Aldehydes and Ketones
Nomenclature - form text.
The best way to think of an aldehyde or ketone (or just about any carbonyl compound) is
with a slight positive charge on carbon, and a slight negative charge on oxygen:
R
O
R'
!
+
!
-
Just about all of the chemistry of carbonyl compounds is explained by the oxygen being slightly
nucleophilic (thus easily protonated) and the carbon being strongly electrophilic. Remember
this!
Preparation:
Aldehydes:
1) Oxidation of a primary alcohol with PCC
2) Ozonolysis of an alkene
REVIEW IT!
3) Reduction of an Acyl Halide.
Acyl halides can be reduced with a special reagent – lithium tri(t-
butoxy)aluminum hydride, LiAl(Ot-Bu)
3
H :
R
O
Cl
O
LiAl(
)
3
H
R
O
H
Your text states that aldehydes can be easily prepared from esters with DIBAH
(diisobutylaluminum hydride). Typically, it is easier to reduce all the way to a primary alcohol
(you need 2 equivalents of DIBAH for this), then re-oxidize:
R
O
OR'
Al
H
(Diisobutyl aluminum hydride,
or DIBAH, or DIBAL-H)
R
OH
PCC
R
O
H
Ketones
1) Oxidation of secondary alcohols – usually be the Swern oxidation, or with PCC
2) Ozonolysis of an alkene.
3) Friedel-Crafts Acylation.
Below is the preparation of a ketone sequentially from a primary alcohol (through an
intermediate aldehyde):

OH PCC
O
Li
OH
PCC
O
Some ketones can also be prepared from acyl halides and organo-copper reagents (called
lithium dialkylcuprates), as shown below:
Li
CuBr
Cu
+ LiBr
Li
CuLi
2
Lithium dialkylcuprate
O
R
Cl
O
R
Further oxidation of aldehydes and ketones:
As you might imagine, most ketones are inert to all but the harshest oxidative conditions,
and thus there is no synthetic utility in trying to oxidize them. However, aldehydes can generally
be oxidized to carboxylic acids under relatively mild conditions:
O
R
H
Ag
2
O / H
2
O
NH
4
OH / EtOH
O
R
OH
Reactivity of Aldehydes and Ketones.
These carbonyl compounds generally have two reaction pathways – they react with
strong nucleophiles (generally, strong nucleophiles have a formal negative charge) under neutral,
generally anhydrous conditions, or with weak nucleophiles (those with lone pairs, but no charge)
under mild acid catalysis. If you take a good look at the nucleophile and reaction conditions,
you’ll be able to figure out which way it will go...
Reactivity – aldehydes are much more reactive than ketones. ‘nuff said.
Addition of water or alcohols (to from a hydrate or alcoholate (ketal)).
Ketones and aldehydes in aqueous or alcoholic media frequently react with the medium
to form hydrates (or alcoholates). The extent to which this occurs correlates to many things,
including the electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon. While acetophenone exists mostly as the
ketone, trichloroacetaldehyde (chloral) exists almost entirely as the hydrate (if exposed to water):
O
H
2
O
O
HO
OH
Very little
O
H
Cl
Cl
Cl
H
2
O
H
Cl
Cl
Cl
O
H
Cl
Cl
Cl
HO
OH
Very little
Similar things happen in neutral alcoholic medium - take chloroacetaldehyde in methanol, for
example:
O
H
Cl
H
Cl
HO
OMe
MeOH
Why do these hydrates form better w/ e
-
-withdrawing substituents? Remember the first
figure shown in these notes.....
