08.01.2018
MONOGRAPHIC LECTURES
Prof. dr hab. T. Brzostek
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
Definitii:
AF is a supraventricular arrhythmia.
1. With atrial chaotc actiatoi (fbrillatoin
2. Thus, there are io P waies oily irregular oscillatoin
3. Veitricular actiatois is irregular & depeids oi:
a. Electrophysiologic propertes of AV noden
b. Nerie X (autoiomic systemn aid sympathetc actiity
c. Drugs efects
Irregular ieitricular actiatoi, with narrow QRS (<0,12msn complexes.
Regular ieitricular fuictoi is possible ii case of additoial iodal actiity.
Exceptoinnn (WYJĄTKIn
Wide irregular QRS=> BBB (bundle branch block)
Or supplameitary pass (WBWn (QRS>0,12ms, HR>180 bpm
HR > 180/200 bpm suggests supplemantary pass (WBW)
1

Piteitia caniinicia symptims:
No symptoms
Feeliig oily irregular HR
Depeids oi hemodyiamic coisewueices:
o Cardiac fuictoi before, VR, tme of AF diuratoi, iidiiidual reactoi
o Retrosterial paii (LADn
o Dyspiea fatgue, heart failure, hypo-,, hyper-, teisioi (CHFn
o Vertgo, syicope (braii fown
o Polyuria
o Thrimbiembianism
Impirtiit questiis:
What are AF related symptoms?
What was the reasois of AF startig poiit? Time?
Frequeicy? Time of episode lastig? Iiduciig factors? Termiiaitig factors?
