netter6
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
Synaptic Transmission: Neuromuscular Junction
r
Acetylcholine receptor
vesides
MyofibrHs
Synaptic cleft
Postsynaptic membranę
Junctional told
Sarcoplasm
AcetylchoBne receptor sites
Myelin sheath Neurilemma Axopłasm Schwann celi MiitKhondria Basement membranę
celi
membranę
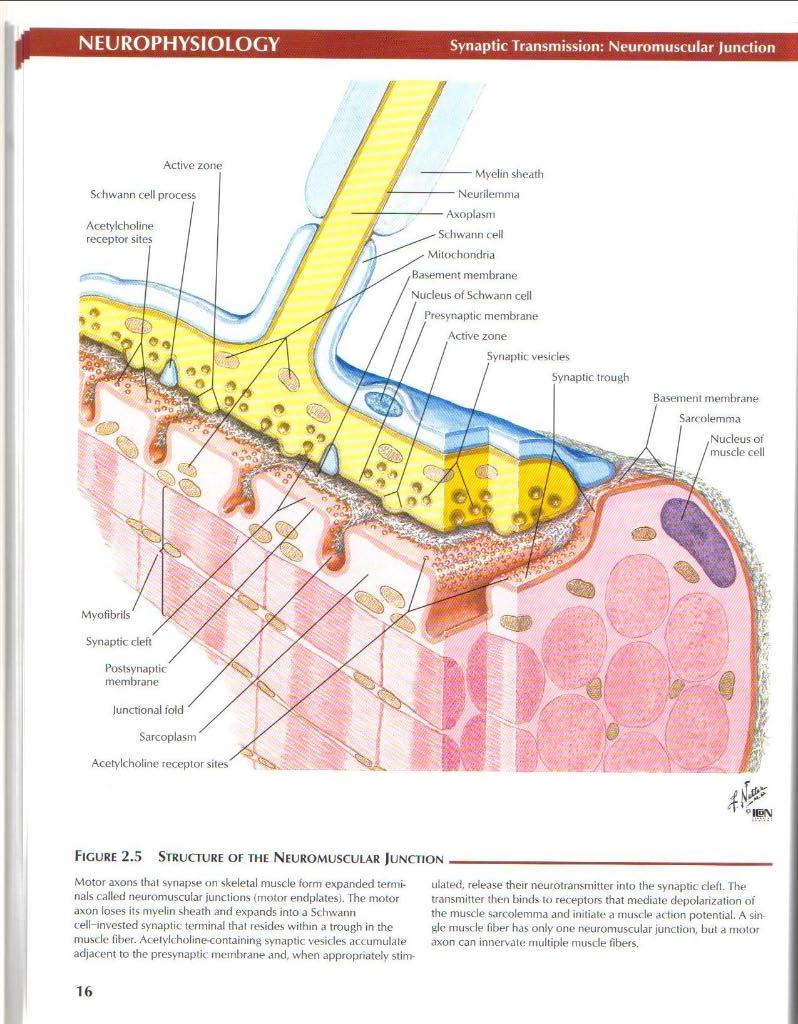
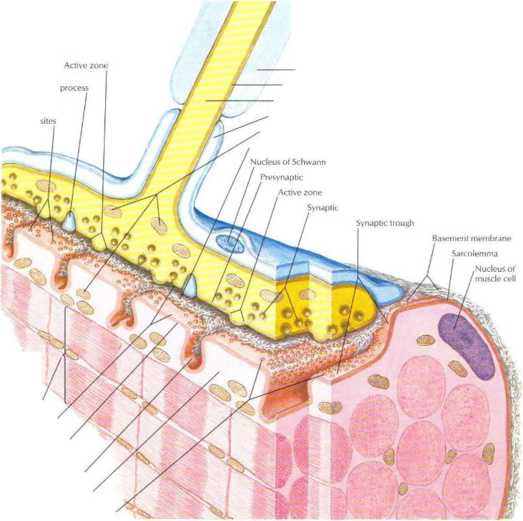
Figurę 2.S Structure of the Neuromuscular Junction
Motor axons (hal synapsę on skeletal muscle form expanded ternie nals called neuromuscular junction* (motor endplates). The motor axon loses its myelin sheath and expands into a Schwann cełl-invested synaptic terminal thal resides within a trough in the muscle fiber. Acetylcholine-containing synaptic vesides accumulate adjacent to the presynaptic membranę and, when appropriately stim-ulated, release their neurotransmitter into the synaptic defl. The transmitter then binds to receptors that modiate depolarization of the muscle sarcolemma and initiate a muscle action potential. A single muscle fiber has only one neuromuscular junction, but a motor axon can innervate multiple muscle fibers.
16
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
47720 netter8 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYSynaptic Transmission: Inhibitory Mechanisms Figurę 2.7 Synaptic Inhibi
17540 netter9 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYSynaptic Transmission: Chemical Synaptic Transmission s &nb
netter5 NEUROPHYSIOLOCYSynaptic Transmission: Morphology of Synapses Numęrous boutons (synaptic knob
netter7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYSynaptic Transmission: Yisceral Efferenł Endings ■ A. Smooth musclc B. Gland
netter10 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYSynaptic Tr.insmission: Temporal and Spatial Summation C. Icmporal exritator
netter11 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYCerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): Brain Ventricles and CSF Composition Frontal (ant
netter2 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Central sulcus (Rotando)Organizalion of Ihe Brain: Cerebrum Postcentral gyru
netter20 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYThe Cerebral Cortex Sm!,} Spn4,,,v Sensory Promotor; orientation, eye and
netter24 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYCutaneous Sensory Receplors Melanoryte Arrectot muscle ofliair, Sebaceous gl
netter30 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Sensory Pathways: I Spinothałamic iract lower part of medulla
netter36 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Audilory System: Pathways temporal lobe cortex Medial geniculate body High
netter40 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYGustatory (Taste) System: Pathways Sensory cortex łjust below face area) Lat
więcej podobnych podstron