
Brian Mac Namee
„Using Situational Intelligence to Create Support Characters in
Character-Centric Computer Games”, University of Dublin, Trinity
College, 2004
Part IV
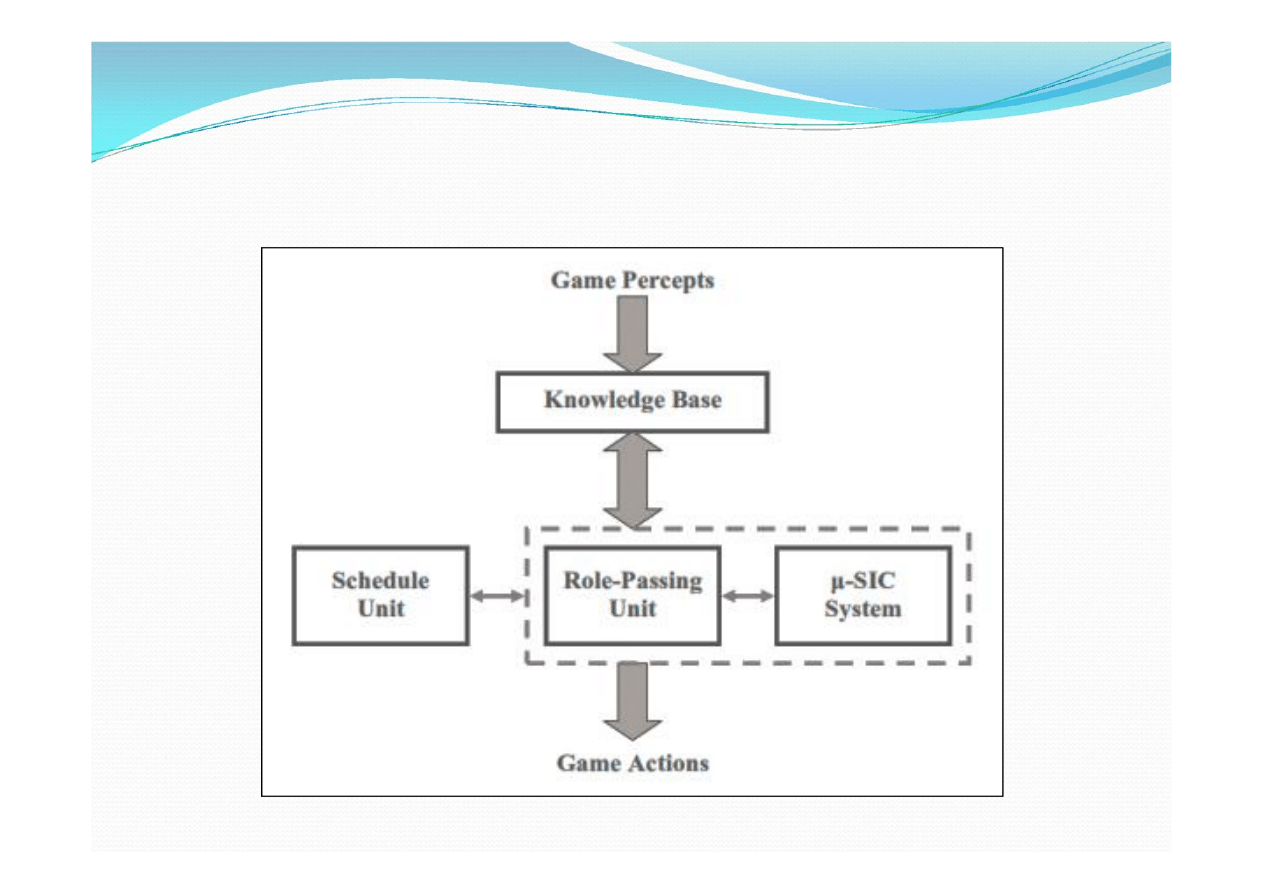
Proactive Persistent Agent
Architecture (PPA)
wg. Brian Mac Namee
Using Situational Intelligence ..."
2

The Schedule Unit
Within a game world, NPCs created using the PPA
architecture must give the impression of having a life
beyond their association with players.
For example, a character might begin her day at home in the
morning, then go out to work, visit a bar after work and,
finally, return home again. Players should notice that NPCs
perform these different tasks, and in this way
the illusion
that characters have lives beyond their involvement with
players is created.
In order to achieve this, each NPC is given a schedule which
divides a simulation day into a
set of time periods, for each
of which it is indicated where the character should be and
how they should behave. The great advantage of using a
schedule is that it endows agents’ behaviour with a large
degree of believability, without requiring any sophisticated
computation.
wg. Brian Mac Namee
Using Situational Intelligence ..."
3

