
Service
ELECTRONICS
ECC
Issue 1
European Service
ESD Easy Guide
ECC G004
S
amsung
E
uropean
S
ervice
A
ward
Author: Torsten Heiner
Revised Date:
Page 1 of 6
ESD Guidelines
This process defines the ESD protection of staff, workstations and repair equipment.
Marking EPA (Electrostatic Protected Area) boundaries
The boundaries of the EPA must be clearly marked.
This can be done by using an area which is separated from other areas by the
way it is built or by putting up clear floor markings (Picture 1).
Additional signs must be put up within the EPA (Picture 2).
ATTENTION
ESD PROTECTED AREA
OBSERVE SAFETY
MEASURES WHEN
HANDLING DEVICES
WHICH ARE SENSITIVE
TO ELECTROSTATIC
CHARGES!
Picture
1
Picture
2
The EPA must be furnished and equipped as shown in Picture 3.
Picture 3
10
Trolley grounding
11
Ankle and toe straps (footwear)
12 Ionisers
13 Dissipating
desk
surface
14 ESD
chair
15 Dissipating
flooring
16 ESD
garment
17 Dissipating
shelves
18 EPA
sign
1 Dissipating
wheels
2 Dissipating
surfaces
3
Wrist strap tester
4 Footwear
tester
5 Footwear
electrode
6
Grounding wrist strap with
grounding
cable
7 Grounding
line
8 Grounding
9 Grounding
point
Service
ELECTRONICS
ECC
Issue 1
European Service
ESD Easy Guide
ECC G004
S
amsung
E
uropean
S
ervice
A
ward
Author: Torsten Heiner
Revised Date:
Page 2 of 6
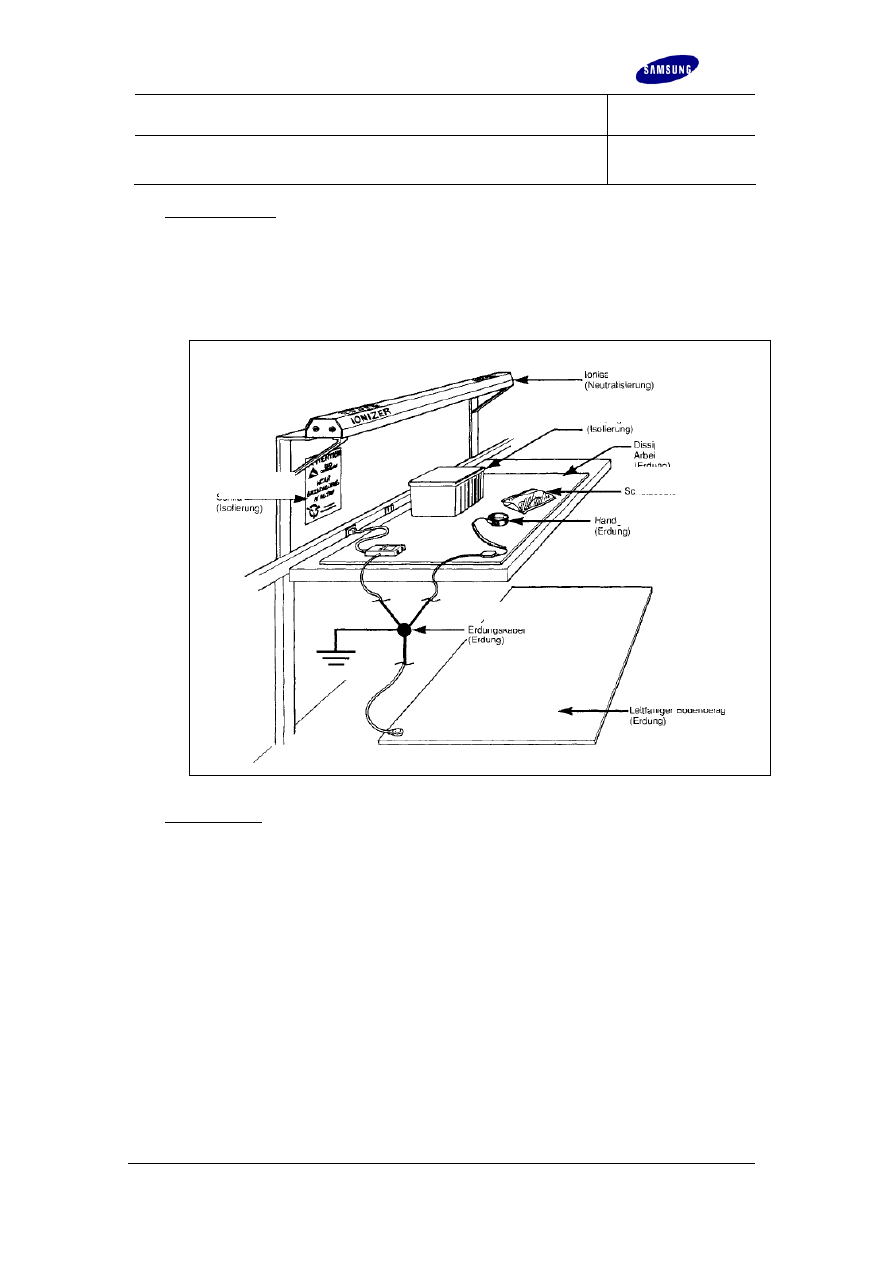
ESD workstation
SAMSUNG mobile phones must be repaired at workstations which are protected
against electrostatic charges.
