NAME: DATE: 2002/2003
BIOCHEMISTRY - Example Exam // (US I/4 & N - II/6)
ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS:
Proteins & Enzymes
1. Which of the following statements in respect to collagen synthesis is true?
A. all collagen alpha chains have the same primary structure.
B. the N-terminal and C-terminal peptides of procollagen are cleaved off immediately before the tropocollagen is excreted.
C. assembly of tropocollagen into fibers is catalyzed by lysine oxidase.
D. collagen fibers are crosslinked by oxidized Lys derivatives.
E. after assembly of collagen fibers proline is hydroxylated to form hydroxyproline.
2. The quaternary structure of hemoglobin is:
A. not important for the functioning of this protein
B. rigid and is not affected by oxygen binding
C. maintained by hydrophobic, ionic, and hydrogen bonds
D. stabilized by glycosidic bonds
E. similar to that of myoglobin
3. The sickling of red blood cells in individuals with sickle cell anemia is caused by:
denaturation of hemoglobin.
oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+.
aggregation of oxyhemoglobin.
aggregation of deoxyhemoglobin.
formation of the hemoglobin R state.
4. A mutation that causes a substitution of glycine onto another amino acid alters the mobility
of a protein in native gel electrophoresis at neutral pH as shown here. Which substitution
would most likely cause this change?
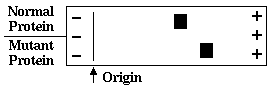
glycine to lysineglycine to arginine
glycine to tryptophan
glycine to glutamate
glycine to isoleucine
5. Denaturation of protein is usually caused by the disruption of all the following linkages
EXCEPT:
ionic bonds (salt bridges)
hydrogen bonds
hydrophobic bonds
peptide bonds
van der Waals bonds
6. The protein has a domain structure if:
it is composed of more than one polypeptide chain
its tertiary structure contains both α-helical and β-structural fragments
it can change its quaternary structure upon ligand binding
its polypeptide chain (even if single) is folded into more than one compact globular unit
it separates into several polypeptide chains upon denaturing conditions
7. Unlike serum, plasma contains:
albumin
fibrinogen
hemoglobin
red blood cells
γ-globulins
8. The most abundant protein of human organism is:
fibrinogen
collagen
albumin
immunoglobulin G
hemoglobin
9. Which of the vitamins is a precursor of diphosphothiamine (DPT) coenzyme:
A. vitamin B1
B. vitamin B2
C. vitamin B6
D. folate
E. vitamin H.
10. Choose the best definition for the Michaelis-Menten constant (KM):
the minimal concentration of an enzyme for initiation of catalysis
the substrate concentration required for half-maximal velocity
the reciprocal of the substrate concentration required for maximal velocity
the minimal substrate concentration required for initiation of product formation
the reciprocal of the enzyme concentration required for half-maximal velocity.
11. The activity of enzymes in the living organism is regulated via:
proteolytic degradation of the initialy inactive polypeptide(s)
covalent modification of the enzyme
allosteric modulation
changes in the expression of encoding gene(s)
all the mechanism that are listed above (answeres A - D)
12. Protein kinases are enzymes that phosphorylate amino acid side chains of proteins in
ATP- dependent reactions. A protein kinase can be classified as a(n):
oxidoreductase
hydrolase
isomerase
lyase
transferase
13. Values of Vmax and KM determined for an enzyme with and without its inhibitor are:
No inhibitor: KM = 0.5 (mmol L-1) Vmax = 0.15 (mmol L-1 min-1)
With inhibitor: KM = 0.5 (mmol L-1) Vmax = 0.03 (mmol L-1 min-1)
What kind of inhibition is observed?
