netter179

ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY
Insulin Secretion

|. Perkins
MS. MFA
- wyry
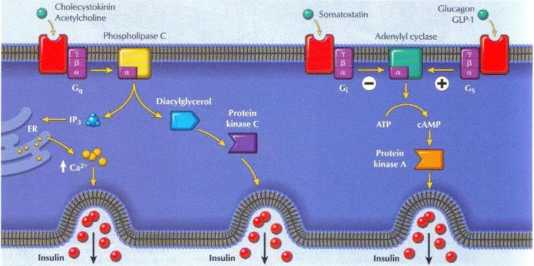
Figurę 8.19 Insulin Secretion_
The most important factor regulating insulin secretion is the glucose concentration ot the blood. When the Nood glucose concentration inereases, insulin secretion is stimulated. Glucose enters the celi. where its metabolism ineroasos intracellular ATT levels. The inereased ATP lev-ds dose an ATP-dependent K channd in the plasma membranę and tbereby depolarize tlw? membranę potential (V„). This membranę iwtential depolarization opens voltage-sensitive Ca:~ channels, and the intracellular [Ca:*| inereases. The rise in intracellular |Cav' ] triggers exo-cytosis of the insullrvC£>ntaining secretory granukrs. Other tactors poteo tiate this effect of glucose on insulin secielion. Humiones and candi-date hormones released bv neuroendoenne cells in the intestine Huring digestion facilitate insulin seaetion. These hormones and candidate hormones in< Jude cholecystokinin, giucagon-łike peptide (GLP-1) and glucagon. Acetyłcholine (front vagal efferentsj also stimulates insulin secretion. while somatostattn from tlić islet S-cdls inhibits secretion.
198
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter67 Control of Artcriolar TonęCARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Yasopressin (AI)H) J. Pcrkins MS, MfA I
netter165 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Posterior Pituilary: Oxytocin Oxyto<in pickcd up by capillaries of
netter167 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Growth Hormone Increased linear growth : Decreased adiposity Increase
netter183 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Gonad and Genital Duet Formation (pulled aside) I .‘rogemtoi•y Testos
10723 netter177 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Adrenal Medulla CH/-CH-COOH ganglia CH7-CH2-N
32301 netter173 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Adrenal Cortical Hormones JOMN A,CRAC_ao -IBM fe &n
więcej podobnych podstron