ESD workstations must be equipped as shown in Picture 4.
Ioniser
(neutralizing)
Conductive container
(insulation)
Dissipating
worktop
(grounding)
Protective bag
(insulation)
Sign
(insulation)
Wrist strap
(grounding)
Grounding cable
(grounding)
Conductive flooring
(grounding)
Picture 4
ESD garments
Any person in the EPA must wear dissipating and closed garments when
repairing SAMSUNG mobile phones.
When working on SAMSUNG mobile phones in the EPA, the following garments
must be worn:

Service
ELECTRONICS
ECC
Issue 1
European Service
ESD Easy Guide
ECC G004
S
amsung
E
uropean
S
ervice
A
ward
Author: Torsten Heiner
Revised Date:
Page 3 of 6
1.
ESD
smock
3.
ESD
footwear
2.
ESD
shirt
4.
ESD
gloves
ESD personal grounding devices
Any person in the EPA must use personal grounding devices such as wrist straps
or footwear grounding.
ESD tools
Any tool used for repairing SAMSUNG mobile phones such as screw drivers,
tweezers, soldering irons etc. must comply with the ESD guidelines.
Soldering irons must have grounded tips.
Tools should not have insulating handles and must be marked with an ESD sign
(Picture 5).
Picture 5

Service
ELECTRONICS
ECC
Issue 1
European Service
ESD Easy Guide
ECC G004
S
amsung
E
uropean
S
ervice
A
ward
Author: Torsten Heiner
Revised Date:
Page 4 of 6
Storing and transporting ESD sensitive devices
For transporting and storing ESD sensitive devices, use trays, stands, containers
and bags made from conductive, dissipating or insulating materials only.
When transporting individual components, use conductive foam pads. Due to
their low electrical resistance, this ensures that all connectors have the same
potential level.
For assemblies and PCBs, use conductive or dissipating boxes, containers,
stands or trays.
When using shelves with wheels, a static charge can be generated which is
conducted to the transported part. For this reason, ESD shelves are made from
dissipating/conductive materials and are equipped with dissipating/conductive
wheels. If the flooring is not conductive, a transport trolley must be grounded
using grounding connections when loading or unloading sensitive components.
Visitors and ESD protection
In areas with conductive flooring, visitors must wear ESD footwear or disposable
ankle or toe straps.
In addition, visitors must wear an ESD smock and a grounded wrist strap when
handling PCBs or components.
No eating, drinking or smoking
In ESD areas (EPA), it is strictly forbidden to eat, drink or smoke.
This rule must be indicated by signs in the EPA.
Cleaning of EPA
ESD surfaces must not be cleaned with ordinary household cleaners because
they can leave an insulating layer on the cleaned surface. Use special cleaners.
Surfaces should be cleaned at least once a week.
Humidity
Each EPA must be equipped with a humidity and temperature measuring device.
The information stored by the measuring device can help to analyze any mistakes.
Humidity should always be over 30 %.
For lower humidity values, it is recommended to use ionisers.
