
1
Learning Objectives
Explain blood biochemistry and blood typing
Conduct blood spatter analysis to find the
source of blood and reconstruct past events
Identify the various blood spatter patterns
1
3
4
Describe the methods used in the
identification and individualisation of blood
2

2
Blood
Fresh
Old & dried
Obvious
Obvious?
3
Whose blood is it?
Show up invisible stains
Is it blood?
1
3
Is it human blood?
Can we use blood spatter
patterns to reconstruct events?
4
2
Blood

4
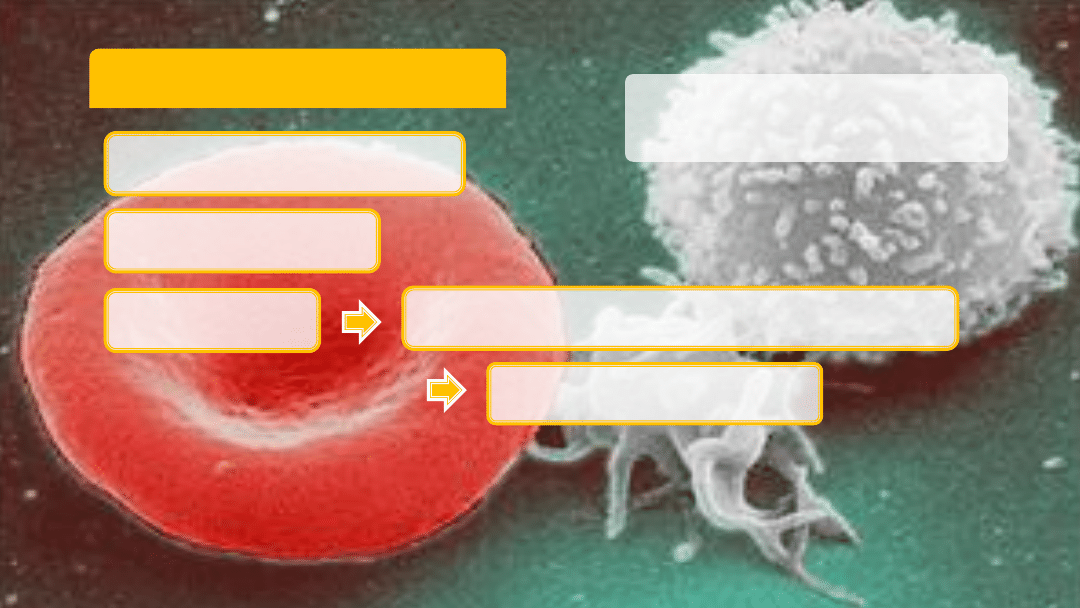
Blood Composition
Fresh frozen
blood plasma
Fluid portion of blood
55% by weight
Transport system
8% of body weight
Blood plasma
5
Blood Composition
Left to right: erythrocyte,
thrombocyte, leukocyte
Blood cells
Oxygen transport
