53514 netter51
MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY
Smooth Muscle: Excitation-€ontraction Coupling
Cuntracliun Cyde
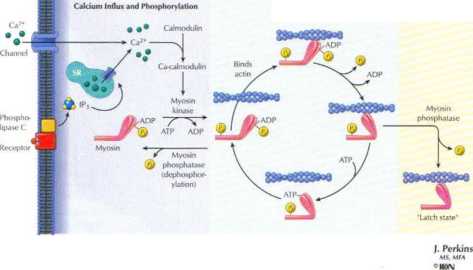
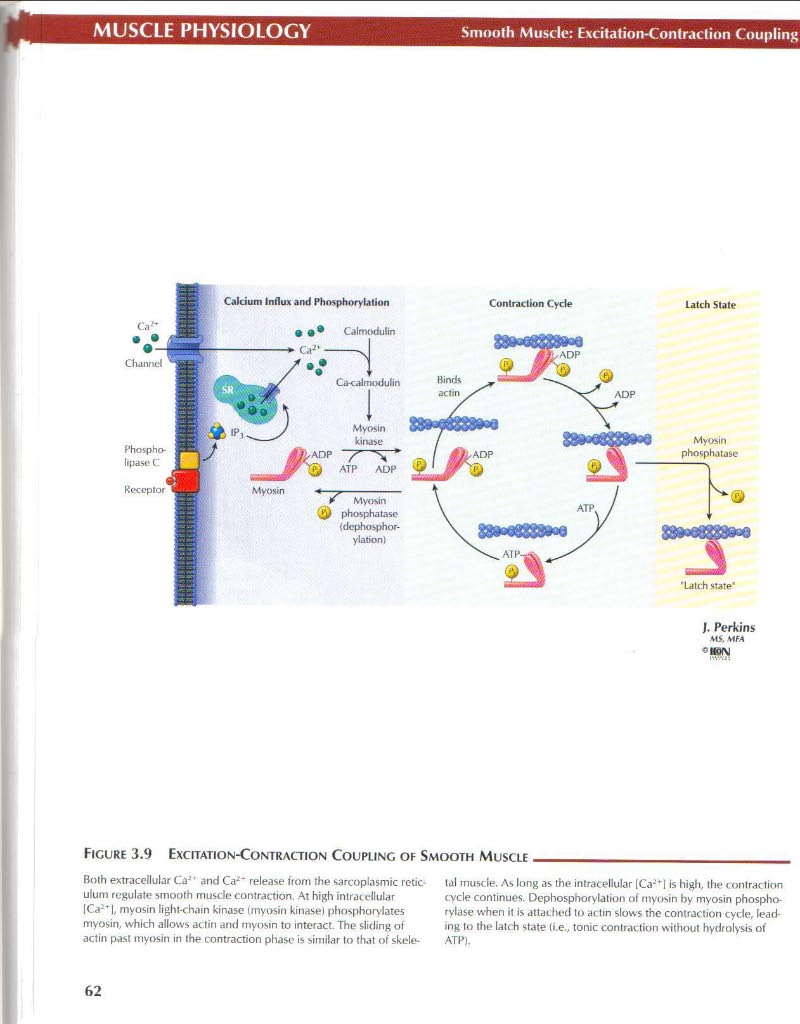
Figurę 3.9 Ekotation-Contraction Coupunc of Smooth Muscle .
Both extraceilular Ca-" and Ca2' release from the sarcoplasmic retic ulum rcgulate smooth muscle contraction. At high intracdlular |Ca2^ |, myosin light-chain kinase (myosin kinase) phosphorylates myosin, which allows actin and myosin to interact. The sliding of actin past myosin in the contraction phase is similar to that of skele-tal muscle. As long as the intracellular lCa*'^| is high, the contraction cyde continues. Dephosphorylation of myosin by myosin phospho-rylase When it is attached to actin slows the contraction cyde, lead-ing to the latch State (i.e., tonie contraction without hydrolysis of ATP).
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter45 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGYSkeletal Mustlc: Excitation-Contracti»n Coupling I Thin Electric impulse
netter47 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGYSkeletal Muscle: Excitation>Contraction Coupling III Actin Troponin
76657 netter188 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGYHormonal Kugulation of thc Monstru.il Cyde Hormonal Reculation o
netter179 ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Insulin Secretion
netter46 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGYSielrtal Musde: Excitation-Contraction Ciiupling II During musde contracti
więcej podobnych podstron