A. competitive
B. noncompetitive
C. uncompetitive
D. allosteric
E. none of the above
14. Methotrexate (amethopterin) and aspirin are used in medical treatment of some diseases.
Methotrexate competes with a substrate for the dihydrofolate reductase active site while
aspirin covalently and irreversibly modifies side chain of the amino acid in the active site
of cyclooxygenase. Choose the statements that correctly describes their effect on the
kinetic parameters of the enzyme-catalyzed reactions:
methotrexate decreases Km while aspirin increases Km
they both increase Km
they both decrease Vmax
methotrexate increases Km while aspirin decreases Vmax
methotrexate and aspirin both decrease Km as well as Vmax
15. Which of the following enzymes would show the greatest increase of the activity in serum
due to viral hepatitis?
A. creatine kinase (CK)
B. alkaline phosphatase
C. alanine transaminase (ALT or SGPT)
D. amylase
E. acid phosphatase
Nucleic Acids, Protein synthesis, Control of gene expression & Biotechnology
16. Which of the following statement concerning DNA structure IS NOT true:
two strands of the Z-DNA helix are antiparallell.
AT rich regions have lower melting temperature than GC rich regions
interactions between adjacent base pairs lead to the decrease of absorbance at 260nm.
palindrome nucleotide sequences are present only in Prokaryotes.
in B-DNA, keto- and amino- tautomeric forms of bases predominate.
17. The proofreading activity of nucleic acid polymerases:
is necessary to remove primers
concerns both DNA and RNA polymerases
requires the 5' 3' exonuclease activity
removes errors caused by rare tautomeric forms of bases
requires 3' 5' endonuclease activity
18. Uracil in DNA:
is found commonly and forms a base pair with adenine.
can never appear.
can appear as a product of deamination of cytosine.
can appear as a product of spontaneous demethylation of thymine.
is commonly observed in viral DNA.
19. Which of the following enzymes IS NOT involved in base excision repair of DNA in E.Coli:
AP-endonuclease
N-glycosylase
ligase
DNA polymerase I
primase
20. The most common mutation, that rate is increased by nitrates (NO2- ) is:
depurination
alkylation
formation of thymine dimers
deamination
breaking of N-glycosidic bonds.
21. In the process of an amino acid “activation” to protein biosynthesis:
A. amino group of the amino acid reacts with 2' or 3' -OH of ribose of the first adenylate in the sequence of tRNA
B. amino group of the amino acid reacts with 2' or 3' -OH of ribose of the last adenylate in the sequence of tRNA
C. carboxyl group of the amino acid reacts with 2' or 3' -OH of ribose of the first adenylate in the sequence of tRNA
D. carboxyl group of the amino acid reacts with 2' or 3' -OH of ribose of the last adenylate in the sequence of DNA.
22. Tetracycline, streptomycin, and erythromycin are effective inhibitors of:
prokaryotic RNA synthesis
eukaryotic mRNA synthesis
prokaryotic protein biosynthesis
eukaryotic protein biosynthesis
prokaryotic and eukaryotic assembly of ribosomes
23. Indicate the FALSE sentence concerning regulation of protein biosynthesis in eukaryotes:
protein biosynthesis may be controlled only at the level of initiation of transcription
synthesis of globin in reticulocytes is tightly dependent on the heme concentration
steroid hormones basically affect gene expression at the level of initiation of transcription
hypermethylated genes are transcribed less efficiently than hypomethylated ones
the same transcription unit may be used to produce different although related proteins
24. All the following enzymes require a DNA or RNA template EXCEPT:
DNA polymerase
Reverse transcriptase
Primase
RNA polymerase II
all enzymes listed above
25. The genetic code is highly degenerate. It means that:
A. each amino acid is specified by single codon;
B. most amino acids are specified by more than one codon;
C. some codons specify more than one amino acid;
D. there are at least 10 different STOP codons;
E. codons are overlapping.
26. Which of the nucleic acids listed below does not function in the cytoplasm?
mRNA
rRNA
tRNA
scRNA
snRNA
27. The nucleic acid chosen as a answer in the above question (23) participates in:
transcription
postranscriptional polyadenylation of hnRNA
nucleotide excision DNA repair
cap formation
splicing of hnRNA
28. DNA replication originates at the indicated origin of replication. Which segment(s) serve
as template(s) for leading strand synthesis?
