networking essentials

|
Layer |
THE OSI MODEL Description |
Implementations Device and Protocols | |
|
Application (7) |
Provides services directly to user applications. Identifies communication partners, identifies quality of service, considers user authentication and privacy, and determines if adequate resources are present. |
Gateway |
SMB, HTTP, SMTP, FTP, SNMP, Telnet, AppleTalk |
Type: 10Base5 (Coaxial)
Name(s): RG-8, RG-11;
Thicknet Coax Spoed: 10 Mbps.
Connector: AUI/DIX Max. Length: 500 meters 11.640 ft.)
Type: 10Base2 (Coaxial)
|
Presentation (6) |
Performs data transformations and services including formatting, compression, and eneryption services to provide a common interface for user applications. |
Gateway and Redirectors |
HTTP. FTP. Telnet, SMTP, AFP, TDI |
|
Session (5) |
Establishes, manages and terminates connections between applications at eacn end. Allows 2 applications to communicate over a network by opening a session and synchronizing the involved computers. |
Gateway |
NetBEUI, TCP, UDP, SPX |
|
Transport (4) |
Provides transparent transfer of data between end systems by insulating layers 5-7 from complexities of layers 1-3. Responsible for end-to-end error recovery and flow control and ensures complete data transfer. |
Gateway |
IP. IPX, NWLink, NetBEUI |
|
Network (3) |
Establishes, maintains, and terminates network connections. Handles traffic management including addressing, routing, switching, forwarding, logical paths and yirtual circuits, error handling, congestion control and packet sequencing. |
Router and Brouter |
IP, IPX, NWLink, NetBEUI |
|
Data Link (2) |
Divided into two sub-layers: The Media Access Control i MAC) sub-layer Controls how a networked Computer gains access to the data and permission to transmit it. The Logical Link Control (LLC) sub-layer Controls frame synchronization, flow control and error checking. |
Switch, Bridge and Router |
Ethernet, PPP, HDLC |
|
Physical (D |
Controls transmission of the bit stream data over the physical medium. Standards for this layer address transmission at the electrical and mechanical levol including signal voltage swing, voltage duration, etc. |
Multiplexer and Repeater |
Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI |
Namels): RG-58. Thinnot Coax Speed: 10 Mbps Connector: BNC
Max. Length: 185 metera <607 ft)
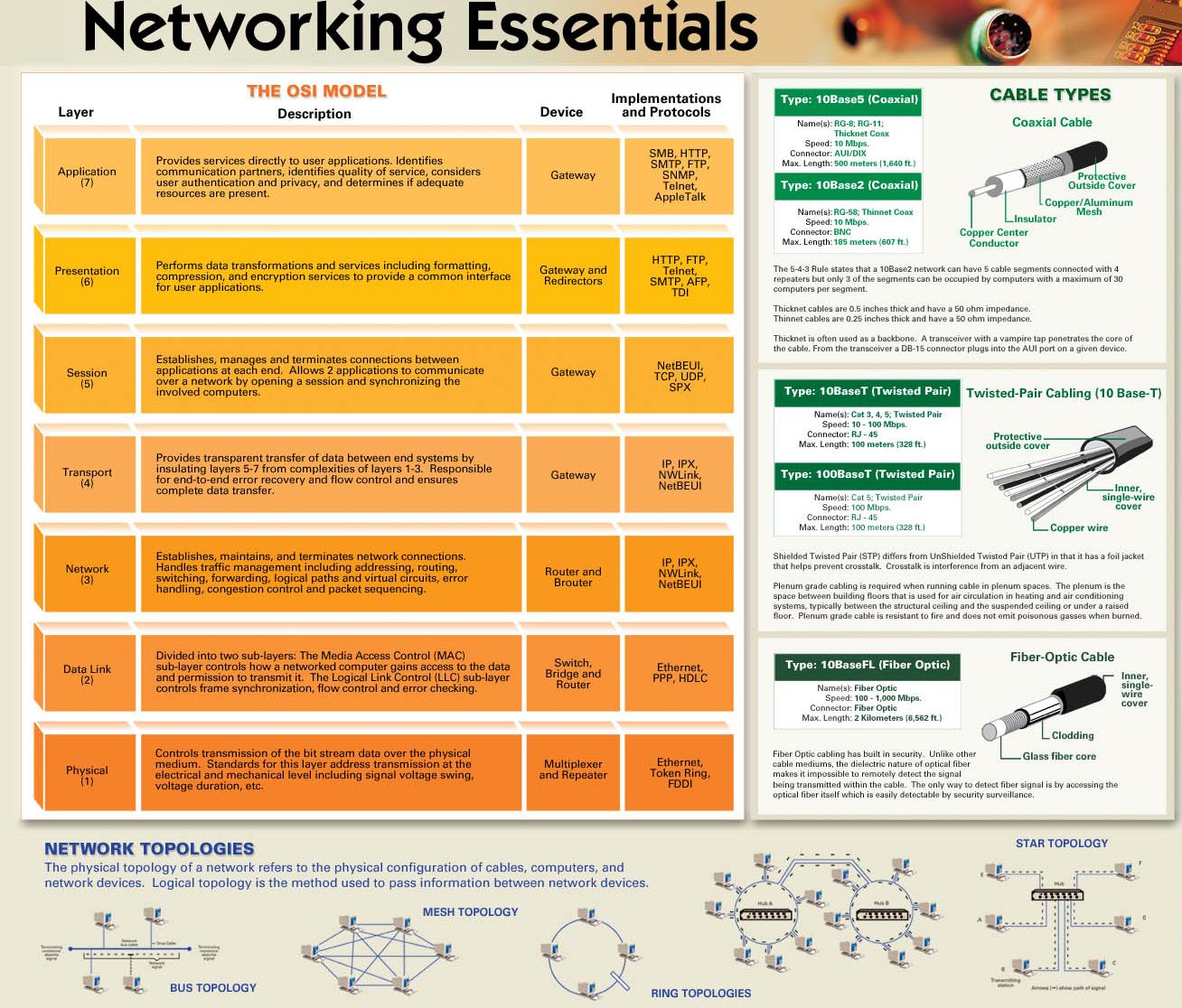
Coppur/Aluminum Mosh
.Insulator
Coppcr Center Conductor
Prołective Outsido Cover
The 5-4-3 Rule States that a 10Base2 nełwork can have 5 cable segments connected with 4 repeaters but only 3 of the segments can be oocupied by computers with a maximum of 30 computors per segment.
Thicknet cables are 0.5 inches thick and have a 50 ohm impedance.
Thinnet cables are 0.25 inches thick and have a 50 ohm impedance.
Thicknet is often used as a backbone. A transceiver with a vampire łap penetrates the core of the cable. From the transceiver a DB-15 connector plugs mto the AUI port on a given dovice.
Type: 10BaseT (Twisted Pair)
Namo(s): Cet 3.4, 5; Twisted Pair Speed: 10-100 Mbps Connector: RJ - 45 Max. Length: 100 nieters (328 fL)
Type: lOOBaseT (Twisted Pair)
Name<s): Cat 5. Twisted Pair Speed: 100 Mbps. Connector: RJ - 45 Max. Length: 100 meters<328 ft.i
Protectivo outsido covor