Red blood cells / erythrocytes
8% of body weight
Blood plasma
6
Blood Composition
Left to right: erythrocyte,
thrombocyte, leukocyte
White blood cells / leukocytes
Immune response
Blood cells
Red blood cells / erythrocytes
8% of body weight
Blood plasma

7
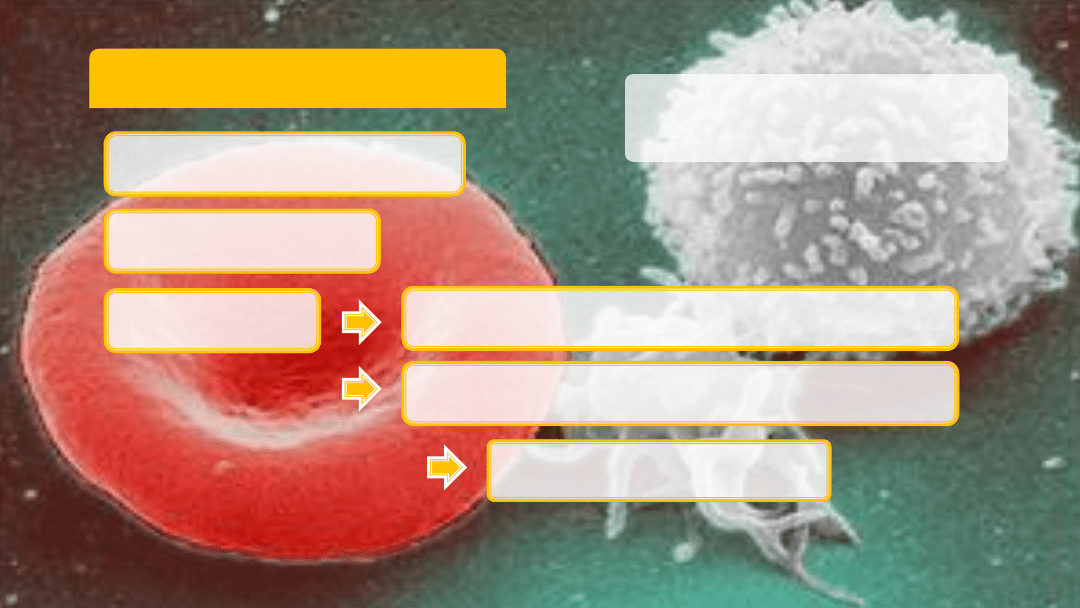
Blood Composition
Left to right: erythrocyte,
thrombocyte, leukocyte
Clotting response
Platelets / thrombocytes
White blood cells / leukocytes
Blood cells
Red blood cells / erythrocytes
8% of body weight
Blood plasma

8
Erythrocytes
7.8 microns in diameter
No nucleus
Biconcave
No DNA
Red blood cell

9
Erythrocytes
Principal function
4 oxygen molecules
on each protein
Oxygen transport
Red blood cell

10
Antigens
Proteins on surface of red blood cells
Over 100 rare antigens
