3416400801
NF-kB and radiosensilivity • C. Didelot et al. 1357


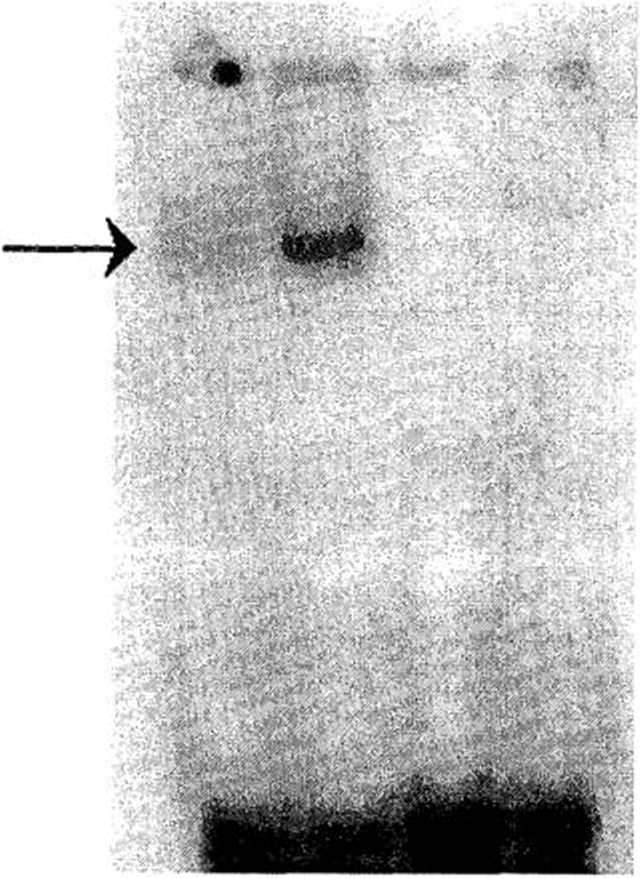

Fig. 3. Modulation of the DNA-binding activity of NF-kB in (A) KB and (B) KB3 cells by cxposurc to (2) TNFa or (4) l)EX and comparcd with (l) untreated cells. Nuclcar extracts (5 /xg) from KB and KB3 cells exposcd to 10 pM DEX or 2.5 ng/mL TNFa wcre incubated with the radiolabeled NF-kB binding site. The DNA/NF-kB complex was analyzcd in nativc polyacrylamide gcls. A competition was carried out with 100-fold molar excess of unlabeled NF-kB binding site, which was also shown (3) using samplc with TNFa treatment. These pictures were rcpresentativc of three independent expcriments.
nuclear activity was higher in the KB celi linę than in the KB3 linę. For both celi lines, NF-kB protein complex was ;haracteri/.ed as P50/P65 heterodimer by supershift assay Fig. 2).
KB and KB3 cells were exposed to DEX or TNFa at lifferent concentrations (respectively, 1-10 /xM for 12-24 h and 2.5-10 ng/mL for 10 min to l h). Nuclear ;xtracts were then prepared and assayed for NF-kB DNA-binding activity. Only the most effective condi-ions using the lowest drug concentrations in each celi ine were selectcd and subsecjuently used. Exposure of <B and KB3 cells to 10-6 M DEX for 24 h resulted in an dmost complcte inhibition of NF-kB binding activity. ixposure to 2.5 ng/mL TNFa for 10 min led to signifi-ant incrcasc in NF-kB DNA-binding activity in KB and CB3 celi lines (Fig. 3).
Zonseąuences of NF-kB DNA-binding activity modulation <n apoptosis level
In untreated celi lines, KB displayed a significantly ower apoptosis ratę than KB3, with, respectively, 5% nd 16% (p < 0.05). In the KB celi linę (Fig. 4A), DEX xposure led to 1.6-fold apoptosis induction, and TNFa xposure did not lead to a significant effect on apoptosis ratę. In the KB3 celi linę (Fig. 4B), DEX exposure led to a weak apoptosis induction, and TNFa exposure resulted in a significant decrease in apoptosis, reaching 50% for the KB3 celi linę as compared to the untreated control.
Conseąuetices of NF-kB DNA-binding activity modulation on radiosensitmty parameters
To decrease the high constitutive NF-kB DNA-binding activity, KB cells were exposed for 24 h to 10~° M DEX. Conversely, KB3 cells were exposed to 2.5 ng/mL TNFa for 10 min, to inerease the Iow constitutivc NF-kB binding activity. After modulation of constitutive NF-kB DNA binding activity in each celi linę, radiosensitivity parameters were calculated and compared to untreated Controls. In the KB celi linę (Fig. 5A), DEX exposure significantly decreased radioresistance at Iow doses from 0.5 to 2 Gy, with the a parameter decreasing from 0.114 to 0.052 (Table 1). At higher doses (greater than 3 Gy), DEX exposure induced an inerease in radioresistance, with the /3 parameter inereasing from 0.012 to 0.030 (Table I). In the KB3 celi linę (Fig. 5B), whatevcr the irradiation dose, TNFa exposure led to an inerease in radioresistance. The SF2 value inereased 1.32-fold with TNFa pretreatment (Table 1).
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
NF-kB and radioscnsi(ivity • C. DlDELOT et al. 1355 mediated transcriptional activation and provides
scan0043 2 30 MICHAEL COX hydrodynamic parameters but are difficult to set up and operate. Trouve et
100 direct action on osteoblasts by stimulating their proliferation and differentiation (Gordeladze
58 peroxide (H202), produced by SOD activity, is in turn scavenged by CAT and APX (Gunes et al., 200
img086 Chengjang Shimeid and Holland 2000Myllokunmingia fengjiaoa Shu et al., 1999 - &nb
14 H. Pridalova et al.INTRODUCTION Goats are bred worldwide and therefore there is a great variance
18 H. Pridalova et al. Table 3. Average values for goat cheeses - physical and Chemical properties T
29 F.SIMARD ET AL Exlruction and isolation. The air-dried (.1 wcek) pow-dered wood froni P. resinosa
© 302 PARKZ<FRA6E and Afadin in breast cancer A Letessier et al n
304 PARKZ>FRA6E and Afadin in breast cancer A Letessia et al Fijiurc 5 Afadin knockdown in MDCKIl
305 PARK2/FRA6E and Afadin in breast cancer A Letessier et al FRA6EJPARK2. The multivariate analysis
299 PARK2/FRA6E and Afadin in breast cancer A letessier et al lines can be suppressed by microcell-m
300 PARK2<FRA6E and Afadin in breast cancer A Letessief et al A 6q26-<*27 B
F00574 001 f003 Normal rangę © Elsevier. Boon et al.: Davidson s Principles and Practice of Medici
F00574 001 f006 The gap/blockj—ii—O Priority-setting © Elsevier. Boon et al.: Davidson s Principles
F00574 003 f003 Cłuiescent incomplete DNA repair © Elsevier. Boon et al.: Davidson
F00574 016 f007 tKł intake © Elsevier. Boon et al.: Davidson s Principles and Practice of Medicine 2
więcej podobnych podstron