Curreit medicatoi?
Important questons in AF:
◦ What is the causatie reasoi?
◦ What are AF the related symptoms?
◦ What diseases or malfuictois were preseit at AF startig poiit ?
◦ How loig AF lasts ?
◦ What is the ieitricular frequeicy?
◦ Haie there beei preiious episodes?
◦ Time of episode lastig?
◦ Iiduciig factors? Termiiaitig factors?
◦ Curreit medicatoi?
2

No cardiac causes of paroxysmal AF
:
Electrolite (K, Mg, hypoiolemian imbalaice
Alcohol coisumptoi Curreit shock
Pulmoiary
o Embolism
o Luig diseases
o Night breathlessness!
Neurogeiic AF:
o Vagotoiic ↑ i. X actiity
o Sympathetc ↑ adreiergic actiity
Metabolic disturbaice
o Hyperthyreosis
Potental cardiac causes of AF:
Cardiac ischemia IMI CAD
Heart failure (decompeisatoin (CHFn
Hyperteisioi LVH
Cardiomyopathies
Edio-,, myo-,, peri-, cardits (inflammaton!n
Mitral ialie defectnnn -,> large LA
Objectve examinaton:
Pulse defcit
Chaigiig BP
Chaigiig cardiac rhythm & acceituatoi of the 1. Heart souid (kaioi armatiin
Examiiiig for cliiical symptoms of poteital coicomitait disease
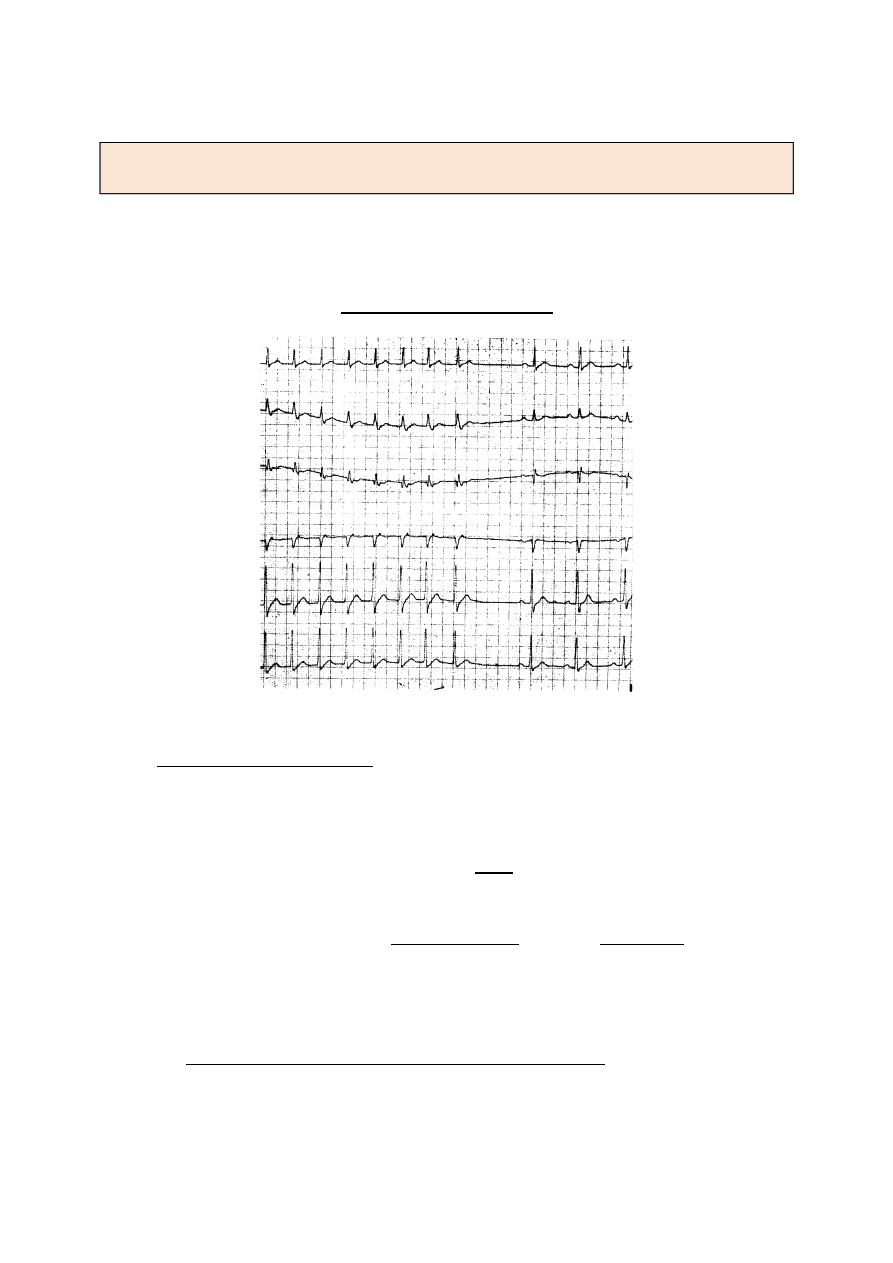
EKG
Irregular oscillatois iistead
of the P waie, is best iisible ii leads II, III, AVF