The Schedule Unit
In a typical example of a schedule, written in XML, an NPC
begins his day at home, assuming the AT-HOME role. This
would instruct him to:
sleep in his bed if he is tired,
go to his kitchen to make a sandwich if he gets hungry,
or, if he gets bored, go to his living room and watch a little TV.
At about 11:00 it is time for the character to go to work, where
he assumes the CHEF role, up to about 23:00. The CHEF role
places the character in a restaurant’s kitchen where he cooks
meals as required by his waiting staff. Finally, approaching
23:00 the NPC adjourns to his local bar for a few well earned
drinks before retiring home and repeating the process on
each subsequent day.
wg. Brian Mac Namee
„ Using Situational Intelligence ..."
4
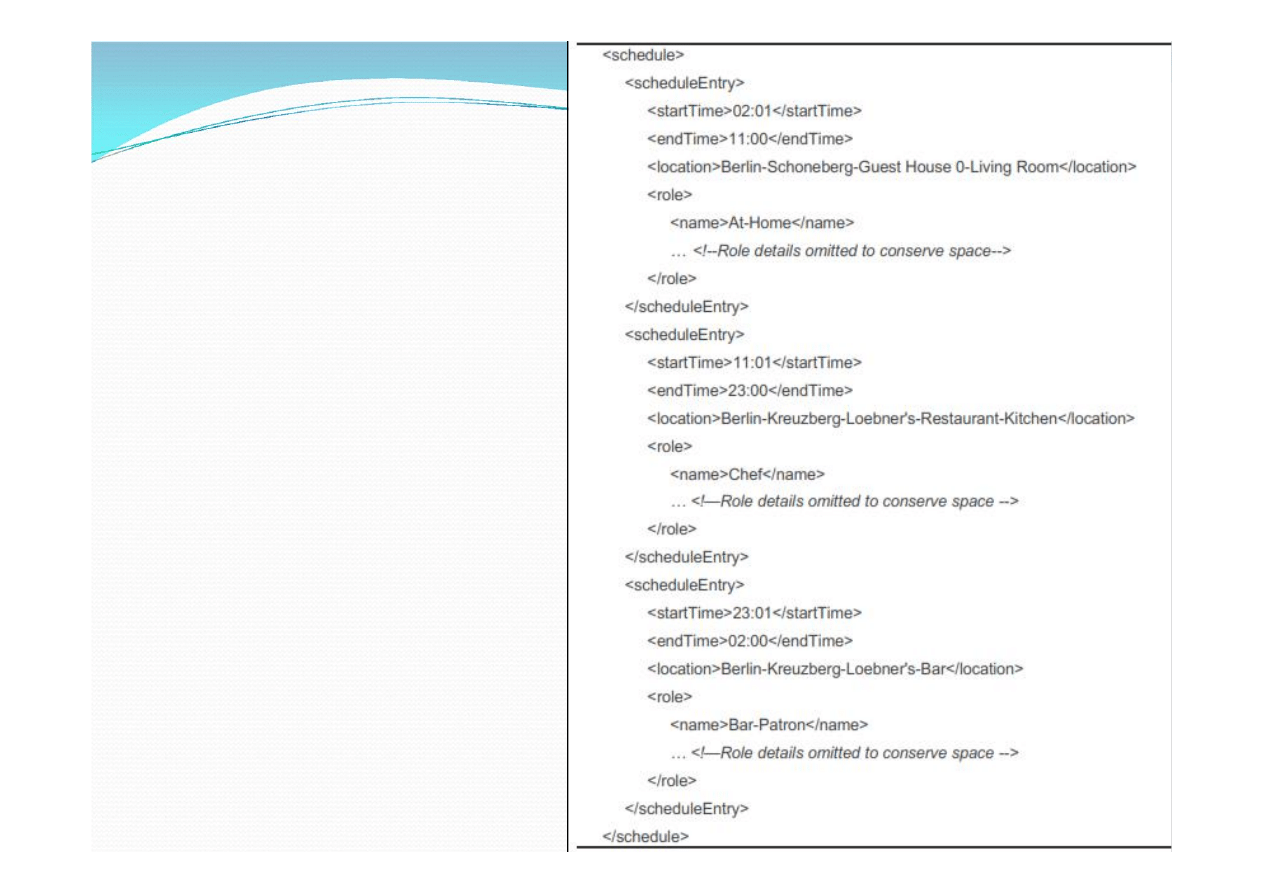
Example of
a schedule
wg. Brian Mac Namee
Using Situational Intelligence ..."
5