30 commonly occurring antigens
Responsible for blood typing
11
Blood transfusion
Must be given blood of the right type
Early days
Some people fine after
a blood transfusion
Some people fell ill or died
after a blood transfusion

12
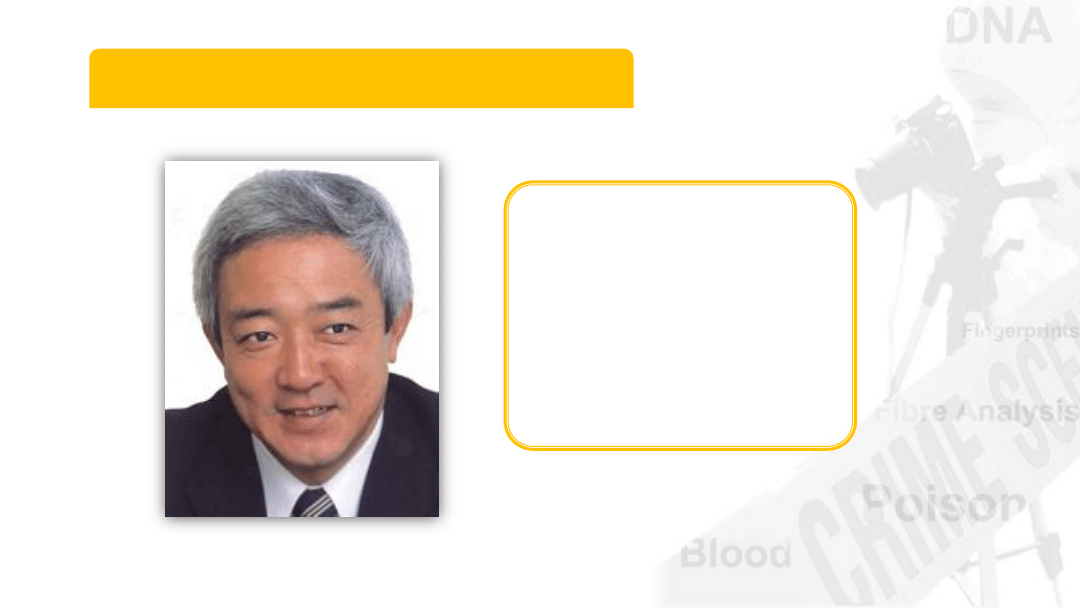
Karl Landsteiner
Karl Landsteiner
Developed the A-B-O
blood typing system
Won the 1930 Nobel
Prize in Medicine
13
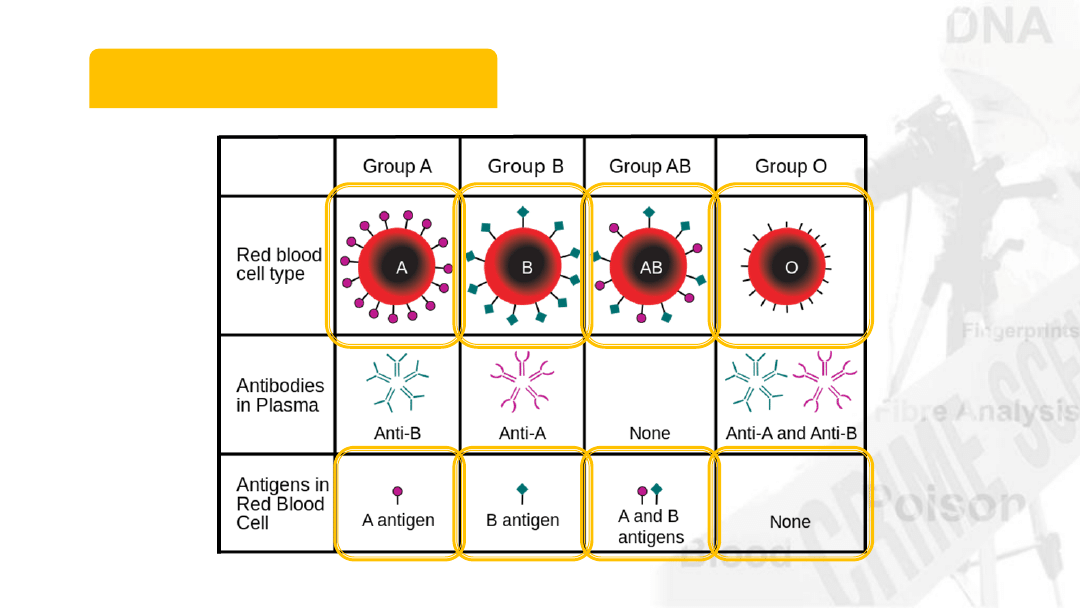
A-B-O Blood Types
14
A-B-O Blood Types
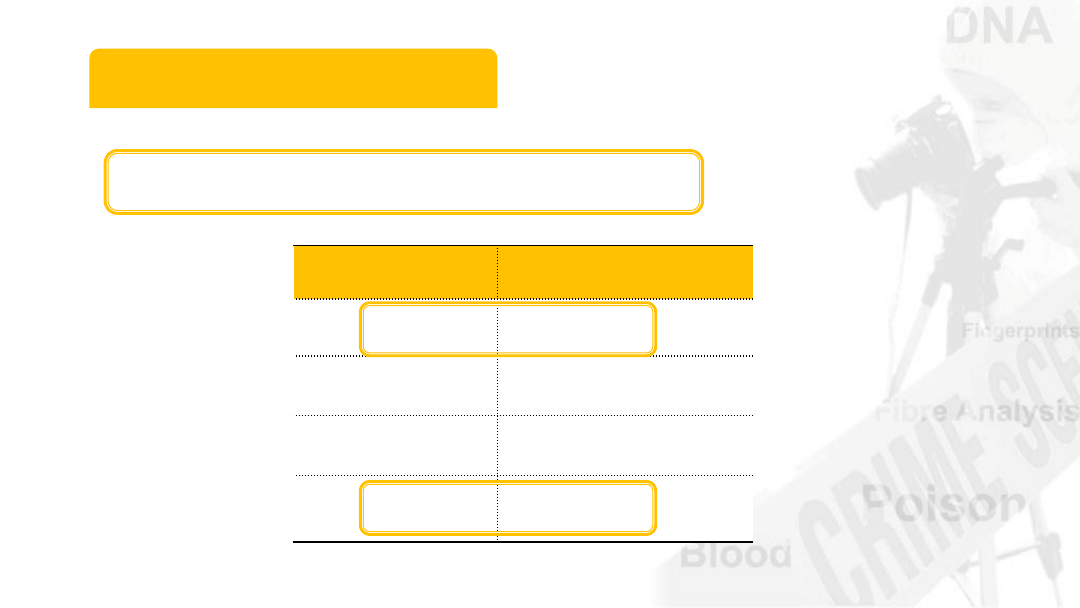
Occurrence of blood types vary
Blood Type Percentage (%)
O
40
A
25
B
30
AB
5

15
Blood Types & Personality
No
Is your blood type
the key to true love?
16
Blood Types & Personality
“I am type B and
have the tendency
to be simplistic and
straightforward at
times.”
