8342936728

PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY
^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ

a = Ua —
The maximum value of #w, for Qon = 0 (zero advance angle), is given by motor design:

(1.26)
where: 6m - aligned position angle, Nr - number of rotor poles (teeth).
The base speed cOo corresponds to #wmax and single voltage pulse Ud with maximum flux linkage ^/max, which is dependent on machinę design and the level of saturation. Thus, to reach higher speeds co (above co*,), we have to saturate the magnetic Circuit of that machinę (Eąuation 1.25). This is called flux weakening.
The smaller the angle 0off - 6m, the smaller the negative torque "contribution" of the phase going off. In reality at 6= 6m (aligned position) if the current im is already less than (25 -30%) of the peak current, the negative (generating) torąue influence becomes smali.
Once one phase is turned-off at 0C another one is turned-on, eventually soon, to contribute positive torąue such that to lower the total torąue pulsations caused by the reduction of torąue in the phase going off.
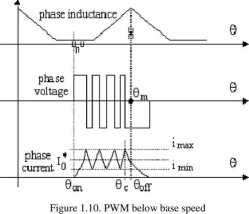
It is now evident that the entire magnetic energy of each phase is "pumped" in and out for each conduction cycle. There are mNr cycles per mechanical revolution. A part of this energy is passed over to the incoming phase through the power electronic converter (P.E.C.) and the rest to the DC bus filtering capacitor of P.E.C. Below base speed COo the current is limited (and controlled) through PWM (Fig. 1.10, Fig. 1.8).
i
KAPITAŁ LUDZKI
NAROOOWA STRATEGIA SPÓJNOŚCI
UNIA EUROPEJSKA
EUROPEJSKI FUNDUSZ SPOŁECZNY

Materiały dydaktyczne dystrybuowane bezpłatnie.
Projekt współfinansowany ze środków Unii Europejskiej w ramach Europejskiego Funduszu Społecznego
12
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ a = Ua — The maximum value of #w, for Qon = 0 (zero ad
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Fig. 1.15. Instantaneous value of voltage and current
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Fig. 1.15. Instantaneous value of voltage and current
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY ^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ dr inż. Adam BiernatElectrical Machines in the Power
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Only for the linear case (no magnetic saturation) the
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ phase conducts), and maximum torąue is achieved by max
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ It should be noticed that the interval of conduction i
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ By adjusting the turn-on and turn-off angles so that t
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ The symmetry of magnetic Circuit leads to the almost z
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Using eąuations (1.3) to (1.5), the incremental mechan
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ 1) The torque is proportional to the
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY ^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ dr inż. Adam BiernatElectrical Machines in the Power
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Only for the linear case (no magnetic saturation) the
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ phase conducts), and maximum torąue is achieved by max
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ It should be noticed that the interval of conduction i
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ By adjusting the turn-on and turn-off angles so that t
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ The symmetry of magnetic Circuit leads to the almost z
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ Using eąuations (1.3) to (1.5), the incremental mechan
PROGRAM ROZWOJOWY^1 POLITECHNIKI WARSZAWSKIEJ 1) The torque is proportional to the
więcej podobnych podstron