The Role-Passing Unit
The purpose of this unit is, not only to allow NPCs
display believable behaviour, but also, within a single
simulation, to allow them behave believably in a range
of diverse situations.
The description of this unit will begin with an
explanation of the motivations behind its inclusion,
and move on to a discussion of how it operates. The
latter will mention fuzzy cognitive maps (FCMs) which
are used to control an agent’s behaviour once a
particular role has been adopted.
wg. Brian Mac Namee
„Using Situational Intelligence ..."
6

The Role-Passing Unit
The purpose of this unit is, not only to allow NPCs display
believable behaviour, but also, within a single simulation,
to allow them
behave believably in a range of diverse
situations.
In order to satisfy the need for persistence, NPCs
controlled using the PPA architecture should be capable of
behaving believably in a range of diverse situations. If the
schedule shown before is considered, the character must be
seen at home, working in his kitchen and relaxing in a bar,
all within the same game.
The behavioural requirements of the NPC in each of
these situations are extremely different, and the
challenge of creating a single control system capable of
displaying all of these different behaviours is considered
beyond the capabilities of current AI techniques.
wg. Brian Mac Namee
„ Using Situational Intelligence ..."
7

The Role-Passing Unit
wg. Brian Mac Namee„ Using Situational
Intelligence ..."
8
Technique of role-passing begins with a very simple agent
capable of assuming
different roles as it moves between
different situations. By assuming a new role, an agent
becomes capable of behaving believably in a new situation.
A role can be considered an
agent control system suitable
to a given situation, throughout which it dictates the
agent’s behaviour. By assuming and discarding roles as
appropriate it becomes possible to
create agents which
can behave believably in any number of situations. This sits
comfortably with the notion of situational intelligence, as
agents possess only enough intelligence to behave
believably in their given situation.