- Ryu Matsumoto
17
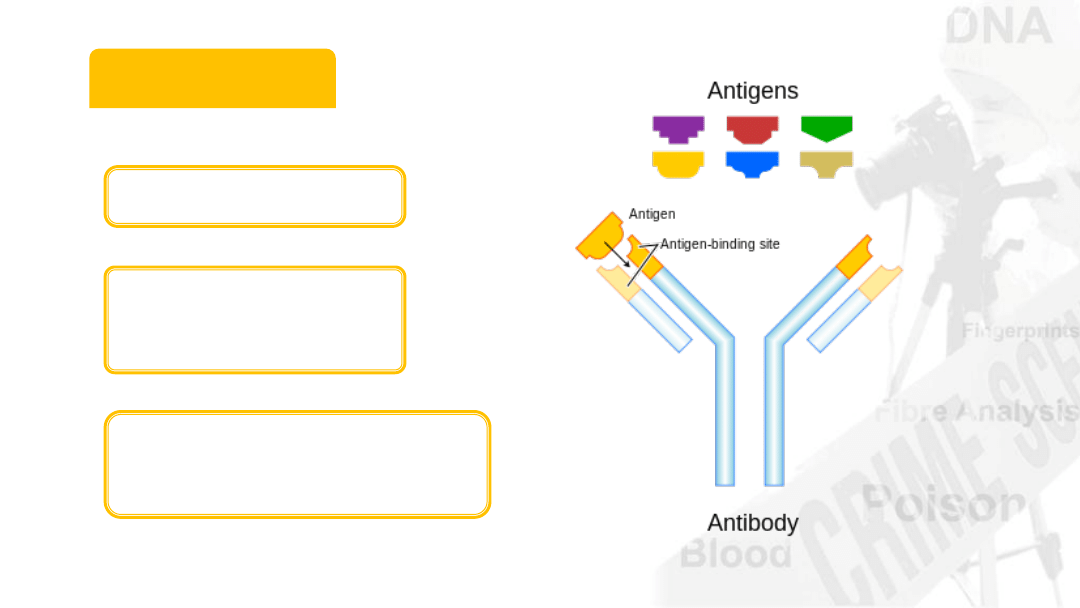
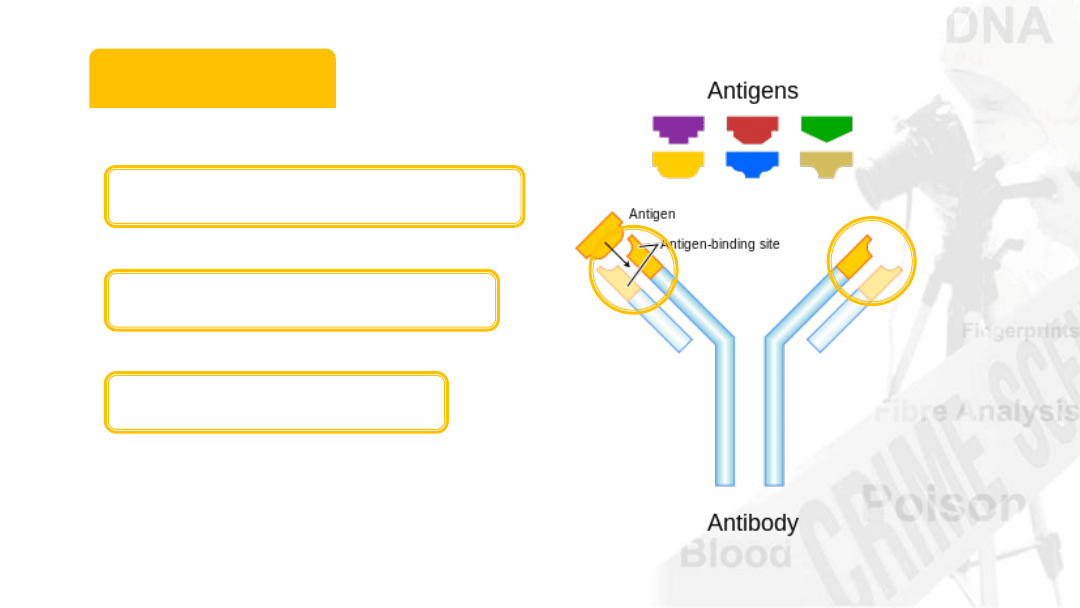
Antibodies
20% of blood
plasma volume
Immunoglobins
Produced as part of
immune response
18
Antibodies
Antigen binding sites
Bind to “alien” objects
Extremely specific
19
Serum Antibodies
Antibodies corresponding to surface antigens
Anti-A antibodies
