12753 skanuj0017 (249)

Posterior lobe of cerebellum
Pineal
Hippocampus
Choroid plexus of lateral ventride
Lateral ventride, central part
Caudate nudeus, body
Insula
Internal cerebral veins
Cerebral
aqueduct
Anterior lobe of cerebellum
iCiomboid
fossa
Choroid plexus offourth ventricle
mmm JIH
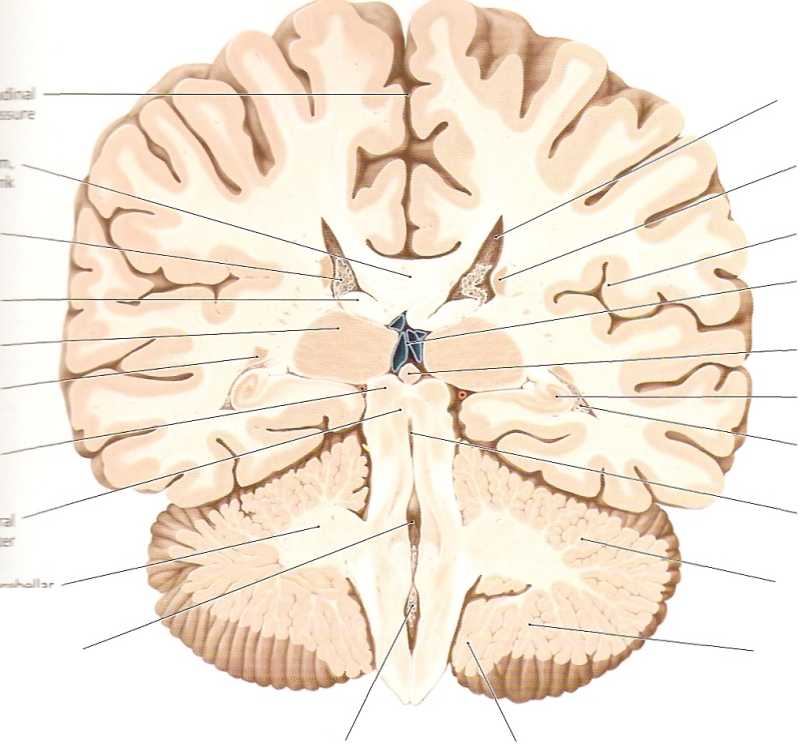
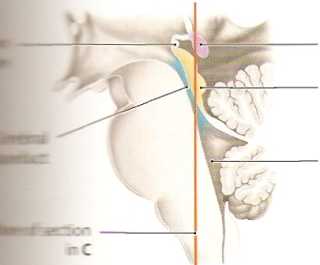
lt«cear smallerthan in previous sections, and morę ■jjBHSseen.This piane passesthrough part ofthece-IhEJńcr-!boki fossa, which forms the floor of the fourth ■stóć in the dorsal part of the brainstem (see D and HbbI piąte (lamina tecti) is also visib!e. Its smaller kortiajlaiiy well displayed in this section, while the aanur: prominent in the next section (see A, p. 300). visible because of its somewhat morę occipi-
Cerebellar
tonsil
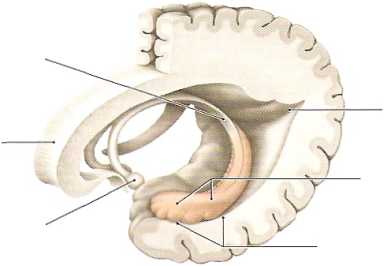
tal location (see D); a fuli cross-section can be seen in A, p.300. The present section shows the division of the paired fornix tract into its two crura (see also D, p. 295). The hippocampus here borders on the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle on each side, bulging into its floor from the medial side (see also the previous sections and E). The hippocampus is an important component of the limbie system and is one of the first structures to undergo detectable morphological changes in Alzheimer’s disease.
Pineal
Quadrigeminal piąte
Rhomboid
fossa
- through the rhombencephalon, Łi*: diencephalon
Crus
offomix
Mammillary
body
Corpus
callosum
Occipital horn
Pes (foot) of hippocampus
Temporal
horn
E Hippocampal formation Left lateral view.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Metastases to the pituitary gland 1 - 4% of oncology units patients on atopsy. Most often in the pos
Parts of the Humań Brain parietal lobe frontal lobe temporal cerebellum spinał cord
skanuj0013 (249) j f."* • hw . ‘ - r ^
skanuj0015 (249) iQ^Pod zjLca......
skanuj0016 (249) 32 Treści kształcenia metod oraz organizowania całej sytuacji dydaktycznej, w które
skanuj0172 „The basie characteristics of the match an organization achieves with its environment is
skanuj0176 „A coherent set of actions aimed at gaining a sustainable advantage over competition im
skanuj0008 (249) 100 Irena Sławińska rakteryzacyjną rolę dialogów i monologów w zakresie prezentacji
więcej podobnych podstron