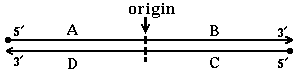
B and DA and C
A and B
Only D
Only B
29. The most efficient expression of lac-OPERON structural genes in bacteria takes place
when the medium in which they grow is:
enriched in glucose and free from lactose
enriched in both glucose and lactose
free from both glucose and lactose
enriched in lactose and free from glucose
enriched in lactose and supplemented with inhibitors of cAMP synthesis
30. The HIV virus causing AIDS is a retrovirus and contains an RNA genome. Which enzyme is responsible for converting this genome to DNA in T lymhocytes?
ligase
restriction endonuclease EcoR1
DNA polymerase
reverse transcriptase
RNA polymerase.
31. Proteins, RNA and DNA were isolated from from brain, liver and muscle of the rabbit.
Which of the methods of analysis should give the same results for each of the tissues:
electrophoresis of the isolated proteins
quantitative determination of the protein content
measurements of the protein biosynthesis rate
analysis of the cDNA libraries
analysis of the DNA restriction fragments length polymorphism.
32. Restriction Fragments Length Polymorphism (RFLP) used in diagnosis of genetic diseases
includes all the following EXCEPT:
comparison of restriction fragments derived from a normal and mutated gene followed their separation and hybridization
treatment of patient and reference DNA with the same restriction enzyme(s)
recombination of restriction fragments with specific vectors allowing for their amplification prior to hybridization with appropriate labelled probe
hybridization of restriction fragments with specific oligonucleotide probe
electrophoretic separation of restriction fragments
33. Chain elongation during protein biosynthesis is:
carboxyl to the amino terminus
amino to the carboxyl terminus
dispersed
palindromic
central to peripheral.
Metabolism
34. How many O2 moles are consumed or produced directly by the reactions of the citric acid
cycle in course of the conversion of 1 mole of acetyl-CoA to carbon dioxide (CO2)?
1 produced
2 produced
1 consumed
2 consumed
0 consumed or produced
35. The protein that binds and directly reduces the terminal electron acceptor in mitochondrial
electron transport chain is:
cytochrome oxidase.
succinate dehydrogenase.
coenzyme QH2
NADH:Q reductase
cytochrome bc1.
36. After complete metabolism of one molecule of glucose to carbon dioxide via the TCA
cycle, what will be the net change in the amount of oxaloacetate in the mitochondrion?
increased by two molecules
increased by one molecule
unchanged
decreased by one molecule
decreased by two molecules
37. Which of the following metabolites can NOT be a substrate for gluconeogenesis?
alanine
acetate
glutamate
lactate
succinate
38. In the breakdown of muscle glycogen, the predominant product is:
glucose
glucose 1-phosphate
UDP-glucose
maltose
maltotriose
For questions 39 - 45
For each numbered item, select the one heading that is most closely associated with it. Each lettered heading may be selected once, more than once or not at all.
HDL
Chylomicrons
VLDL
LDL
Free fatty acids
39. Transports mostly exogenous triacylglycerol. ( A / B / C / D / E )
40. Calories in the form of carbohydrate would increase the blood concentration of this
lipoprotein before the others. ( A / B / C / D /E )
41. The amount of this lipoprotein in the blood depends on the presence of the receptors for
B-100 apolipoprotein in extrahepatic tissues. ( A / B / C / D / E )
42. The site of the LCAT reaction. ( A / B / C / D / E )
43. This lipoprotein has the highest ratio of protein to lipid. ( A / B / C / D / E )
44. Lipoprotein lipase is required for its formation. ( A / B / C / D /E )
45. Activation of hormone-sensitive lipase is required to release them. ( A / B / C / D / E )
46. Cholesterol biosynthesis is similar to fatty acids biosynthesis in that:
the rate limiting enzymes in both pathways are inactive when they are phosphorylated
both pathways utilize mitochondrial acetyl-CoA as the initial compound in the pathway
both pathways use NADH as the reducing agent
both pathways are inhibited by insulin
both pathways have HMG-CoA as an intermediate.
