19734 netter107
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
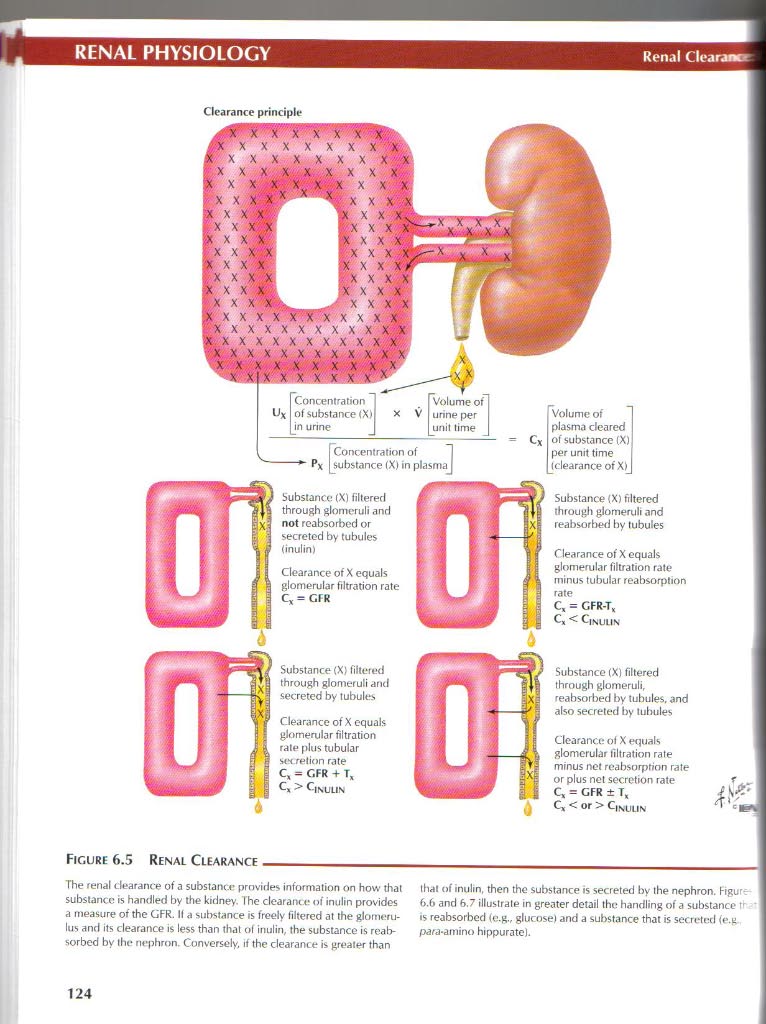
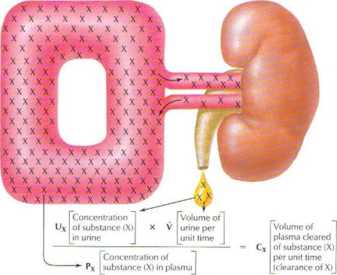
Clearance principk*

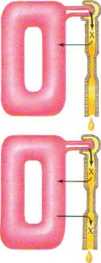
Substance (X) filtered through glomeruli and not roabsorbed or secreted by tubules <inulin)
Clearance ot X equals glomerular filtration ratę Cx = GIK
Substance (X) filtered through glomeruli and secreted by tubules
Clearance of X equals glomerular filtration ratę plus tubular sch relion ratę Cx = GFR + T„
Cx > C|NUUN
Substance <X) filtered through glomeruli and reabsorbed by tubules
Clearance of X equals glomerular filtration ratę minus tubular reabsorpfion ratę
C, = GFR-T,
Cx < Cinulin
Substance (X) filtered through glomeruli, reabsorbed by tubules, and also secreted by tubules
Clearance of X equals glomerular filtration ratę minus net reabsorption ratę or plus net secretion ratę Cx = GFR ± T,
Cx<°r> Cinuun
Figurę 6.5 Renal Clearance__
The renal clearanc e of a substance* provides intormation on how that tbat of inulin, then the substance is secreted by the nephron. Figurę substance is handled by the kidney. I he clearanc e of inulin provides 6.6 and 6.7 illustrale in greater detail lho handling of a substance tr
a measure of the GFR. Ii a substance is freely filtered at the glomeru- is reabsorbed (e.g., glucose) and a substance that is secreted fe.g
lus and its clearance is less than that of inulin, the substance is reab- para-amino hippurate). sorbed by the nephron. Conversely, if the clearance is greater than
124
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter119 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Renal HCO, Reabsorption Factor Principal Site of Action Increased H+
netter105 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Bowman s capsule Parietal epithelium Visceral epithelium (podocytes) Mesa
26834 netter121 Anatomy of the Kidney: The Nephron RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Cortical nephrons dilute the uri
netter109 Renal Clearance: IIRENAL PHYSIOLOGY PRINCIPIE OF TUBULAR SECRETION LIMITATION (Tm) USINC P
netter120 ienal Produclion of New HCO,RENAL PHYSIOLOGY NH4A - acid Net Acid txcretion(NAE)«(UuxV) -
netter176 AldosteroneENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOCY Blood volumc Renal factors Hyperkalemia
Ck-.ir.mte: II RENAL PHYSIOLOCY PRINCIPLE Or TUDUIAR RIAOSORrTION LIMITATION (Tmi USINC CLUCOSE AS
77431 netter112 - Cocicentralion RENAL PHYSIOLOGY WATER, ION, AND UREA EXCHANCE IN PRODUCTION OF HYP
więcej podobnych podstron