netter5

NEUROPHYSIOLOCY
Synaptic Transmission: Morphology of Synapses

Numęrous boutons (synaptic knobs) of presynaptic neurons terminating on a motoi neuron and its dendrites
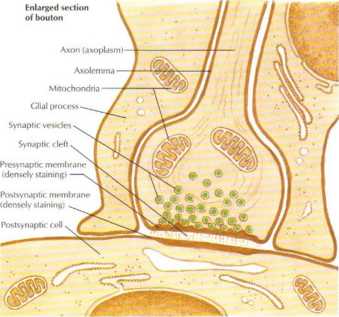
Figurę 2.4 Morphology of Synapses_
Neurons communicate wdlh each other and wilh effector targets at specialized regions called synapses. The top hgure shows a typical motor neuron that receives numerous synaptic contacts on its celi body and associated dendrites. Incoming axons lose thoir myelin sheaths, exhibii extensive branching, and terminale as synaptic bou-tons (synaptic tcrminals Or knobs) on tire motor neuron. The lowcr figurę shows an enlargement of one such synaptic bouton. Chemical neurotransmiłlers are contained in synaptic vesides, which can fuse with the presynaptic membranę, release the transmitters into the Synaptic cJeft. and then bind to receptors siluated in the postsynaptic membranę. This synaptic transmission results in excitatory, inhibitory, or modulatory effects on the target celi.
15
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
47720 netter8 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYSynaptic Transmission: Inhibitory Mechanisms Figurę 2.7 Synaptic Inhibi
17540 netter9 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYSynaptic Transmission: Chemical Synaptic Transmission s &nb
netter7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYSynaptic Transmission: Yisceral Efferenł Endings ■ A. Smooth musclc B. Gland
netter6 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYSynaptic Transmission: Neuromuscular Junction r Acetylcholine
netter2 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Central sulcus (Rotando)Organizalion of Ihe Brain: Cerebrum Postcentral gyru
netter30 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Sensory Pathways: I Spinothałamic iract lower part of medulla
więcej podobnych podstron