47. Which of the following amino acids contributes both carbon and nitrogen atoms to the
purine ring?
A. aspartate
B. glycine
C. glutamine
D. lysine
E. cysteine
48. What is the major nitrogen containing end-product you would expect to find in human
urine from the metabolism of guanine?
A. urea
B. allantoin
C. hypoxanthine
D. inosinic acid
E. uric acid
49. Insulin inhibits:
fat mobilization from adipose tissue
cholesterol biosynthesis
fatty acid synthesis
the transport of glucose into muscle cells
the transport of glucose into liver cells.
50. Muscle proteins (amino acids) are the origin of most of glucose in the period(s) represented by:
A only
B only
C only
B and D
C and D
51. Glucagon:
increases glycogen formation by liver
inhibits gluconeogenesis in liver
inhibits glucose production in hypoglycemia
increases glucose transport into skeletal muscle cells
increases lipolysis in adipose tissue cells
52. Most of our energy reserves are stores as fat because
adipose cells have a high biosynthetic capacity to synthesize fatty acids de novo.
the energy spent to store glucose as fat is less than that spent to store glucose as glycogen.
the recruitment of fat from adipose can be regulated independently of glycogen breakdown.
fat is anhydrous and more reduced than carbohydrate.
adipose cells have a high level of glycerol 3-kinase activity.
53. Which of the following statements is TRUE for vitamin A, vitamin D, estrogen and
cortisol?
Humans can synthesize all of these molecules de novo.
They are all stored in large quantities in the liver.
Hormones produced by the hypothalamus and pituitary play an important role in the regulation of the synthesis of all of these molecules.
Each of these molecules binds to the same nuclear receptor which mediates their activity.
They are all fat soluble molecules that activate separate receptors through which they can increase or decrease the rate of transcription of specific genes in target cells.
54. Indicate a pathway/step of carbohydrate metabolism that is stimulated by insulin in
muscle, but not in liver:
glycolysis
gluconeogenesis
glycogenolysis
glycogen synthesis
glucose transport.
55. Indicate the expected laboratory findings for a fasting blood sample of a patient suffering
from glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency in hepatocytes:
high glucose, low lactate, low FFA
low glucose, high lactate, high FFA
low glucose, low lactate, low FFA
high glucose, high lactate, high FFA
56. Indicate key enzyme in the biosynthesis of cholesterol:
3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG) synthase
HMG reductase
HMG lyase
mevalonate kinase
squalene synthase
57. Choose the amino acid that is used to transport amino group (NH2-) from most peripheral tissues to the liver:
glutamate
aspartate
asparagine
serine
glutamine
58. Which of the following types of amino acids are precursors for synthesis of nucleic acids?
nonessential amino acids
basic amino acids
aromatic essential amino acids
aliphatic hydrophobic amino acids
none amino acids are required
59. Classical galactosemia is caused by the deficiency or lack of activity of:
hexokinase
glucose-6-phosphatase
galactose-1-phosphate / UDP-glucose UDP transferase
UDP-galactose epimerase
any of the enzymes listed above (A - D)
60. A gallstone that blocked the upper part of the bile duct would cause an increase in:
the formation of chylomicrons
the formation of chylomicrons
the excretion of bile salts
the excretion of fat in the feces
the deposition of triglycerides in adipose tissue
61. The source of energy in case of erythrocytes is:
both ketone bodies and glucose
only glucose
both short chain fatty acids and glucose
only short chain fatty acids
both glucose and lactate
62. Liver produces fats mostly from:
acetyl CoA derived from degradation of adipose tissue fatty acids
acetyl CoA derived from glucose delivered from glycogen
exogenously delivered glucose
acetyl CoA derived from degradation of fatty acids delivered with VLDLs and HDLs
ketone bodies
63. The accumulation of toxic derivatives of phenylalanine, such as phenylpyruvate, is a
symptom of phenylketonuria, which is caused by a defect of:
tyrosine transaminase
tyrosine hydroxylase
tyrosinase
phenylalanine transaminase
phenylalanine hydroxylase
64. In the normal adult, the fuel store that contains the most calories is (are):
adipose triacylglycerols
liver glycogen
blood glucose
muscle protein
muscle glycogen
65. Pyruvate carboxylase is a key enzyme of:
glycolysis
citric acid cycle
gluconeogenesis
glycogenolysis
pentose phosphate pathway
66. The principle function of the TCA cycle is to:
transfer electrons from the acetyl portion of acetyl-CoA to NAD+ and FAD
generate CO2
oxidize the acetyl portion of acetyl-CoA to oxaloacetate
dispose of excess pyruvate and fatty acids
generate heat from the oxidation of the acetyl portion of acetyl-CoA
67.
