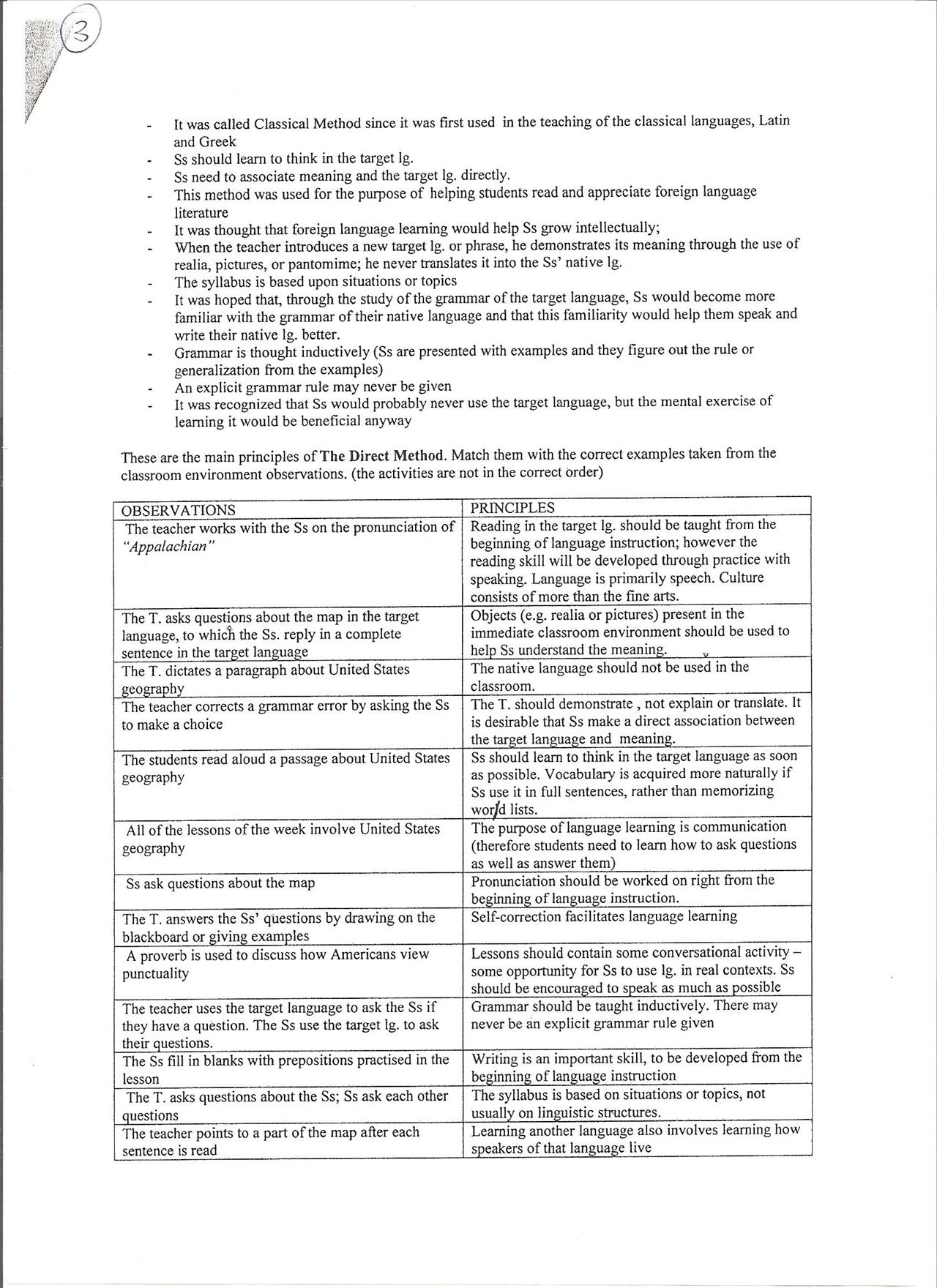
These are the main principles of The Direct Method. Match them with the correct examples taken from the classroom environment observations. (the activities are not in the correct order)
|
OBSERVATIONS |
PRINCIPLES |
|
The teacher works with the Ss on the pronunciation of “Appalachian " |
Reading in the target lg. should be taught from the beginning of language instruction; however the reading skill will be developed through practice with speaking. Language is primarily speech. Culture consists of morę than the fine arts. |
|
The T. asks questions about the map in the target language, to which the Ss. reply in a complete sentence in the target language |
Objects (e.g. realia or pictures) present in the immediate classroom environment should be used to help Ss understand the meaning. |
|
The T. dictates a paragraph about United States geography |
The native language should not be used in the classroom. |
|
The teacher corrects a grammar error by asking the Ss to make a choice |
The T. should demonstrate , not explain or translate. It is desirable that Ss make a direct association between the target language and meaning. |
|
The students read aloud a passage about United States geography |
Ss should leam to think in the target language as soon as possible. Vocabulary is acquired morę naturally if Ss use it in fuli sentences, rather than memorizing wor/d lists. |
|
Ali of the lessons of the week involve United States geography |
The purpose of language learning is communication (therefore students need to leam how to ask questions as well as answer them) |
|
Ss ask questions about the map |
Pronunciation should be worked on right from the beginning of language instruction. |
|
The T. answers the Ss’ questions by drawing on the blackboard or giving examples |
Self-correction facilitates language learning |
|
A proverb is used to discuss how Americans view punctuality |
Lessons should contain some conversational activity -some opportunity for Ss to use lg. in real contexts. Ss should be encouraged to speak as much as possible |
|
The teacher uses the target language to ask the Ss if they have a question. The Ss use the target lg. to ask their questions. |
Grammar should be taught inductively. There may never be an explicit grammar rule given |
|
The Ss fili in blanks with prepositions practised in the lesson |
Writing is an important skill, to be developed from the beginning of language instruction |
|
The T. asks questions about the Ss; Ss ask each other questions |
The syllabus is based on situations or topics, not usually on linguistic structures. |
|
The teacher points to a part of the map after each sentence is read |
Leaming another language also involves learning how speakers of that language live |
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Sew a christmas message 1 r caraboard as you cut it a little smaller. 7. Beginning in the lop left&n
skanuj0113 2 Reyiew used in the study by Annane and associates.14* Since the cut-ofF values for bene
This is the motorbike that was used in the film The Motorcycle Diana. It is a 1939 Norton 500cc
11 8 If the speech has (o coiwince (he audience, not not interest it, the arguments should be used i
wheel Wheel construction Outside edge of wheel has a "crown" to it. Wheel is wider in the
49 (197) 4: Dermatophytosis Ketoconazole is a fungicidal azole drug, used in the treatment of dermat
383123$5665192170067!2147665521820X5654!25520104 n CAN YOU BELIEYE IT?? This guy wins $181 million i
w25E A: the castle of Imola, east of Bologna, as it would have appeared in the early 14th century. B
anon The Image (SB) The Image and other classic French stories of submission The Image was first p
i * i * signs. or complexes of symptoms and signs. The “diagnoses** of the screening method use
S5002146 gp c [1 frag., Fig. 20:6), D [4 1 Fig. 20:2,3], H [1 frag.]. >n was carried out in the a
497 on SWB. The analysis was conducted with the application of an ordered logit model. The dala used
By the use of thinner and heavier Lines in the map a very plastic and measurable image was created.
więcej podobnych podstron