8342936740

PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY
^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ
The symmetry of magnetic Circuit leads to the almost zero mutual flux linkage in the SRM phases even under saturated conditions. This means that the SRM may work with m - 1 phases sińce no induced voltage or current will appear in the short-circuited phase. Hence the SRM is morę fault tolerant than any AC motor where the interaction between phases is at the core of their principle of operation. The self-inductance of each phase alone thus plays the key role in torąue production.
In the absence of magnetic saturation, the phase self-inductance varies linearly with rotor position, while, in presence of saturation, the respective dependence is non-linear (Fig. 1.4).
--- nonsaturated
------ saturated
|
L»(S) | |||||||
|
Lb(S) |
0° 3 |
0 61 |
0 91 |
1° 12 |
0° 15 |
0° 18 |
0° |
|
Lc(S) |
X"® |
motoring ® generating
Figurę 1.4. The phase inductances and the operation modes of three phase 6/4 SRM.
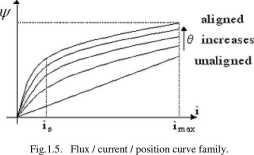
If the phase flux linkage y/'\s calculated and plotted versus current for various rotor positions, the (//(#, i) curve family is obtained (Fig. 1.5). The influence of magnetic saturation is evident from Fig. 1.5 and it is a practical reality in well designed SRMs.
Phase coil has N turns, and when it is excited with current I, the coil sets up a flux 0. Increasing the excitation current will make the rotor pole (armaturę) move towards the stator pole. The flux vs. magnetomotive force (mmf) is plotted for two values of rotor position xl and x2 as shown in Fig. 1.6. The flux vs. mmf characteristic for xl is linear because the reluctance of the air gap is dominant, making the flux smaller in the magnetic Circuit.
UNIA EUROPEJSKA
EUROPEJSKI FUNDUSZ SPOŁECZNY

a
Materiały dydaktyczne dystrybuowane bezpłatnie.
Projekt współfinansowany ze środków Unii Europejskiej w ramach Europejskiego Funduszu Społecznego
5
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ The symmetry of magnetic Circuit leads to the almost z
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ 1) The torque is proportional to the
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ 1) The torque is proportional to the
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Ćwiczenie 7 „Czujniki pól magnetycznych. Badanie
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Ćwiczenie 9 „Czujniki pól magnetycznych. Badanie
i PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Power and
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Warsaw Uniyersity of Technology Faculty of Power and
i PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Warsaw University of Technology Faculty of Power and
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Only for the linear case (no magnetic saturation) the
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ a = Ua — The maximum value of #w, for Qon = 0 (zero ad
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ It should be noticed that the interval of conduction i
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Only for the linear case (no magnetic saturation) the
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ a = Ua — The maximum value of #w, for Qon = 0 (zero ad
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ It should be noticed that the interval of conduction i
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY ^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ dr inż. Adam BiernatElectrical Machines in the Power
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ By adjusting the turn-on and turn-off angles so that t
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Fig. 1.15. Instantaneous value of voltage and current
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY ^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJPROGRAM ROZWOJOWY 2. PERMANENT MAGNET BRUSHLESS MOTOR
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Using eąuations (1.3) to (1.5), the incremental mechan
więcej podobnych podstron