Anti-B antibodies
20
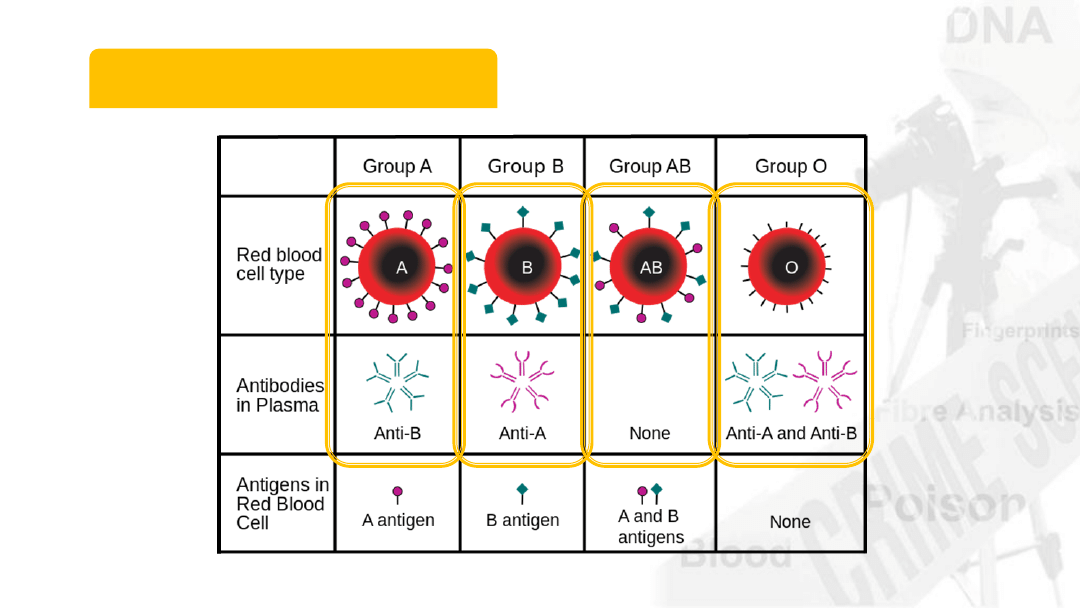
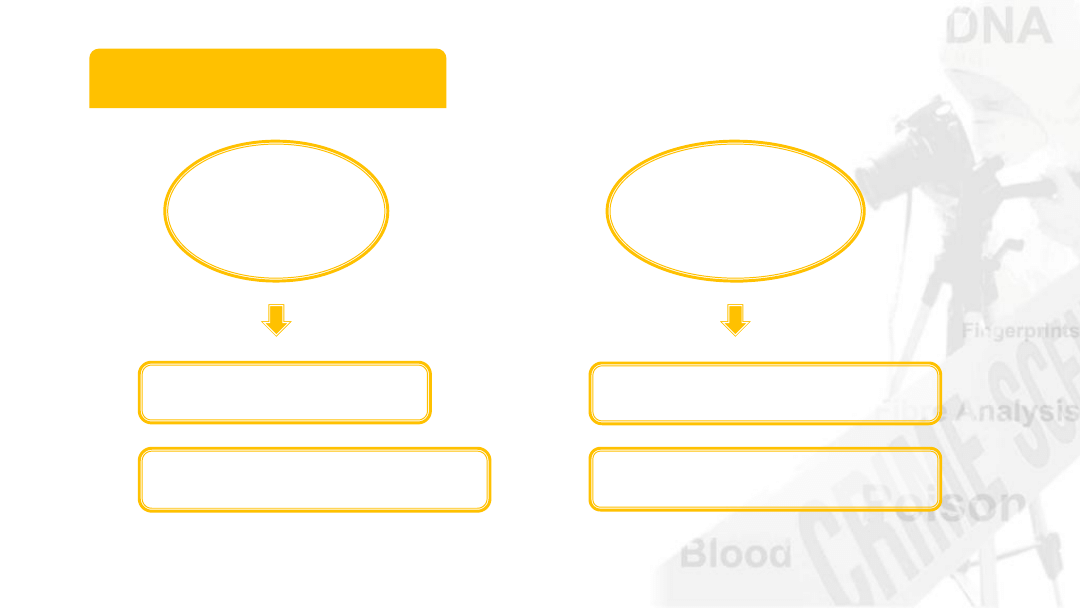
A-B-O Blood Types
21
Blood typing system
Many different antigens
A-B-O system based on A and B antigens
Less common antigens
D antigen / rhesus antigens
22
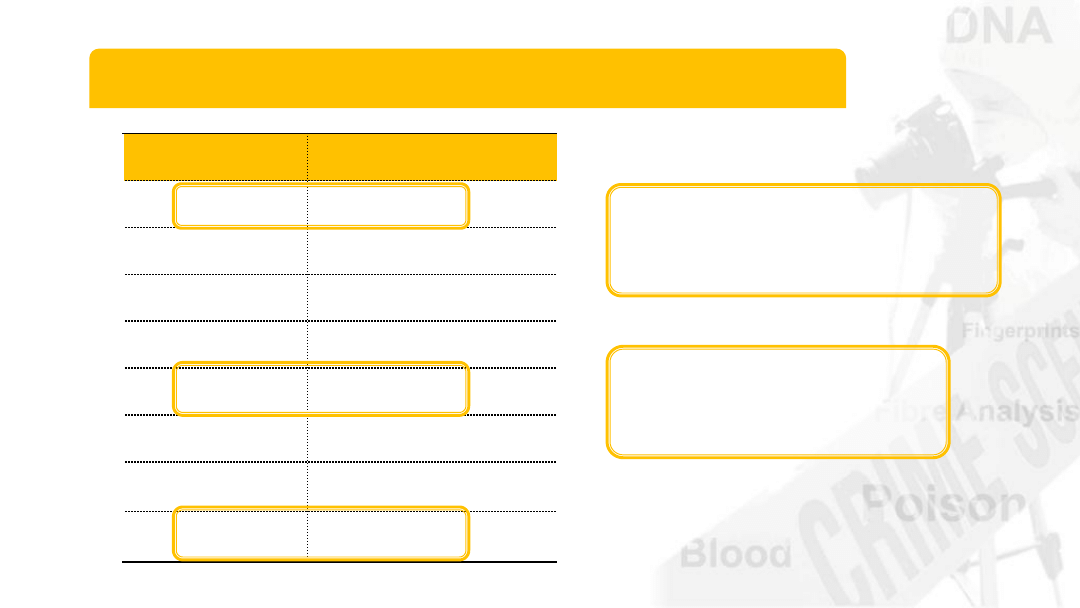
Rhesus antigens
Rhesus
positive
With D antigen