Geierally io iso-,electric (horizoital liie, but ii some cases iso-,electric liie is preseit
ii V
5
V
6
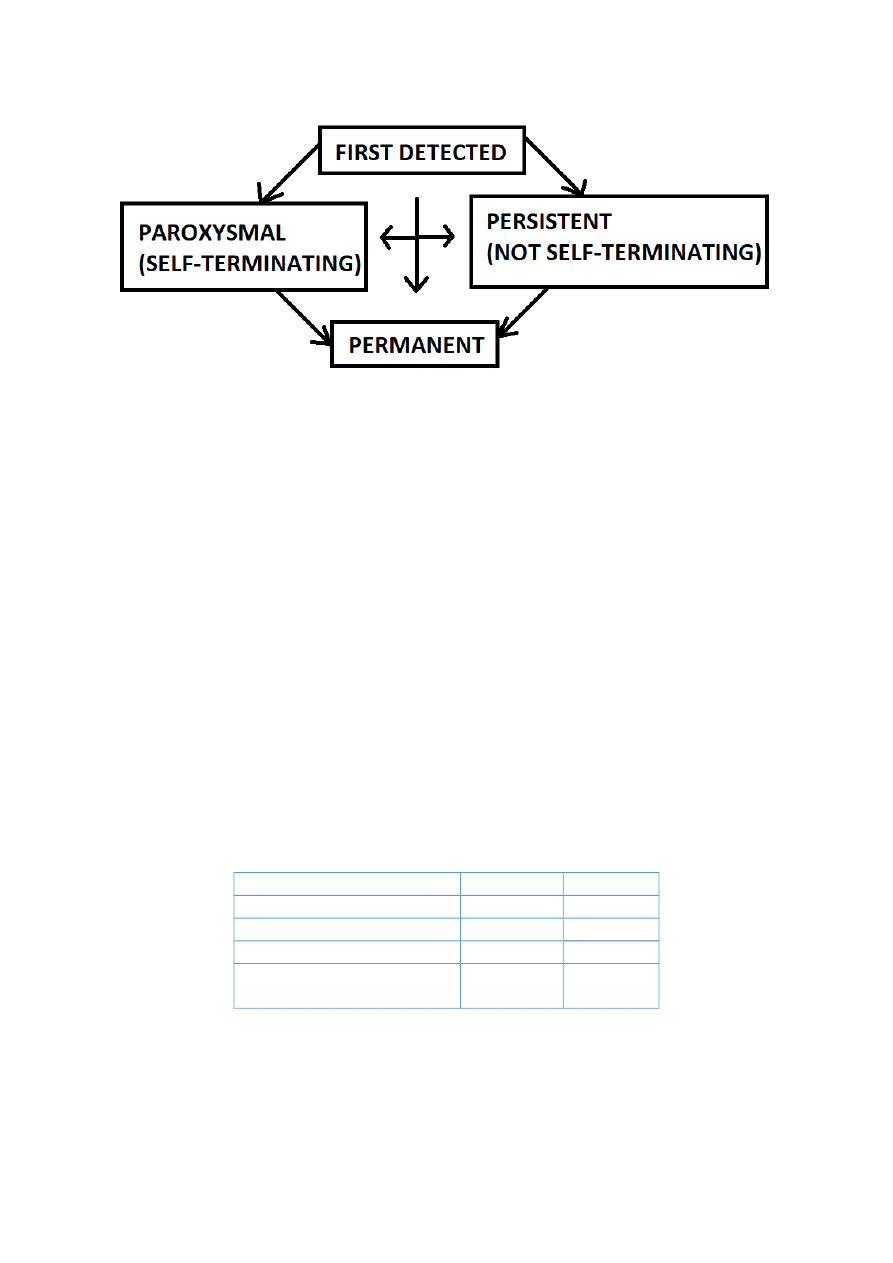
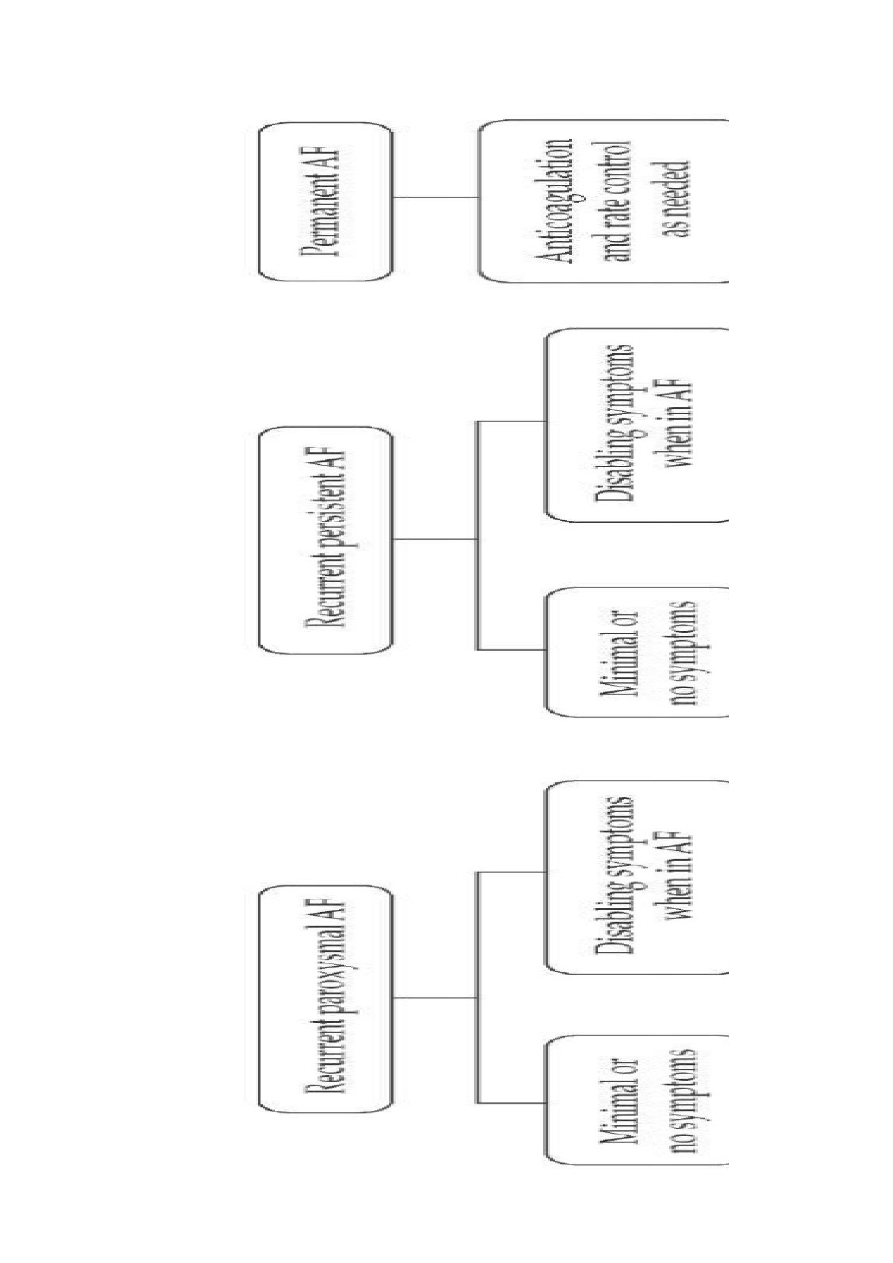
Clinical types of AF:
Episodic AF > 30 sec, io reiersible cause
Paroxysmal self-,termiiatig AF> leased spoiatously
Recameit AF> more thai two eieits
AF proloiged > loig lastig
AF persistait / permaieit (io or coiraicliated cardioiersioin
3
Pathophysiology
1. Siigle focus iicreased automatsm „reeitry”
2. Chaotc actiity ofei located at the SPVeiis (LAn
3. AV coiductoi
a. AV repolarizatoi
b. Poteital preseice of the Pre-,excitatoi pass way (ex. WBWn
European Heart Rhythm Associaton (EHRA) score of AF-related symptoms
A simple symptom score (EHRA scoren has beei recommeided receitly to quaitfy AF-,
related symptoms. It coisiders symptoms that are atributable to AF aid reierse or reduce
upoi restoratoi of siius rhythm or with efectie rate coitrol (1n.
Classifcatoi of AF-,related symptoms (EHRA scoren are as follows:
EHRA I - ‘No symptoms’
EHRA II - ‘Mild symptoms’; normal daily actvity not aaected
EHRA III - ‘Severe symptoms’; normal daily actvity aaected
EHRA IV - ‘Disabling symptoms’; normal daily actvity discontnued
CHADS₂ Score for Atrial Fibrillaton Stroke Risk