Innor, singio-wiro cover
Copper wire
Shielded Twisted Pair <STP) differs from LfnShielded Twisted Pair (UTP) in that it has a foil jacket that helps prevent crosstalk. Crosstalk is interference from an adjacent wire.
Plenum grade cabling is roquired when running cable in plenum spaces. The plenum is the space between buildiny floors that is used for air circulation in heating and air condilioning systems. typically between the structural ceiling and the suspended ceiling or undor a raised floor. Plenum grade cable is resi&tant to fire and does not omit poisonous gasses when bumed.
Type: lOBaseFL (Fiber Optic)
Namefs): Fiber Optic Speed: 100 -1.000 Mbps. Connector: Fiber Optic Max. Length: 2 Kilometers <6.562 ft)


Inner,
singio-
wiro
cover
Clodding
Fiber Opt»c cabling has built in security. Unlike other _Glass fibor coro
cable mediums. the dielectric naturę of optical fiber makes it impossible to remotely detect the signal
being transmitted within the cable The onły way to detect fiber signal is by accessing the optical fiber itself which is easify detectable by security surveillance.
NETWORK TOPOLOGIES
The physical topology of a network refers to the physical configuration of cables, computers, and network devlces. Logical topology is the method used to pass information between network devices.
BUS TOPOLOGY
MESH TOPOLOGY
RING TOPOLOGIES
STAR TOPOLOGY
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Networking Essentials Layer THE OSI MODEL Description Implementations Device and
2. -QP CodęCu) Messa ge segmemation and te-assembly is the task ol OSI model. 1) Transport 2) Sessio
18.3 million NOK is the cost of the all the essential GMS network eąuipment for the cities of Stavan
essent?rving?53 C A R V I X G A X ABSTRACT Fic 14.7 ,Vortex>— caruing in elder employing the same
00427 a5a3b4846efe962a975cb55bde8e8b 431 Process Capability: Engineering and Statistical Issues so
The devices and computers connected to Ethernet must have their own addresses to communicate on the
IDEA #3 TConnect IN : Creating a digital networking channel for the university campus Mehul Khoont M
Contents i/// 5.5 Advantages of the OSI Reference Model 42
image 4 Share Box Go to (Social Networks) Tab on the left to choose scoial share buttons you want to
TCPIP Model bmp OSI Model and TCP/IP Encapsulation Layer Na me Encapsulation Segment Packet Fra
NetWork Probes The network probes monitor the transfer of information from the MySQL server and clie
Passive operating system fingerprinting using neural networks... 19 too. The multi-stage architectur
le cnamGSM - Early 1980 s, several cellular networks in Europę -
136GEOMORPHOLOGICAL AND HYDROLOGICAL EFFECTS OF UNMETALLED ROAD NETWORK FUNCTIONING ON THE EXAM
Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data-Link Physicalmodel OSI różnorodny
essent?rving?51 First Cuts: Chip C a r v i n g Fig 3.14 Startinga morę complex flower. The centre ri
essent?rving?99 C A R V 1 N C IN THE R O U X D CON VEYING A SENSE OF DEPTH If you are drawing with a
więcej podobnych podstron