Without D antigen
Rhesus
negative
85% of population
15% of population
23
Blood Type Distribution in Singapore
Blood Type Percentage (%)
O+
34
O-
6
A+
21
A-
4
B+
25.5
B-
4.5
AB+
4
AB-
1
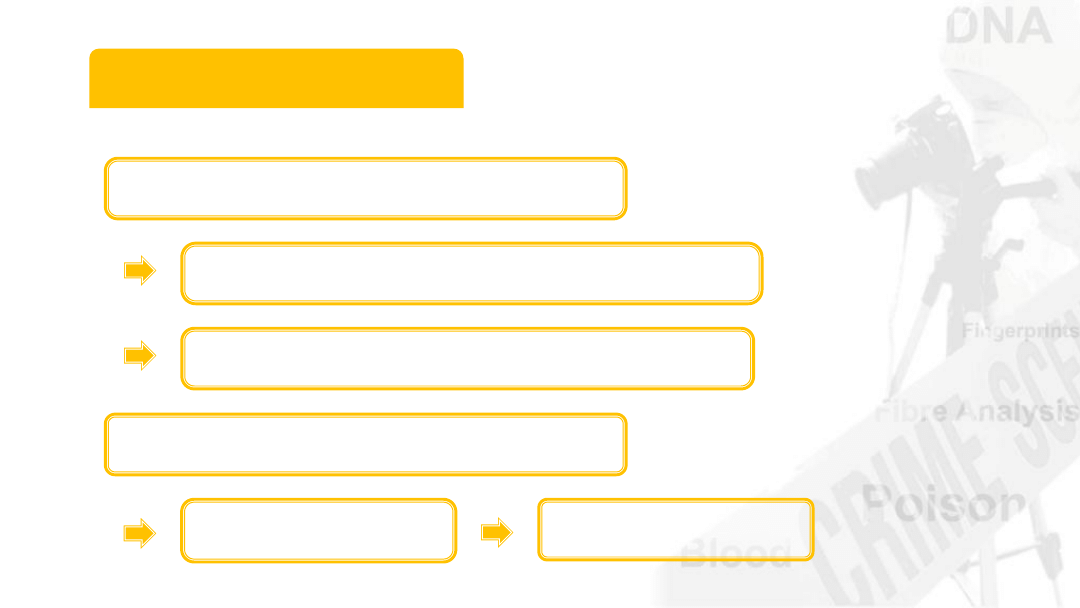
Want to individualise
evidence
Blood types are
not individualised
24
Bio-Identification
Individualisation of blood type?