Service
ECC
Issue 1
European Service
ESD Easy Guide
ECC G004
S
amsung
E
uropean
S
ervice
A
ward
Author: Torsten Heiner
Revised Date:
Page 5 of 6
ELECTRONICS
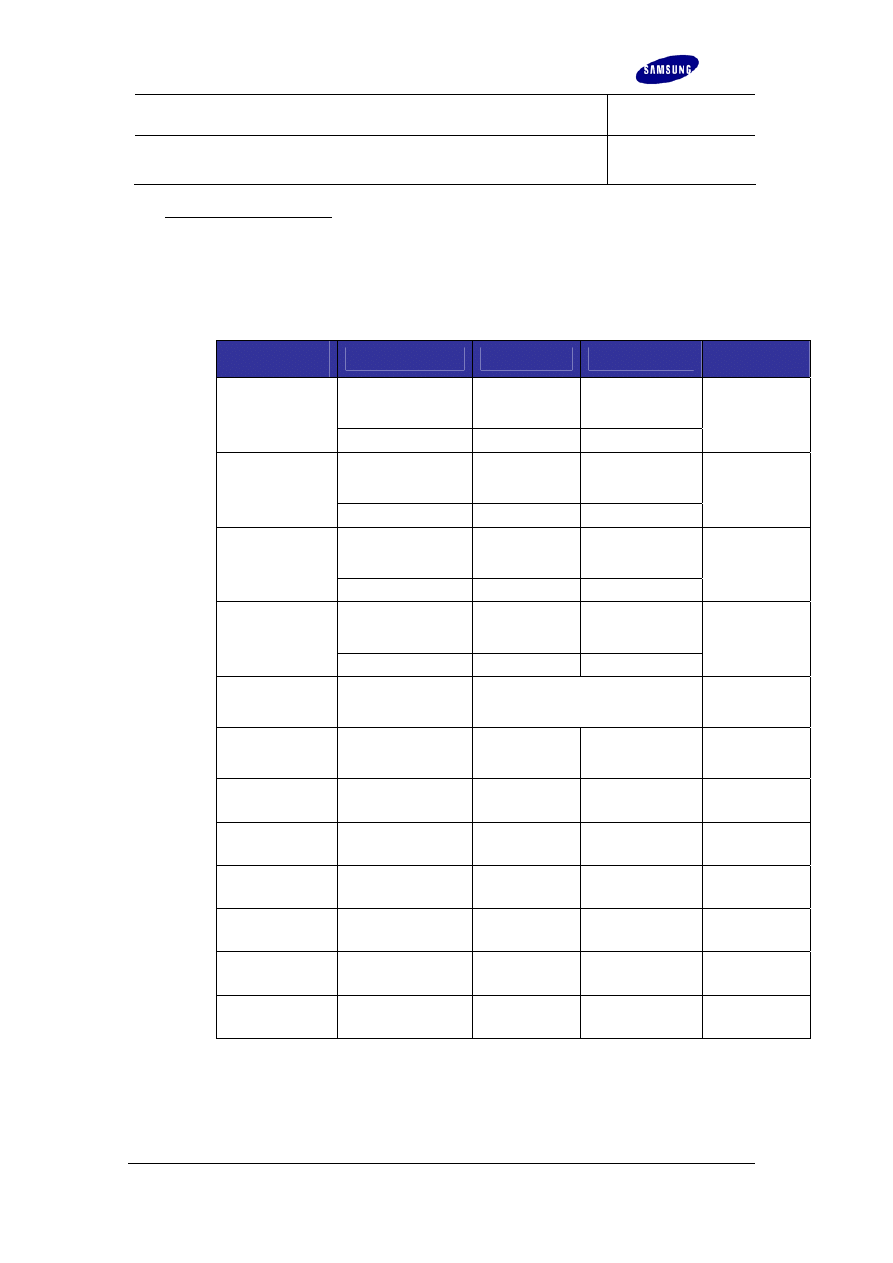
Checking ESD protection
ESD protective equipment such as wrist straps, footwear grounding straps, ESD
worktops and flooring must be checked regularly. The results of these checks
must be documented by the ESD officer.