The mechanism for these additions is relatively straightforward:
O
H
Cl
H
Cl
HO
OMe
MeOH
O
Me
H
H
Cl
O
O
H
Me
Proton-
transfer
This is the mechanism for the reaction in neutral media. The mechanism in basic media is left as
an exercise for the reader (i.e. you!). In acidic alcoholic media, the reaction behaves like the
Energizer™ Bunny - it just keeps going and going, until a completely new product is formed. It
is called an acetal:
O
H
Cl
H
Cl
HO
OMe
MeOH
H
3
O
+
H
Cl
MeO
OMe
The mechanism is quite straightforward:
O
H
Cl
H
Cl
O
OMe
MeOH
H
3
O
+
H
Cl
MeO
OMe
H
O
H
H
O
H
Cl
H
O
Me
H
H
Cl
HO
O
H
Me
O
H
H
H
H
O
H
H
H
Cl
O
OMe
H
H
O
Me
H
H
Cl
OMe
H
Cl
MeO
OMe
H
O
H
H
Basically, a series of protonation, nucleophile attack, deprotonation steps.
Big Note: Acetal formation CANNOT occur under basic catalysis. Convince yourself that this
is true...if you can’t, come see me.
Remember that these reactions are all in equilibrium - it can be forced to the acetal by
doing it under anhydrous conditions (or by distilling off the water), or forced back to the
ketone/aldehyde by the addition of excess water (making it the perfect protecting group!):
H
O
H
EtO
OEt
H
EtO
OEt
Br
Br
H
EtO
OEt
H
O
H
EtOH / H
+
Benzene
Br
2
KOH
H
2
O / H
+
R
EtO
OEt
1) BuLi
2) Alkylation,
etc.
In general, simple alcohols like methanol and ethanol are not used in the formation of
acetals (particularly from less-reactive ketones!) The main reason is entropy - you’ve got to get
three molecules together to form one - that’s not so good! The very common way around this is
to use a glycol - ethylene or propylene glycol – to form a cyclic acetal:
O
TMS
TMS
OH
HO
H
+
/ benzene TMS
TMS
O
O
As you would expect for ethers, acetals are stable to base and most nucleophiles, such as
Grignard reagents and alkyllithiums. They revert back to the carbonyl compound on exposure to
aqueous acid.
Enamines:
Just as with alcohols, amines can add to ketones and aldehydes. Primary amines add to
give imines, while secondary amines give enamines (pronounced ene-amines). The reactions are
generally catalyzed by a small amount of acid, and need to be buffered to a pH of ~4.5.
An Imine (in this case, the amine is hydrazine, and the product is called a hydrazone):
N
R
O
H
2
N NH
2
N
R
N NH
2
trace H
+
EtOH
The mechanism (shown here for cyclobutanone) is pretty straightforward:
O
H
2
N NH
2
O
N
H
H
NH
2
proton
transfer
HO
N
H
NH
2
H
O
H
H
H
2
O
N
H
NH
2
N NH
2
H
H
O
H
N NH
2
In the case of secondary amines, we have a lack of protons that can easily be removed
from the amine – the mechanism thus requires that the offending positive charge be neutralized
by removing a proton from the alkyl group:
Overall:
N H
O
N
O
O
N
H
proton
transfer
HO
N
H
O
H
H
H
2
O
N
N
H
O
H
N
H
N
No proton on amine to remove!
-> remove proton from former
ketone...
H
H
De-Oxygenation reactions.