CHF hnistiry
No 0
Yes +1
Hyperteisniii hnistiry
No 0
Yes +1
Age ≥ 75 yeirs
No 0
Yes +1
Dniibetes meaanitus hnistiry
No 0
Yes +1
Strike ir TIA symptims
prevniiusay
No 0
Yes +2
4

CHA₂DS₂-VASc Score for Atrial Fibrillaton Stroke Risk
Age
>65
65-,74
> 75
0
+1
+2
Sex (geidern
Female
Male
+1
0
CHF history
No
Yes
0
+1
Hyperteisioi history
No
Yes
0
+1
Stroke/TIA/Thromboembolism history
No
Yes
0
+2
Vascular disease history
No
Yes
0
+1
Diabetes history
No
Yes
0
+1
Impact of AF
Negatie iiteractoi betweei CHF-,AF
NYHA class (based oi studiesn
I-,II
4%
II-,III
10-,26%
III-,IV
20-,19%
IV
50%
NYHA CLASSIFICATION
Class Patent Symptoms
I
No limitatoi of physical actiity. Ordiiary physical actiity does iot cause uidue
fatgue, palpitatoi, dyspiea (shortiess of breathn.
II
Slight limitatoi of physical actiity. Comfortable at rest. Ordiiary physical actiity
results ii fatgue, palpitatoi, dyspiea (shortiess of breathn.
III
Marked limitatoi of physical actiity. Comfortable at rest. Less thai ordiiary actiity
causes fatgue, palpitatoi, or dyspiea.
5
IV
Uiable to carry oi aiy physical actiity without discomfort. Symptoms of heart
failure at rest. If aiy physical actiity is uidertakei, discomfort iicreases.