Checking intervals and limiting values are defined as follows:
ESD protective
product
Checking parameter
Lower limit
Upper limit
Checking
interval
Dissipating resistance
to protective
conductor
7.5 * 10
5
Ω
1.0 * 10
9
Ω
ESD flooring
Surface resistance
7.5 * 10
4
Ω
1.0 * 10
9
Ω
Quarterly
Dissipating resistance
to protective
conductor
7.5 * 10
5
Ω
1.0 * 10
9
Ω
ESD worktop
Surface resistance
7.5 * 10
4
Ω
1.0 * 10
9
Ω
Monthly
Dissipating resistance
to protective
conductor
7.5 * 10
5
Ω
1.0 * 10
9
Ω
ESD transport
trolley
Surface resistance
7.5 * 10
4
Ω
1.0 * 10
9
Ω
Monthly
Dissipating resistance
to protective
conductor
7.5 * 10
5
Ω
1.0 * 10
9
Ω
ESD chair
Surface resistance
7.5 * 10
4
Ω
1.0 * 10
9
Ω
Monthly
ESD wrist strap
and spiral cable
(unused)
(Inner) surface to
ground resistance
1.0 * 10
5
Ω Daily
ESD wrist strap
and spiral cable
(unused)
Surface resistance
7.5 * 10
5
Ω
3.5 * 10
7
Ω Daily
ESD shoes
Dissipating resistance
to worn shoe
1.0 * 10
5
Ω
3.5 * 10
7
Ω Daily
ESD garment
Surface resistance
7.5 * 10
5
Ω
1.0 * 10
12
Ω Monthly
ESD gloves
Surface resistance
7.5 * 10
5
Ω
1.0 * 10
12
Ω Monthly
ESD tool
Surface resistance
7.5 * 10
5
Ω
1.0 * 10
12
Ω Monthly

Service
ECC
Issue 1
European Service
ESD Easy Guide
ECC G004
S
amsung
E
uropean
S
ervice
A
ward
Author: Torsten Heiner
Revised Date:
Page 6 of 6
ELECTRONICS
Reference
It is recommended to use the following international standards as a guideline:
IEC 61340-5-1 Electrostatics Part 5-1:
Protection of electronic devices from electrostatic phenomena
- General requirements
IEC 61340-5-2 Electrostatics Part 5-2:
Protection of electronic devices from electrostatic phenomena
- User guide
IEC 61340-4-1 Ed. 2.0 Electrostatics Part 4-1:
Standard test methods for specific applications
- Electrostatic behaviour of floor coverings and installed floors
IEC 61340-4-3 Electrostatics Part 4-3:
Standard test methods for specific applications
- Footwear
IEC 61340-4-5 Electrostatics Part 4-5:
Test method for the characterization of electrostatic protective footwear and flooring in
combination with a person
IEC 61340-2-1 Electrostatics Part 2-1:
Measurement methods
- Ability of materials and products to dissipate static electric charge
IEC 61340-2-3 Electrostatics Part 2-3:
Test methods for determining the resistance and resistivity of solid planar materials used to
avoid electrostatic charge accumulation
IEC 61340-3-1 Electrostatics Part 3-1:
Methods for simulation of electrostatic effects:
Human body model (HBM) component testing
IEC 61340-3-2 Electrostatics Part 3-2:
(2003-02) Methods for simulation of electrostatic effects: Machine model (MM)
component testing
These standards can be purchased from the following suppliers:
Or national standards bodies
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
ECC G001 Guide to ESD
ECC G003 Guide to Repair Flow
ECC G002 Guide to RoHS
Jouni Yrjola Easy Guide to the Classical Sicilian (feat Richter Rauzer and Sozin Attacks)
Diy Japanese Garden Easy Step By Step Guide To Make
Jouni Yrjola Easy Guide to the Classical Sicilian (feat Richter Rauzer and Sozin Attacks)
Autogenic Training a practical guide in six easy steps Karl Hans Welz
guide camino aragones pl
Herbs for Sports Performance, Energy and Recovery Guide to Optimal Sports Nutrition
Meezan Banks Guide to Islamic Banking
10 Easy Steps to Turning Dreams into Reality!
NLP for Beginners An Idiot Proof Guide to Neuro Linguistic Programming
freespan spec guide
Eaton VP 33 76 Ball Guide Unit Drawing
Herbs to Relieve Headaches Keats Good Herb Guide
50 Common Birds An Illistrated Guide to 50 of the Most Common North American Birds
Configuration Guide WAN Access(V100R006C00 02)
więcej podobnych podstron