There are two general reactions for the complete de-oxygenation of ketones and
aldehydes. The general scheme for de-oxygenation is:
O
R
R'
R' can = H
De-Oxygenate
R
R'
The two methods are the Wolff-Kishner (runs under basic conditions) and the Clemmensen
(under acidic conditions). Below find an example for each one:
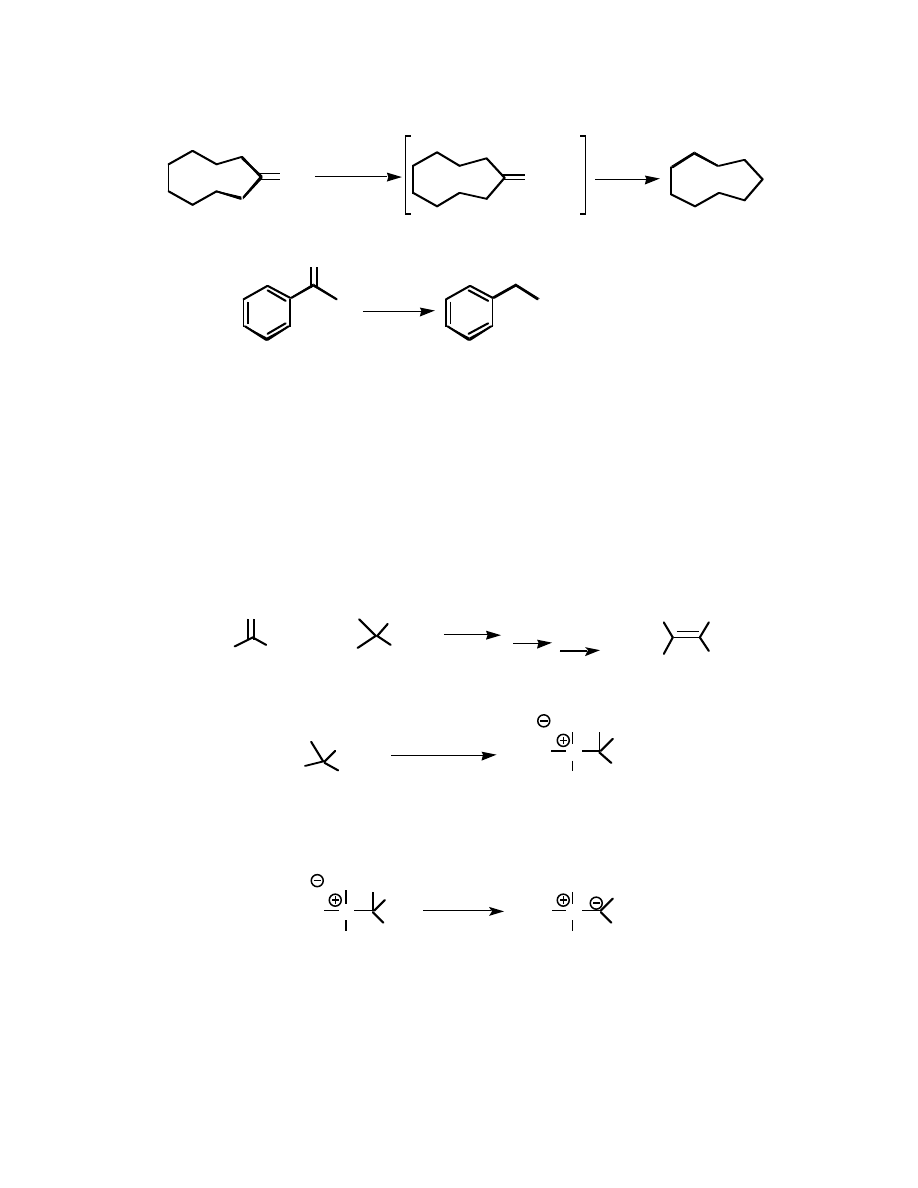
Wolff-Kishner:
O
H
2
NNH
2
KOH
HEAT!
NNH
2
Clemmensen:
O
Zn(Hg)
HCl
Heat
The Greatest Double Bond Forming Reaction Ever Invented:
The Wittig Reaction
This reaction is what I would call “cute” chemistry. One of the cool thing about Wittig
reactions is that they just about always work.
The most general scheme, an alkyl halide (usually the bromide) and an aldehyde or
ketone are taken to an alkene. If an aldehyde is used with a primary alkyl halide, generally the
trans product results.
