netter69
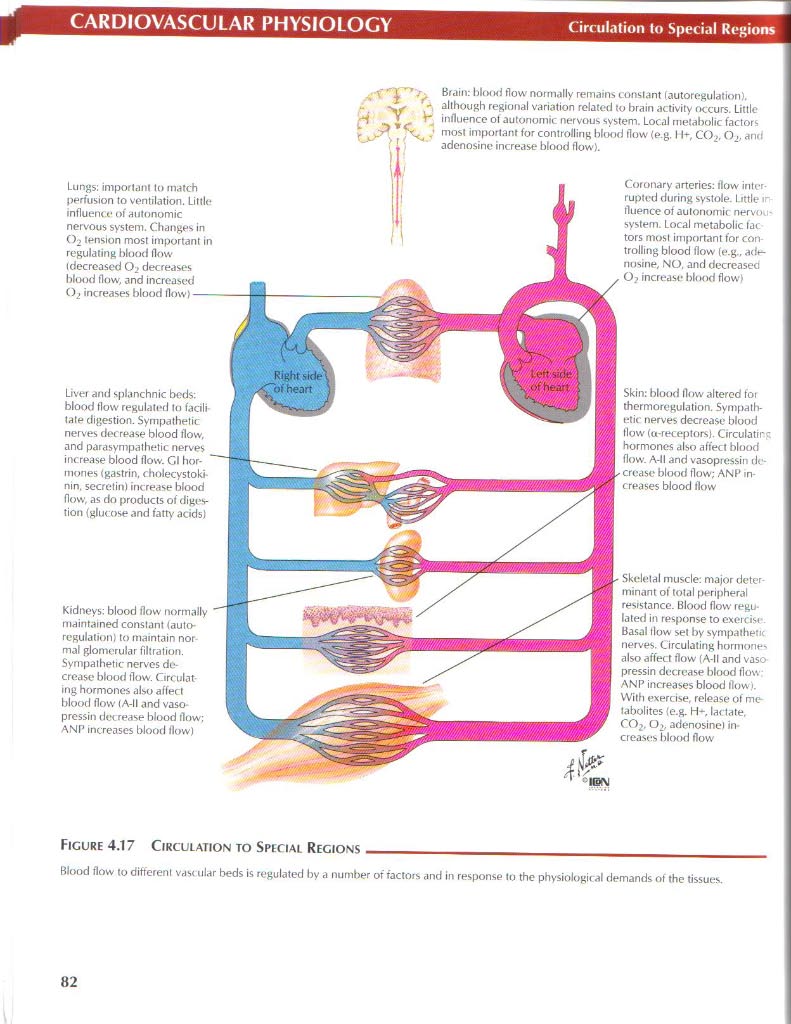
Brain: blood (Iow normally remains constant fautoregulation). allhough regional varia(ion rełatcd to brain activity occurs. Littlc influence of autonomie nervous system. LocaJ metabolic factors most important for controlling blood (Iow (e.g. IK C02, Oj, and adenosine inerease blood flow).
Lungs: important to inatch perfusion to ventilation. Littlc influence of autonomie nervou$ system. Changes in O2 tension most important in regułating blood flow tdecreased Oj decreases blood flow, and incrcased Oj inereases blood flow)-
Liver and spłanchnic bods: blood flow regulati*d to facili-tate digestion. Sympathetic nen.es decrease blood flow, and parasympathetic nerves inerease blood flow. Cl hor-mones (gastrin, cholecystoki-nin, sccretin) inerease blood flow, as do products of digestion (glucose and fatty acids)
Kidneys: blood flow normally maintained constant tauto-regulation) to maintain nor mai glomerular filtration. Sympathetic nerves decrease blooci flow. Grculat-ing hormones also affect blood flow (A-ll and vaso pressin decrease blood flow: ANP inereases blood flow)
Coronary arteries: flow inter-rupted during systole. Little fluence of autonomie nervo. system. Local metabolic tac tors most important for controlling blood flow (e.g., adenosine, NO. and decreased 0? inerease blood flow)
Skin: blood flow altered fot thermoregulation. Sympalh-etic nerves decrease blood flow (a-receptors). Circulatirc. hormones also affect blood flow. A-ll and vasoptessin de-crcase blood flow; ANP in-creases blood flow
Skclelal muscle: major determinant of total peripheral resistance. Blood flow regu-lated in response to exeirisc. Basai tlow set by sympathetic nerves. Circulating hormone' also affect flow (A-ll and vaso pressin decrease blood flow ANP inereases blood flow). Wilh exercise, release of me tabolites (e.g. H-, lactate. COj, O), adenosinei inereases blood flow
Figurę 4.17 Circulation to Spegial Regions_
Blood flow to ditterenl vas< ular beds is regulated by a number of factors and in response to the physiologic al demands of the tissues.
82
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
59840 netter71 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOCY Short-Term Regulation of Blood Pressure 2/3t „NE Ganglion-
netter53 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Overview of thc Cardiovascular System Pulmonary
52194 netter63 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Cardiac Output: Function Curves vascular function curves, a
netter124 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Lowrr Esophageal Sphincter mm Mr Normal LES tonę is physiologi
netter176 AldosteroneENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOCY Blood volumc Renal factors Hyperkalemia
netter189 ProlactiENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Prolactin-inhihiting factor (PIF), thought to bc dopamine, mo
netter89 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pulmonary Circulation Distribution of Pulmonar> Blood Flow
więcej podobnych podstron