6585844972
India
178
_1
2.54
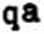
Later on Mohan et al (1971) suggested
Ncd = 1*5 M for depth upto 4 m. and Hcd = 1.75 H for depth from 4 to 9 m.
Whcf) bentonite aluriy ls used, then Ncd = K
Ihus, It was possible to Bakę use of all the correlations and curves available for predlctlng various soli parameters from Standard Penetratlon test (N values)
In thdr 1 atest report, the Irrlgation Research Institute, Roorkee have repo-rted to the Board of Irrlgation and Power (Siaima, Oarg, Ehargava & Gupta* 1973) based on a nunber of test on dlfferent sites that the cones (dry pro bing) can be used for explorlnę foundatlons upto shallow depths of 3-5 m for whlch a oorrelatlon of Ncd=l*7 Ks has beei obtalned. The 63 mm cone drlven wlth clrcul&tion of bentonite slurry has been found to explore foundatlons upto 15 m depth In sandy strata for whlch a oorrelatlon of Ncd=Ns has been detennined.
In practice, however, this raethod ls belng used fbr depths upto 30 m and even morę (Report on Haldla Port).
Ihe techninue ls now belng wldely adopt-ed by practislng fiims. It ls accępted as an Indian Standard ISx 4968 (Part-II), 1968 wlth sllght modlflcatlon. Ihe .oone slze ls rounded off to 65 mm.
Mohan et al (1971) have extended the use of 63 mm dla. cone to the gravdly solis. Ihey have oorrelated the cumu-lative no. of blows ln dynamie oone tests wlth allowabię load at a glven settle-ment by the eąuatlom
Ncd. Są Dc-Bf where
qa = allo wabię load t/m2
NCd = cumulatlve no. of blows corres-pondlng to a depth Dc.
Bf = Slze of foundatlon - metres
Sa = Defoimatlon - cm.
2.4 STaTCC CONS PaiBTRATION TESTS
Ihls test provldes a useful method of reoordlng vaiiatlons ln the in-situ penetratlon resistance of solls. It ls al so used fbr detennlnlng the bearlng capaclty of the soli at varlous
depths. It ls possible to detennlne skin frlctlon constants by thl s test alongwlth length of plles reąulred ln a ?lven sltuatlon. The statlc oone test ls most successful ln soft or loose
solls like sil ty s&nds, loose sands, layered deposlts of sands, sllts and clays as well as ln dayey deposlts.
Ihls test ls consldered as an inespen-slve and fast method of soundlng. In areas vhere some Information regardlng the foundatlon strata ls already avail-able, the use of test plles and loadLng tests can be a^olded by ocnductlng statlc oone penetratlon tests.
Ihe Indian Standard I Si 4968 (Part-ITI) 1971 generally covers the procedurę for detennlnatlon of the statlc cone red stance and frlctlon resl stance of soli at varlous depths below ground surface.
2.4.1 SąUPMSIT AND TEST PRDCEDORE
Ihe eąulpment conslsts essentlally of a steel oone wlth an apex angl© of 60° and overall base diemeter of 35.7 mm glvlng a eross-sectional area of 10 cm2. Ihe cone snould be so designed as tc prevent the lntruslon of soli particles ln the movlng parts of tne cone assembly. The base of the cone should be attached to a round steel rod of i5 mm dlameter called the soundlng red tfiich can be extended wlth addltlonal rods of one metre length. The soundlng rod should be gulded through a seamless tubę of Insi de dl am et er of 16 mm called the mantle tubę* Ihe mantle tubę should al s> be ln lengths of l metre wlth flush coupllng. Ihe dlameter of mantle tubę may be non-uniform or unifbm. The non-uniform type should be generally used wlth manually operated ecuipment due to less frlctlon on rods. Ihe rod attached to the cone cannot generally be pushed out of the mantle tubę fbr morę than 5 to 7 on. Ihe eąuipmaat should allo w for pushlng of the cone alone and the 36 mm OD frlctlon Jack et fltted immed-iately above the cone and the cone alteroately lnto the ground. Ihe cone and the mantle tubę may also be advanced contlnuously, if skin frlctlon readings are not reąuired to be detezmined separately. Ihe thrust for advanclng the cone or frlctlon Jacket and cone should be read on Bourdon gauges or provlng riLngs oonnected to the loadtiLng systen of the drlylng mech ani sn.
Ihe drlving mech ani sn should have a capadty of 2 to 3 t fór the manually operated eąulpment and 10 t for the mechanlcally operated eąulpment. Ihe drlvlng mech ani sn essentlally conslsts of a rack and pinlon arrangenent operated by a winch. Ihe reactlon for the thrust may be obtalned by suitable devices capable of taklng loads greater than the capadty of the eąulpment.
Ihe manually operated winch may be pro-vided wlth han dl es on bo th sldes of the
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Fig. 1. Geological-structural map of the eastern part of Polish Carpathians (modified, based on Żytk
18 H. Pridalova et al. Table 3. Average values for goat cheeses - physical and Chemical properties T
7. Opublikowane badania własne J Ontl et al/Futl 117(2014) 224-229 3. Results and dlscussion The dat
968 A. Edorh et al. tumors were associated with advanced clinical and histological markers. The esti
284 Z. KORUBA ET AL. 3. Control of motion of the launcher on a moveable base The launcher under cons
14 M. Sajewicz et al. Table III. Dependence on the method of extractiona of the relative amountsb of
16 M. Sajewicz et al. Table V. Dependence on the method of extraction* of the relative amountsb of v
54 although observations for periods shorter than 6 months are also available (Bozinovic et al.t 200
M. Lazar et al. Designing Low Gas Flow Meters Based on the Calometric Principle... REFERENCES 1.
M. Lazar et al. Designing Low Gas Flow Meters Based on the Calometric Principle... Device the most c
M. Lazar et al. Designing Low Gas Flow Meters Based on the Calometric Principle... The relationship
M. Lazar et al. Designing Low Gas Flow Meters Based on the Calometric Principle... total output prov
M. Lazar et al. Designing Low Gas Flow Meters Based on the Calometric Principle... The temperaturę d
M. Lazar et al. Designing Low Gas Flow Meters Based on the Calometric Principle... Yohunetric flow r
M. Lazar et al. Designing Low Gas Flow Meters Based on the Calometric Principle... Theoretical corre
M. Lazar et al. Designing Low Gas Flow Meters Based on the Calometric Principle... The constant of
M. Lazar et al. Designing Low Gas Flow Meters Based on the Calometric Principle... DISCUSSION As fol
więcej podobnych podstron