R
R'
O
Either R' or R'' MUST be hydrogen
R''
R'''
Br
H
+
R'
R
R''
R'''
In a more detailed picture of this reaction, the alkyl bromide is allowed to react with
triphenyl phosphine to form an alkylphosphonium salt:
R
R'
Br
H
PPh
3
Ph
P
Ph
Ph
R
R'
H
Br
These salts are generally quite stable, and can be stored over long periods of time (i.e. many of
these salts are even sold commercially). The phosphonium salt is then deprotonated (usually
with sodium hydride, or butyllithium) to form the ylide. An ylide is simply a charge-separated
species, as shown below:
Ph
P
Ph
Ph
R
R'
H
Br
NaH
Ph
P
Ph
Ph
R
R'
"ylide"
This ylide is then allowed to react with a ketone or aldehyde, to form a betaine
intermediate. This intermediate cyclizes to form another intermediate, an oxaphosphetane:
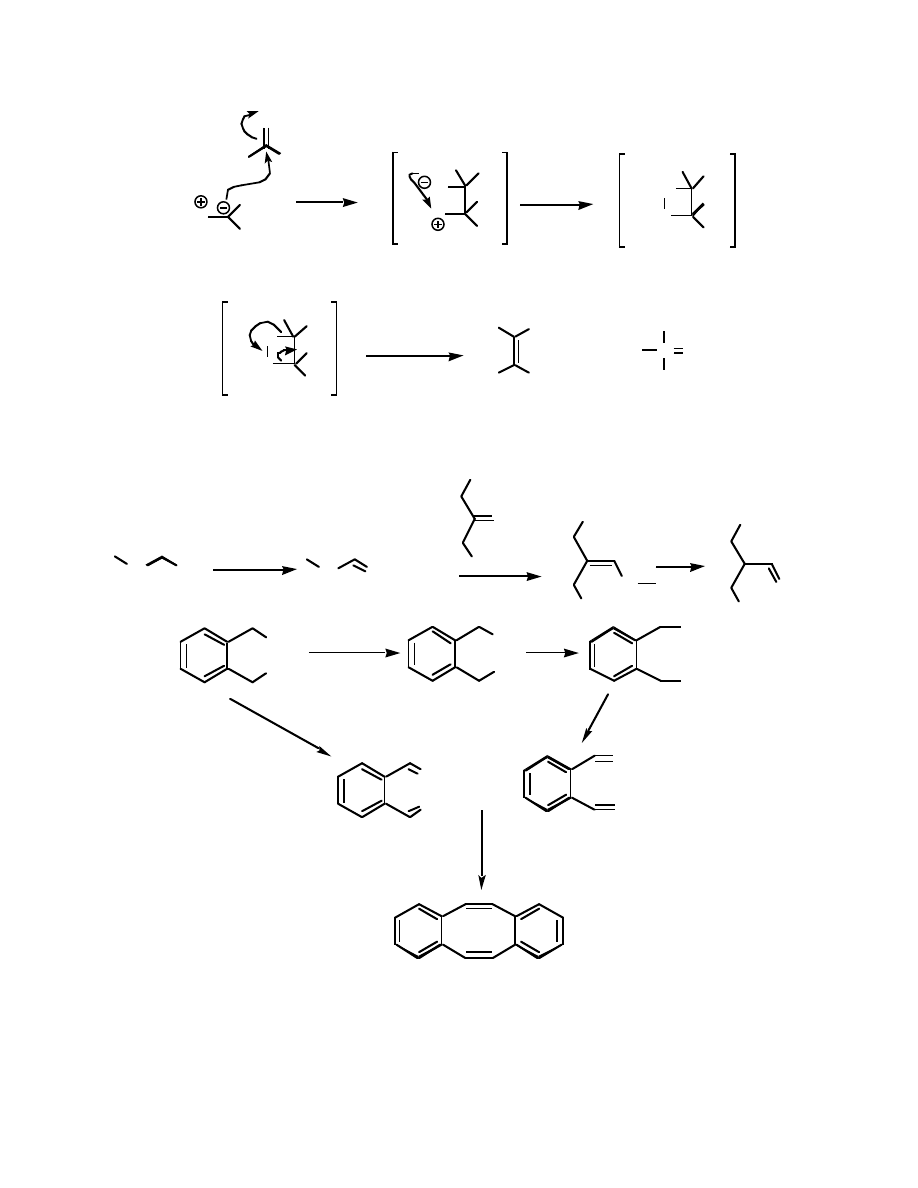
Ph
3
P
R
R'
O
R'''
H
Ph
3
P
R
R'
R'''
O
H
Ph
3
P
R
R'
R'''
O
H
betaine
oxaphosphetane
The oxaphosphetane decomposes rapidly to form the alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide:
Ph
3
P
R
R'
R'''
O
H
H
R'
R
R'''
+
Ph
P
Ph
Ph
O
The main driving force for this reaction is the formation of the phosphorous-oxygen double bond
- this is one of the strongest bonds known, and its formation pulls the reaction to completion.