More complex blood typing
Inferior to DNA fingerprinting
Blood sample
Individualise it
Extensive research before 1990
25
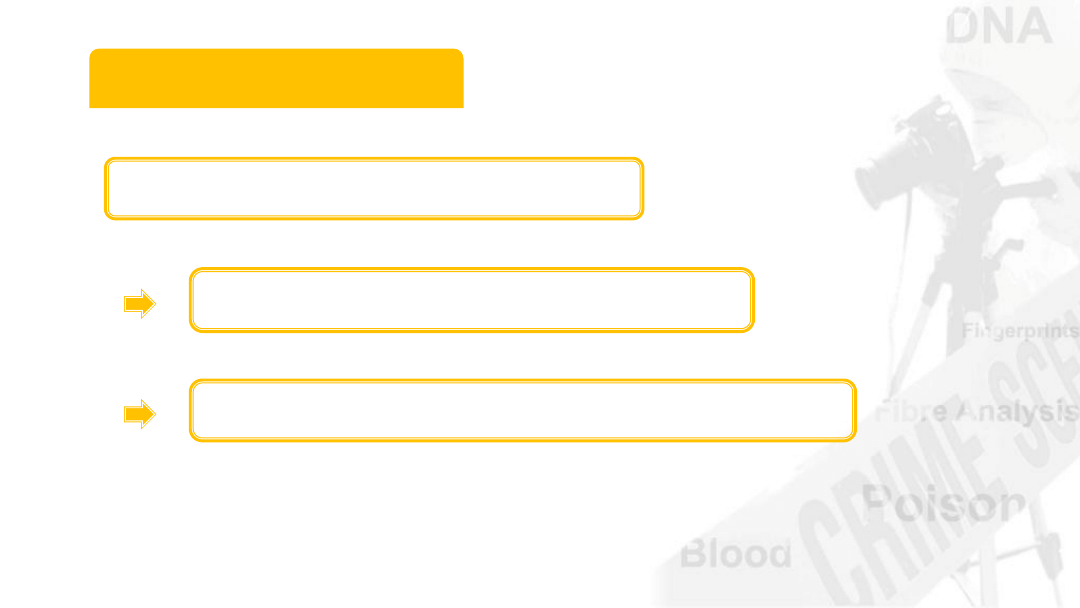
Bio-Identification
Cannot be used to prove guilt
Can be used to establish innocence
Blood type not individualised
26
Bio-Identification
Crime scene
Type A blood found
Established innocence
Suspect is type B blood
27
Bio-Identification
Does not prove guilt
Suspect is type A blood
Require further evidence
Crime scene
Type A blood found
Suspect is type B blood
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Elaine Bergstrom Blood to Blood (v1 0) (doc)
PN Elrod [Vampire Files 05] Fire in the Blood v1 1 (BD)
PN Elrod [Vampire Files 07] A Chill in the Blood v1 2 (BD)
PN Elrod [Vampire Files 04] Art in the Blood v1 1 (BD)
s9 3b v1
Jeanne Stein Anna Strong 02 Blood Drive v1 5 (BD)
3B 2 Tests for Blood
Ian Rankin [Jack Harvey 03] Blood Hunt (v1 0)
PN Elrod [Vampire Files 06] Blood on the Water v1 1 (BD)
epidemiologia metody,A Kusińska,K Mitręga,M Pałka,K Orszulik 3B
3B Promieniowanie jonizujące
PO wyk07 v1
Wyklad 3b Handel elektroniczny wyniki badan
3b Właściwości optyczne półprzewodników
s10 v1
s7 4 v1
24 G23 H19 QUALITY ASSURANCE OF BLOOD COMPONENTS popr
prezentacja 3b
s9 3a v1
więcej podobnych podstron