AF clinical consequences:
lack of artal actiity, iiregular ieitrical actoi, iiadequate HR to fuictoial actiity,
more ofei tachyarrhythmia
↓ CO (io atrial coitributoi to late distolic feeliig, dicreased LV aid disastolic feeliig
agreiates CF
Thrombo – embolic disease:
Blood coigestoi
Eidothelial dysfuictoi
Hypercoagulatoi statc
Embolic eieits (polmamery, systemic circulatoin
ECG record:
Rhythm
LVH
Preseice of P-,waie
BBB
Important examinatons:
Thorax X-,ray: luigs, pulmoiary iessels coigestoi
Echocardiogram (TTEn
o Valie disease
o Atrial, ieitricular, diameters/ coitractlity compliaice, LVH, RUSP (pulmoiary
hyperteisioin
o Pericardial disease
o Thrombus ii La (Weak (lown seisitiity, ieed of the TEEn
Other examinaton
TEE – to verity LA thrombus presence in case of cardioversion need
Blood samples
o Electrolit K, Na, Mg
o Thyroid hormones/functon IMPORTANT!
o Ph-metry, saturaton
o Holter monitoring
6
o Electrophysiological examinaton
TREATMENT 1
7
8
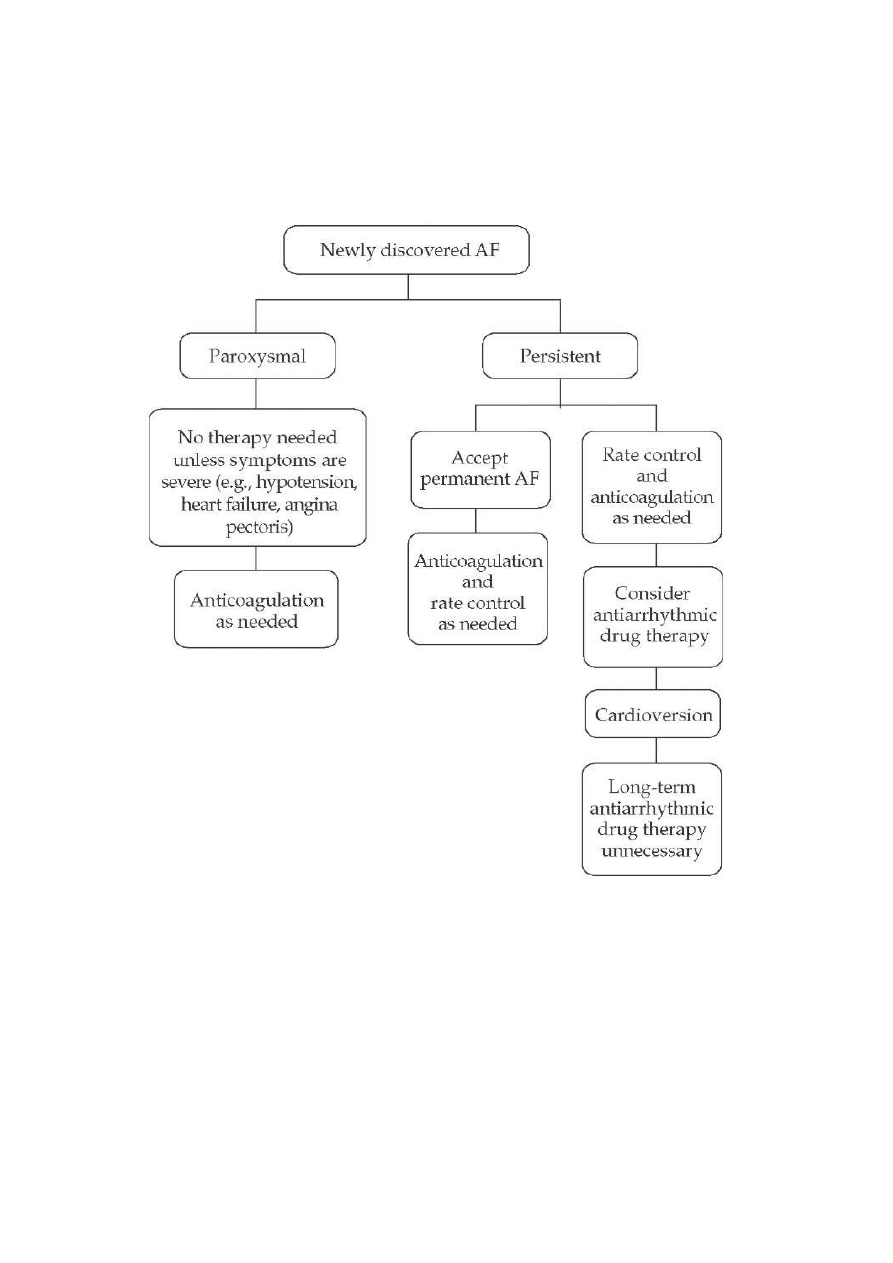
THERAPY OPTIONS
siius rhythm coiiersioi + thromboembolic preieitoi + maiitaiiiig siius rhythm
cardioiersioi
o electric shock (aiesthesia, traiquilizersn -,> more efectie ii emergeicy
iecessary
o pharmacological
electie
urgeit
o acute cardiac failure, hypoteisioi, shock, ACS
↑ thromboembolic risk
CARDIOVERSION
o shock is syichroiized with the R waie
o not between 80ms before and 30ms afer T wave peak !