Below are a few examples of the Wittig reaction at work:
O
Cl
1) PPh
3
2) BuLi
O
PPh
3
O
OTMS
OTMS
OTMS
OTMS
O
H
+
OH
OH
O
OH
OH
PCC
O
O
PBr
3
Br
Br PPh
3
PPh
3
Br
PPh
3
Br
PPh
3
PPh
3
+
NaH
A simple modification of the Wittig reaction leads to a dibromo-olefin, which is an
excellent precursor to alkynes:
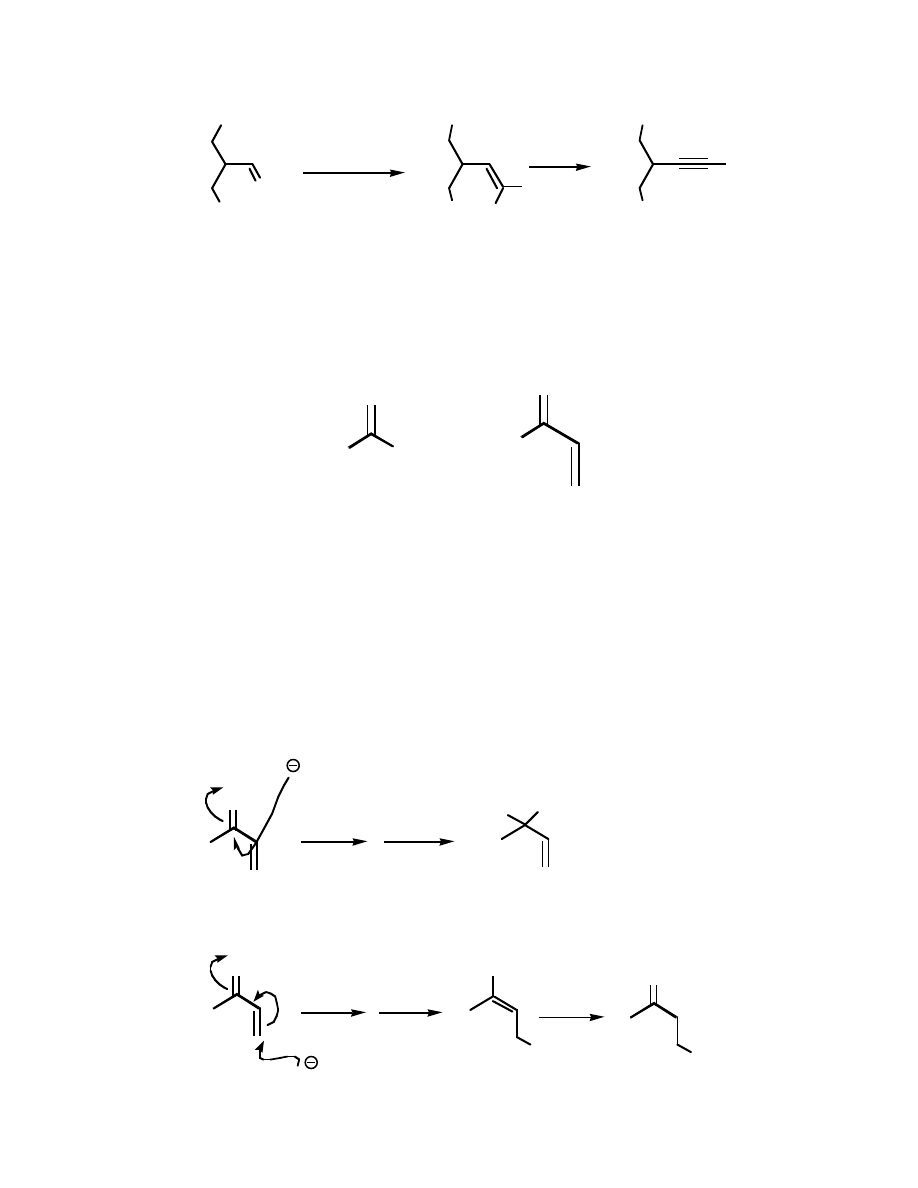
TMSO
TMSO
O
PPh
3
/ CBr
4
TMSO
TMSO
Br
Br
BuLi
TMSO
TMSO
H
Conjugate Addition
Okay, I’m afraid things are going to get a bit ugly again. We now focus on conjugated
carbonyl compounds. If you look at resonance structures for these (particularly in comparison
with the figure on the top of page 1):
O
R
R'
O
R
!