The Role-Passing Unit
Role-passing is closely related to the “old AI” idea - a
technique used for discourse understanding. This
technique involves writing scripts to describe the processes
involved in different situations.
Discourse understanding is made easier by the fact that,
once the current position in a script is determined, a
context for language understanding and the resolution of
ambiguity is created. The role-passing process is related to
scripts in that the behaviour of each agent within a
simulation is contextualised by the situation in which they
find themselves.
wg. Brian Mac Namee
„ Using Situational Intelligence ..."
9
The Role-Passing Unit
wg. Brian Mac Namee
„ Using Situational Intelligence ..."
10
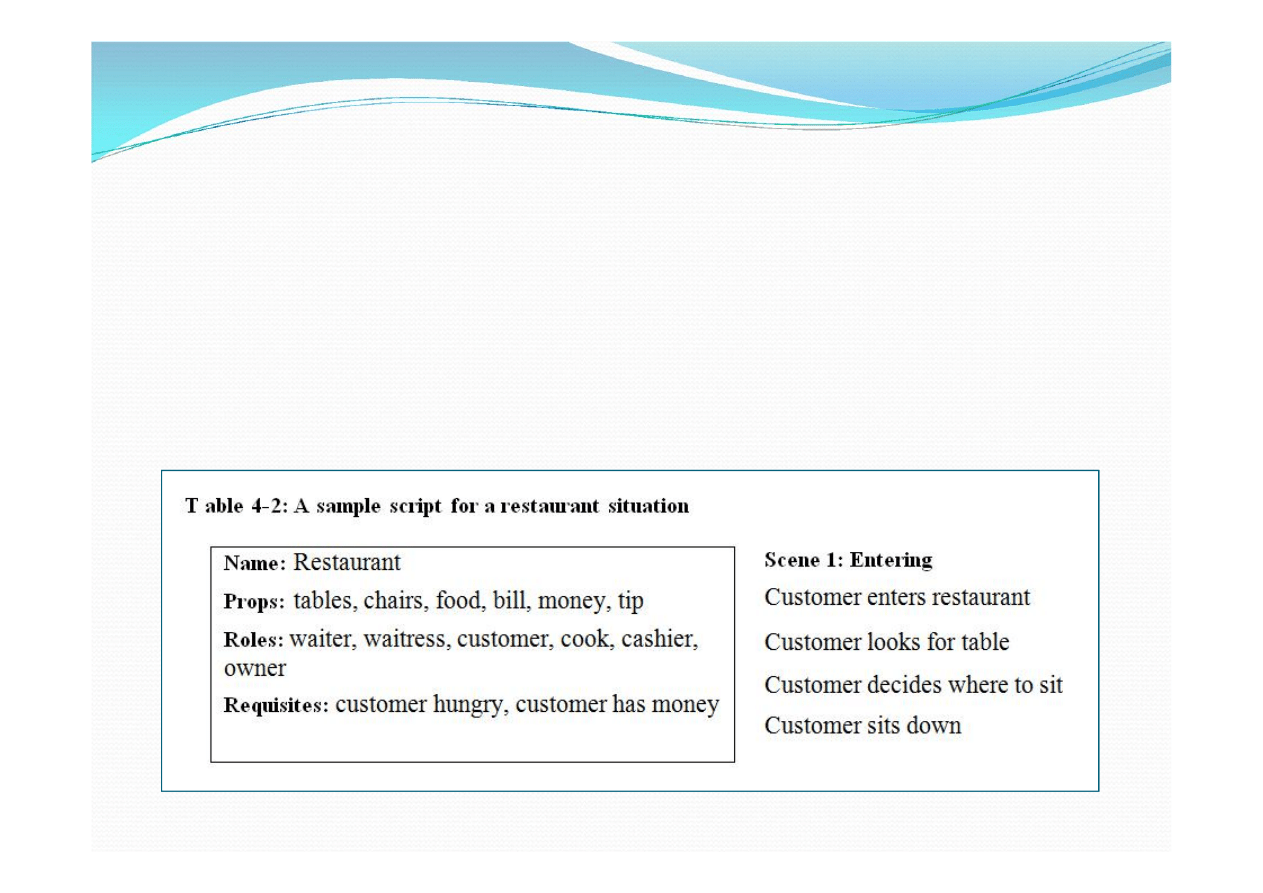
For example, a restaurant script would indicate that the
important actors in a restaurant situation are waiters,
customers and chefs; that the important props include
tables, menus, and food and that the sequence of events
upon a customer entering a restaurant proceeds with the
customer choosing a table, the waiter taking their order,
the food arriving and so on.

PPA Fuzzy Cognitive Control System
For the purposes of the PPA architecture, an FCM based
system - the proactive persistent agent fuzzy cognitive
control system (PPAFCCS) - has been created.
The PPAFCCS augments the original FCM system with a
number of node types which allow the input of activation
to the system from agents’ personal motivations and
perceptions of events in the game world, and for the
extraction of agents’ chosen behaviours.
Along with the original concept nodes, the
extra nodes
used within the PPAFCCS represent motivations, event
occurrences, rules, persistent flags and actions. When
these extra nodes are included in graphs they are referred
to as proactive persistent agent fuzzy cognitive maps
(PPAFCMs), rather than as FCMs.
wg. Brian Mac Namee
„ Using Situational Intelligence ..."
11

PPA Fuzzy Cognitive Control System
Motivations, rules and persistent flags always link
exclusively to concept nodes and never amongst each
other. Concepts output activation only to other
concept nodes, and action nodes. Similarly, action
nodes take input only from concept nodes, and very
rarely persistent flag objects.
Each concept is labelled and has a set of input links
(coming both from other concepts and nodes of the
other possible types) the activations of which are
summed and then passed onto a set of output links
emanating from the node.
wg. Brian Mac Namee
„ Using Situational Intelligence ..."
12

