11871 netter148
Pancreas Structuri-
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY
V / Root of
Superior mesenteric vessels mesentery
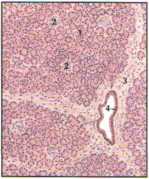
Low-power section of pancreas 1. Acini, 2. islet, 3. interlobular septum, 4. interlobular duet
High magnification: acini, intercalated duet and zymogen granules
Common bile duci Principal pancreatic ducl (Wirsung's)
Accessory pancreatic duet (Santorini's)
Pancreatic islet: A (=«-).
B i = |J—), and D 1=6-) cells. 1. Reticulum, 2. acini
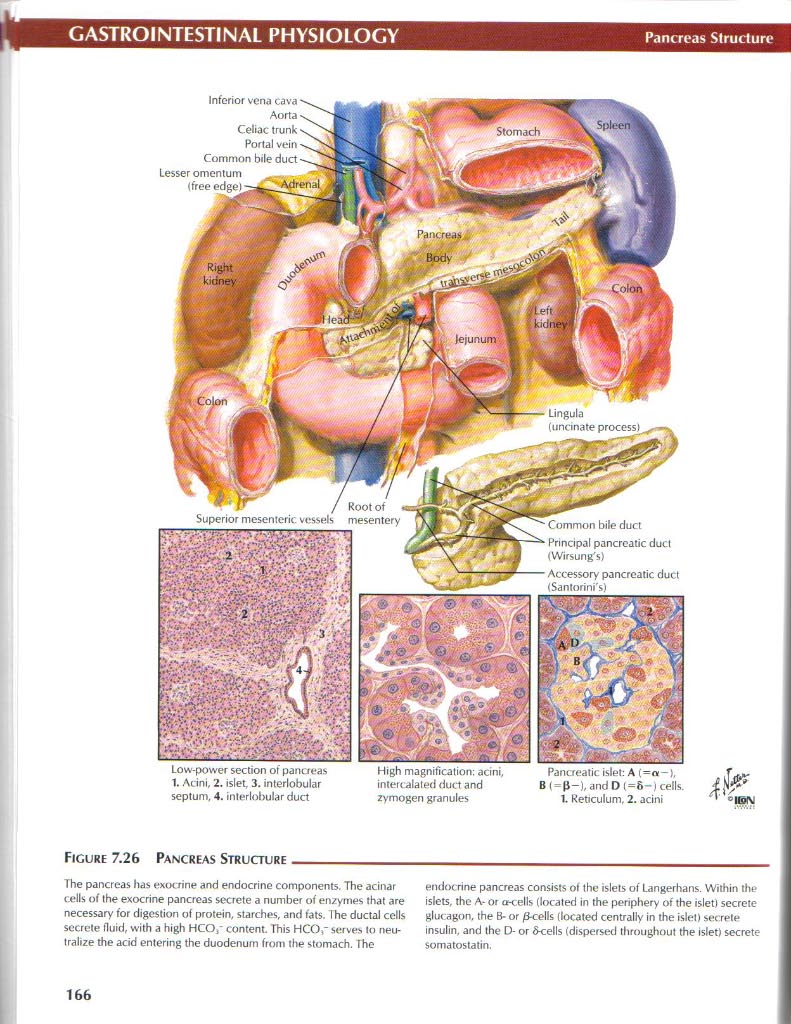
Figurę 7.26 Pancreas Structure_
The pancreas has exocrine and endocrine components. The acinar cells of the exocrine pancreas secrete a number of enzymes that are necessary for digestion of protein, starches, and fats. The ductal cells secrete fluid, with a high HCO/ content. This HCOr serves to neu-tralize the acid entering the duodenum from the stornach. The endocrine pancreas consists of the islets of Langerhans. Within the islets, the A- or a-cells (located in the periphery of the isletj secrete glucagon, the B- or /3<ells (located centrally in the islet) secrete insulin, and the D- or &cells (dispersed throughout the islet) secrete somatostatin.
166
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter158 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Digestion of Carbohydrales Maftose Pancreatic amyiase
netter156 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Overvievv of Cii Trać! Fluid and Electrolyte Transport Ingest
netter109 Renal Clearance: IIRENAL PHYSIOLOGY PRINCIPIE OF TUBULAR SECRETION LIMITATION (Tm) USINC P
netter136 Gaslric Secretion: IIGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Secrelions of gastric acid (H* ) by parie
netter78 Airway Structure: EpithcliumRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Mucus- Goblet (mucous)
16523 netter73 Rrsponse to txeras»CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Anticipation of exercise stimulates
netter73 Rrsponse to txeras»CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Anticipation of exercise stimulates
16523 netter73 Rrsponse to txeras»CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Anticipation of exercise stimulates
netter140 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Smali Intestinc Structure: III Mitochondria Tight junctions ■
netter49 I I Cardiac Mustlt*: StructureMUSCLE PHYSIOLOGYFlCURF 3.7 SCHEMA OF STRUCFURt OF CARDIAC MU
więcej podobnych podstron