+
!
-
!
-
!
-
!
+
!
+
Unconjugated
Conjugated
You see that in conjugated systems, there are TWO sites for nucleophilic attack. Let’s do a little
nomenclature before we continue - when we look at carbonyl compounds, the carbonyl carbon is
the real center of attraction. Any carbons directly attached to the carbonyl are called the alpha
(α) carbons (in the case above, the one with the slight negative charge). As you’ll see in
upcoming chapters, the alpha carbon is often quite nucleophilic...
Unsurprisingly, the carbon attached to the alpha carbon is called the beta (β) carbon.
And as you can see, in the case of conjugated carbonyl compounds (which are often called
alpha,beta unsaturated compounds), the beta carbon is electrophilic.
This leaves us with a bit of a puzzle. If we add a nucleophile to this conjugated
compound, will it add to the carbonyl, or to the double bond?:
O
O
Nu
Nu
HO
Nu
OH
Nu
O
Nu
or ???
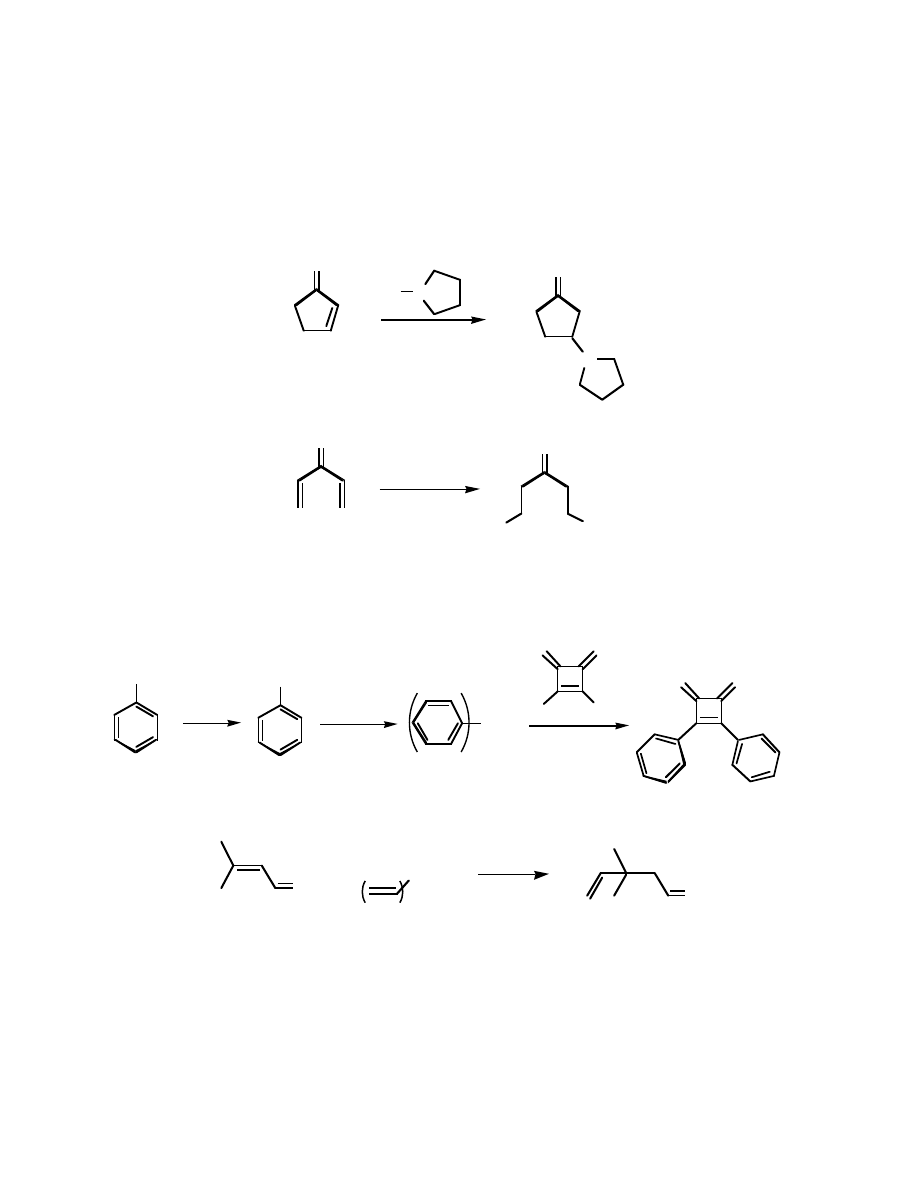
Addition to the carbonyl you’ve seen before. Addition to the double bond (to form an enolate,
which tautaumerizes to the ketone) is new. This type of addition is called conjugate addition, or,
more frequently, Michael addition.
How can we tell if we’ll be getting carbonyl addition or conjugate addition? Fortunately,
it is quite easy. Non-carbon nucleophiles (we frequently call these “soft” nucleophiles) like
nitrogen (amines) and oxygen (alcohols) will always add in a conjugate fashion, particularly if
the reaction is carried out under neutral conditions. Some examples:
O
N
H
EtOH
NO ACID!!
O
N
O
MeOH
NO ACID!!
O
MeO
OMe
A way to force only conjugate addition with a “hard” nucleophile (i.e. RM) is to form the copper
salt - in this case, a dialkylcuprate. You’ve already seen these used to prepare ketones from acid
