leki nasenne0003
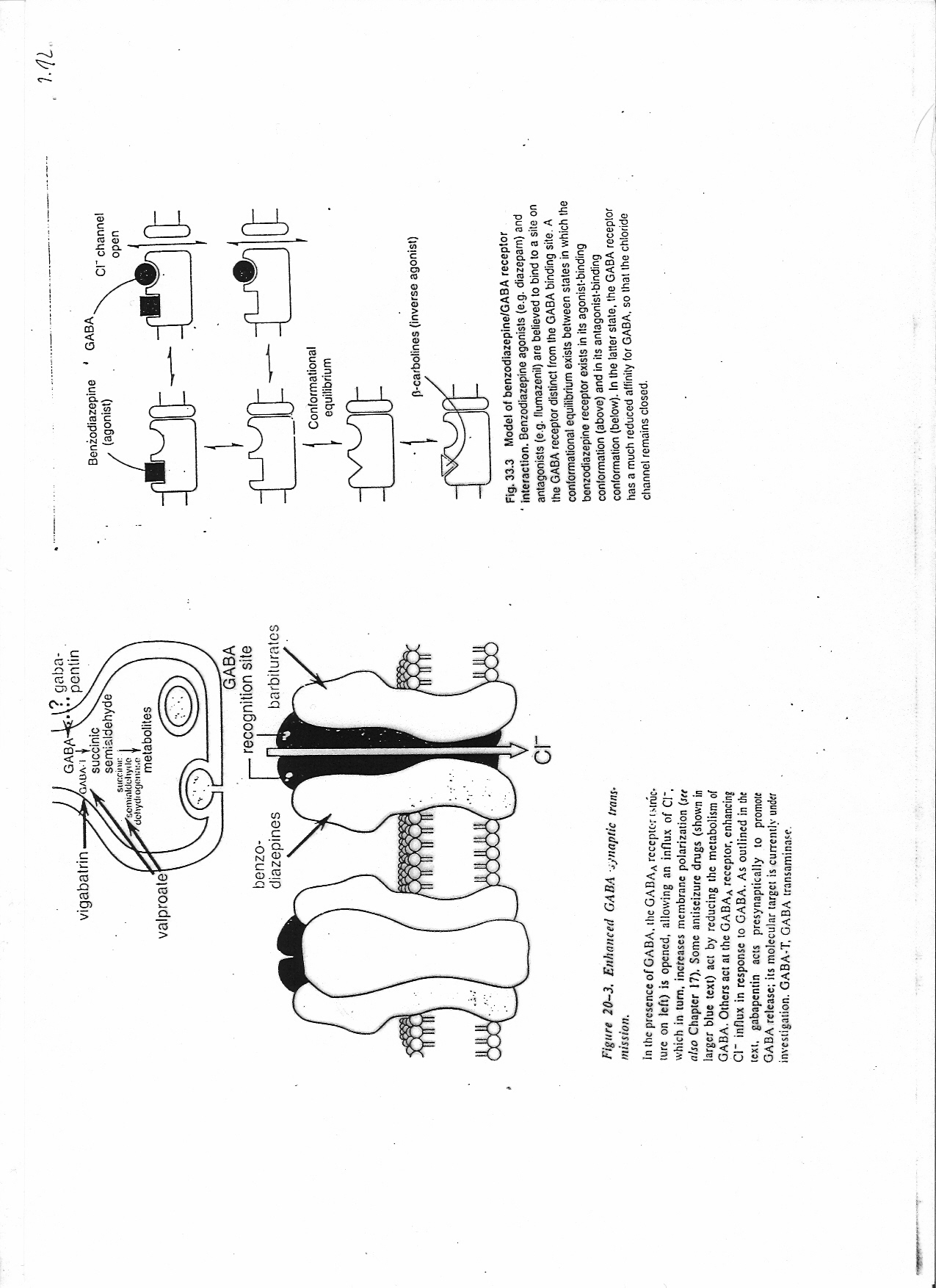
Figurę 20-3. Enhanetd GARA jynapric trans-mission.