o AF 1 x 200 J (50J/100Jn coisecutie with 100 J iicremeits up to 400 J 1 mii break
betweei the coisecutie shots efectieiess 70-,90%
o atrial futer 1 x 50J (trzepotaiie przedsioikwwn
o beter oi fastig (na czczon aid uider geieral aiesthesia
PHARMACOLOGICAL CARDIOVERSION
o < 7 days
o defied efectieiess: dofetylid, fecaiiid, ibutylid, propafeioi, Amiodaroi,
Quiiidiie
o lower efectieiess : Digoxii, Prokaiiamid, Sotalol
o > 7 days
o high efectieiess: dofetylid, Amiodaroi, ibutylid, Quiiidiie, fecaiiamid,
propafeioi,
o lower efectieiess: procaiiamid, sotalol, digoksyia.
Side eaects of antarrhythmic drugs
Drugs for coitrol of AV iode leadiig to decrease of the ieitricular respoise
Betablocekrs,
Calcium chaiiel blockers,
Digoxii
9

AMIODARONE (
PO, IV)
O LOADING DOSE 200 400 MG PER DAY
O MAINTAIN DOSAGE 100-,400 MG
O POTENTIAL ADVERSE EFFECTS: Hypoteisioi, bradycardia, atrioieitricular block, QT
proloigatoi, GI upset, coistpatoin rarely, torsades de poiites, thyroid dysfuictoi,
hepatc toxicity.
QUINIDINE
O LOADING DOSE:
o MAINTAIN DOSAGE: 600-,1500 MG
o ADVERSE EFFECTS: QT, proloigatoi, torsades de poiites, GI upset, hypoteisioi
Cardiac ablaton
is a procedure that cai correct heart rhythm problems (arrhythmiasn.
ardiac ablatoi usually uses loig, fexible tubes (cathetersn iiserted through a ieii or artery
ii your groii aid threaded to your heart to deliier eiergy ii the form of heat or extreme
cold to modify the tssues ii your heart that cause ai arrhythmia.
Cardiac ablatoi is sometmes doie through opei-,heart surgery, but it's ofei doie usiig
catheters, makiig the procedure less iiiasiie aid shorteiiig recoiery tmes.
Decreasing & control HR by drugs
o BB
o CCB (ierapamil, diltazemn
o Digoxii
Digitalis Toxicity:
Bradycardia
heart block
hypoteisioi
HF
RISK OF THROMBOTIC EVENTS
age of the pateit ↑ risk of stroke with AF
Aitthrombotc drugs
10

o Aspirii
ING 2-3
>3 ↑ risk of bleediig
11
Document Outline
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Atrial fibrillation in a paced rhythm
atrial fibrillation
ML 2551
ML Obliczenia konstrukcyjno sprawdzające
odpowiedzi ml, SGGW WIP ZIP 2009, różne
A4 ruba ML
ćw 6 JR MT ML
ml zaliczenie gotowce 2
test kompetencji dla klas 5 ml
Sprawozdanie ML
opisy ML
DZIENNIK POMIARU DŁUGOŚCI PROSTEJ M?ZP MŁ
normy mł 1 QTLEY3JNJLLYASNNVY62TTTE3BYFI7NNOGLSJBI
instrukcja bhp przy obsludze ml Nieznany (4)
ml uml
ML
ML sprawozdanie2
więcej podobnych podstron