chlorides – formation of copper salts is a great way to “soften” a hard nucleophile. The dialkyl
cuprates are usually formed from alkyllithiums (hence, lithium dialkylcuprates). Your text gives
a number of good examples, but I thought I should throw in my two cents on the subject as well:
Br
Li
Li
0.5 CuBr
CuLi
2
O
O
Cl
Cl
O
O
(Think carefully about what's happening here...)
O
+
CuLi
2
O
As you might expect, conjugate addition to an alkynyl ketone leads to a vinyl ketone.
Here is an example using a different kind of “soft” nucleophile (we’ll discuss this type in a few
weeks):
O
OEt
O
NaH
O
OEt
O
O
OEt
O
O
OEt
O
A highly stabilized (and thus, "soft") nucleophile
O
OEt
O
H
O
OEt
C
H
O
EtO
O
O
OEt
H
O
EtO
O
O
EtO
H
O
EtO
O
O
EtO
H
H
+
Of course, as we have already seen, organolithium (e.g. butyllithium) or magnesium
(Grignard) reagents always add to the carbonyl.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
A4 ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
Reduction of adsorption phenomena of volatile aldehydes and
Simple, Highly Active Palladium Catalysts for Ketone and Malonate
Postmodernity and Postmodernism ppt May 2014(3)
Scoliosis and Kyphosis
L 3 Complex functions and Polynomials
4 Plant Structure, Growth and Development, before ppt
Osteoporosis ľ diagnosis and treatment
05 DFC 4 1 Sequence and Interation of Key QMS Processes Rev 3 1 03
Literature and Religion
lec6a Geometric and Brightness Image Interpolation 17
aldehydy i ketony addycja nukleofilowa
Historia gry Heroes of Might and Magic
Content Based, Task based, and Participatory Approaches
Lecture10 Medieval women and private sphere
A Behavioral Genetic Study of the Overlap Between Personality and Parenting
Hine P Knack and Back Chaos
więcej podobnych podstron