netter45
MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY
Skeletal Mustlc: Excitation-Contracti»n Coupling I
Thin
Electric impulse Sarcolemma
Sarcoplasm
/ band Sarcoplasmic
reticulum
Terminalcistern of sarcoplasmic

Terminal cistom ot sarcoplasmic reticulum
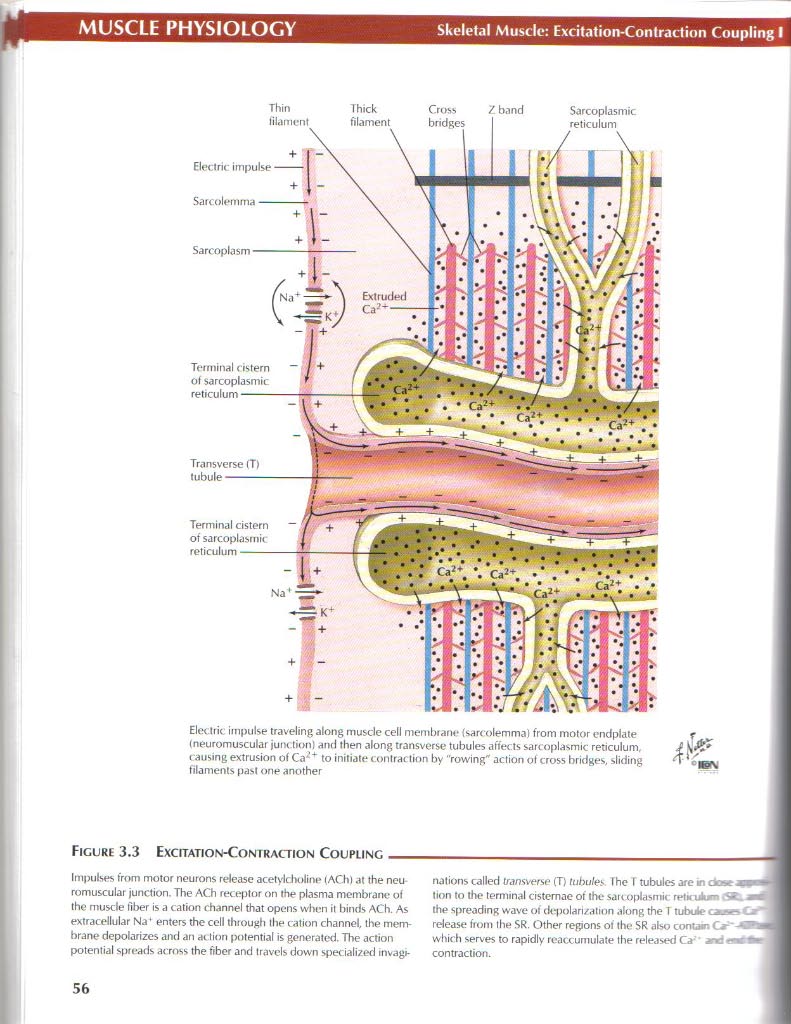
Electric impulse traveling atong muscle celi membrano (sarcolemma) from motor cndplate r
(neuromuscular junctionl and then along transverse tubules aftects sarcoplasmic reticulum, causing extrusion of Ca2 to imtiato contraction by "rowing action of cross bridges, sliding Ą filanients past one another
Figurę 3.3 Excitation-Coniraction Coupling_
Impulsos from motor neurons release acetylcJH>line (ACh) at the neu romuscular junction. The ACh receptor on the plasma membrano of the muscle llber is a cation rhannel that opens whon it binds ACh. As extracellular Na* enters the celi through the cation channol, the membrano depolarizes and an action potential is gonerated. The action potential sproads across the frber and travcls down specialized mvage nations called transverse (T) tubules. fhe I tubules are m dtxt xa tion to the terminal cistemae of the sarcoplasmic retnulum S*.. the spreading wave ot depolari/ation along the T tubułe casc i release from the SR. C)ther regions ot the SR also contam Car' A which serves to rapidly reaccumulate the released Ca-' ane contraction.
56
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter46 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGYSielrtal Musde: Excitation-Contraction Ciiupling II During musde contracti
netter47 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGYSkeletal Muscle: Excitation>Contraction Coupling III Actin Troponin
53514 netter51 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGYSmooth Muscle: Excitation-€ontraction Coupling Cuntracliun Cyde Figu
78877 netter48 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY>*rietal Muscle: Length-Tension Relationship »ariation in Size o
45963 netter43 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGYSkeletal Muscle: Organization Twodimensional schema ot myofilaments.
więcej podobnych podstron