In ihc presence of GADA, ilic GABAa recepto; tsiruc-ture on ieft) is opened, allowing an influx of Cl*, which in tum, inefeases membranę polarization [ser also Chapter 17). Sonie amiseizure drugs (shown in larger blue text) act by reducing the metabolism of GABA. Olhcrs act at the GABAa receptor, cnhancing Cl* influx in response to GABA. As outlined in the text, gabapentin acts presynaptically to promoie GABA rclcase; its molecular target is currcmly under investigation. GABA-T, GABA transaminasr.
-. \
Conlormational
equilibrium
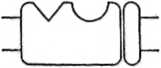
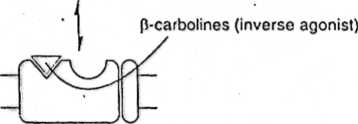
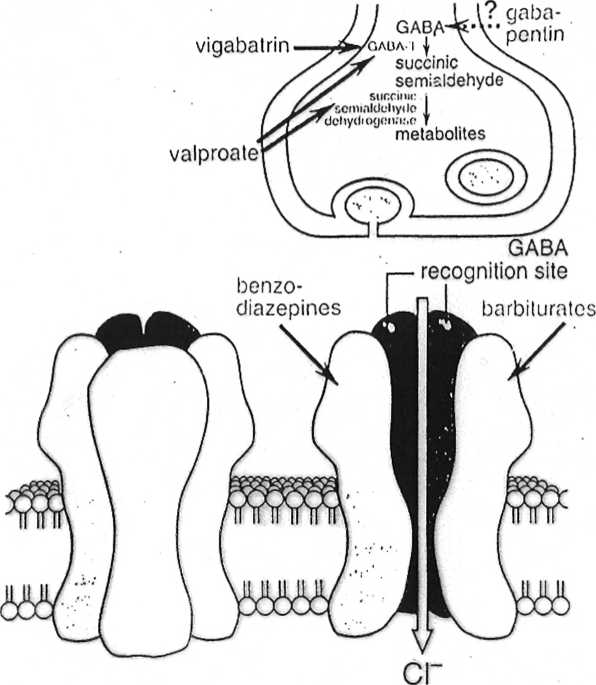
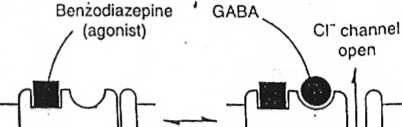
Fig. 33.3 Model of benzodiazepine/GABA receptor interaction. Benzodiazepine agonists (e.g. diazeparn) and antagonists (e.g. flumazenil) are believed to bind to a site on the GABA receptor distinct from Ihe GABA binding site. A conformational equilibrium exists between States in which the benzodiazepine receptor exisls in its agonist-binding conformation (above) and in its aniagonist-binding conformalion (below). In the latter siatę, the GABA receptor has a much reduced attinity (or GABA, so that Ihe chloride channel remains closed.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
FIGURĘ 20.13 Paralogous and Orthologous Sequences In this example, an ancestral gene duplicałed
essent?rving?40 Essen tial Woodcarying Techniques FlG 2.20 Arrow Crosstree (Dick Onians), carued in
essent?rving?04 E S S E N T I A L W O O D C A R V I N G T E C H N I Q V E S (Fig 9.20) bur could hav
leki nasenne i uspokajajace0004 102 Farmakologia Tabela 3.20. Profil farmakologiczny barbituranów or
leki nasenne i uspokajajace0005 3. Leki wpływające na ośrodkowy układ nerwowy kwasu barbiturowego pr
fig20 Figurę 20 One possible Chain arrangement with shears and needle case
figure3 20 madelYiBW matrix stack (32 4x4 mat (1 ces) q p o n mik] h g f Bdcb pro jęc
więcej podobnych podstron