PPA Fuzzy Cognitive Control System
Motivation nodes allow the simulation of an agent’s
internal motivations. A motivation node maintains
two response curves, one which stores the manner in
which a motivation rises, and another for the manner
in which a motivation falls.
These
motivations can rise and fall regularly over
time (motivations such as hunger behave in this way),
or be affected by external events within a virtual world
(such as an increase in a fear motivation due to a
threatening occurrence nearby).
wg. Brian Mac Namee
„ Using Situational Intelligence ..."
13
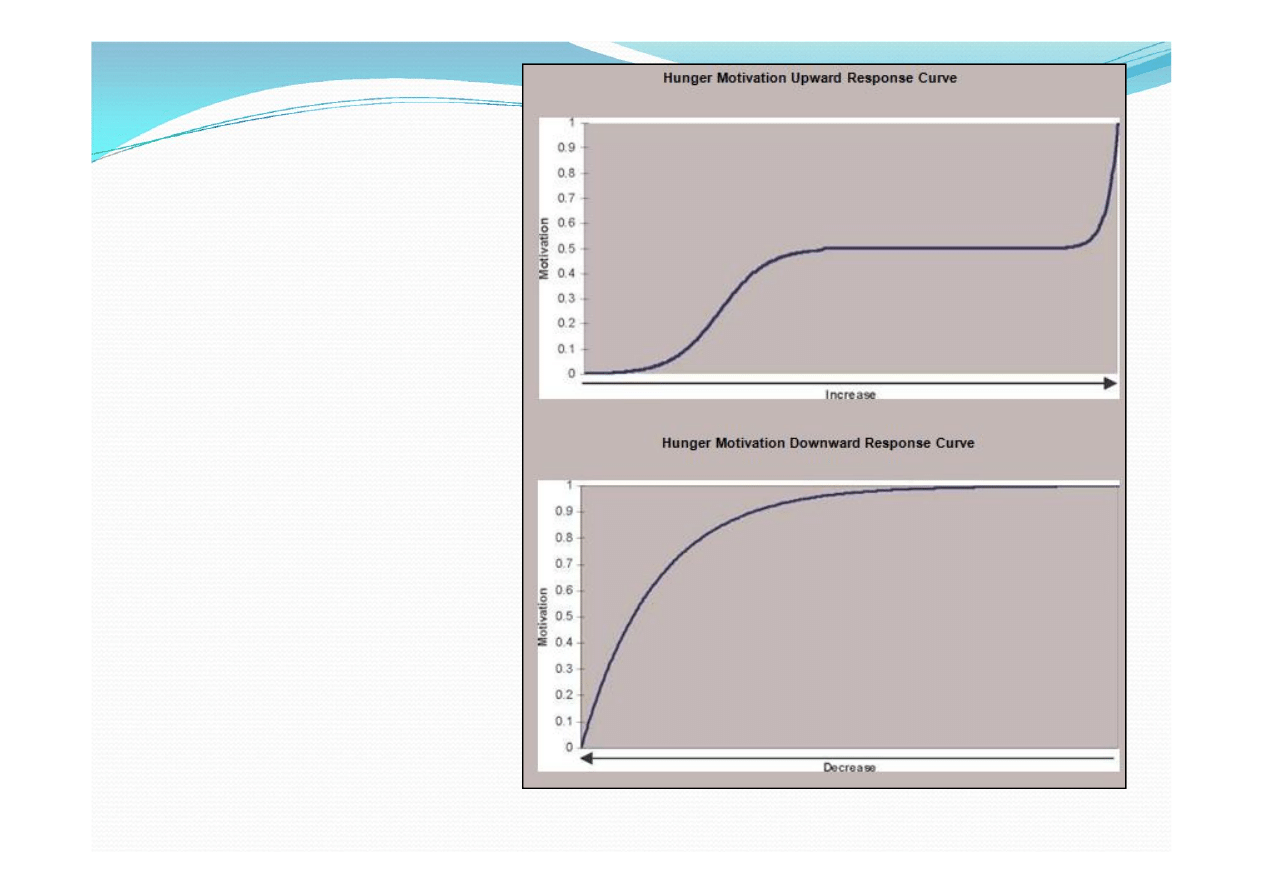
Upward and
downward
motivation
response curves
used by a basic
hunger
motivation
wg. Brian Mac Namee
„ Using Situational Intelligence ..."
14

Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
08 AI PPA Architecture
JDICE EC 08 architecture
ppa, Studia, Sem 3, 01.SEMESTRIII Maja, podstawy projektowania architekt
EC08 COP Architecture 08 May JMU
architektura sk 08
Podstawy urbanistyki i architektury 5.10.08, Szkoła, Architektura i Urbanistyka
Dziennik Ustaw z 2009 r ZMIANA WARUNKÓW TECHNICZNYCH OD 08-07-2009 R, Projektowanie Budownictwo Arch
AI 1 architektura
JDICE EC 08 architecture
ARCHITEKTURA KOMPUTEROW1A
09 Architektura systemow rozproszonychid 8084 ppt
Advanced Polyphthalamide (PPA) Metal Replacement Trends
FP w 08
08 Elektrownie jądrowe obiegi
więcej podobnych podstron