X, Y, Z, V and W in the diagram,
represent gluconeogenic substrates.
Match each compound listed below
with the correct letter.
lactate
malate
aspartate
glycerol
alanine
68. Ketone bodies are formed:
in muscle during fasting period
in liver, if oxaloacetate is in excess in mitochondria
in brain suffering from hypoxia
in hepatocytes during starvation
in adipose with overactive hormone-dependent lipase.
69. Amino acids are precursors of hormones, neurotransmitters, biogenic amines etc. Which
of the following amino acids is involved in biosynthesis of acetylcholine:
tryptophan
glycine
serine
tyrosine
threonine
70. Choose the citric acid cycle intermediate which is a substrate for heme biosynthesis is:
citrate
α-ketoglutarate
succinyl-CoA
succinate
malate
71. When excessive amounts of iron are present in the diet, the excess iron is stored as:
hemoglobin
transferrin
ferritin
cytochrome c
ceruloplasmin
72. Parkinson disease, a neurological disease, is connected with defects in catecholamines metabolism in brain. Which of the following could be included into this group of metabolites:
glycogen
a sphingolipid
dopamine
collagen
putrescine
73. Phenylketonuria, alcaptonuria and albinism are caused by deficiencies in enzymes involved in the metabolism of:
tryptophan
phenylalanine
histidine
valine
lysine
74. The vitamin with antioxidant properties, involved in hydroxylation of dopamine to
epinephrine and influencing absorption of iron from the intestine is:
vitamin A
vitamin E
vitamin C
vitamin K
vitamin B5
Free radicals & biochemistry and disease
75. The major enzymes involved in processes of detoxication via increase of solubilization of
hydrophobic xenobiotics are:
cytochromes P450 and sulfotransferases
superoxide dismutase and catalase
cytochromes b5 and glutathione peroxidase
cytochromes P450 and NADPH oxidase
cytochromes b5 and glucuronyl transferases
76. Which one of the following electron carriers is involved in conversion of xenobiotics:
coenzyme Q
cytochrome b
cytochrome c1
cytochrome P-450
iron-sulfur centers
77. The major organ responsible for detoxification processes is:
spleen
liver
lungs
kidney
intestine
78. Which methods CAN NOT be used in prenatal diagnosis of sickle cell anemia:
electrophoresis and chromatography of trypsin treated hemoglobin
genetic linkage analysis of RFLP
hybridization with allele specific oligonucletide probe (ASO)
amplification and sequencing of gene coding β-chain.
79. The reaction - H2O2 + H2O2 → 2H2O + O2 - is catalyzed by:
glutathione peroxidase
catalase
superoxide dismutase
cytochrome P-450
80. Protooncogenes discovered so far code for all the listed below EXCEPT:
growth factors
serine/threonine protein kinases
some G proteins
membrane bound or cytosolic protein tyrosine kinases
reverse transcriptases
81. The most reactive oxygen form (having the greatest oxidizing potential) is:
O2
H2O2
H3O+
OH•
OH−
82. Choose the enzyme that eliminates excess of H2O2 in course of a reaction:
H2O2 + 2GSH ⇒ 2H2O + GS-SG
catalase
xanthine oxidase
glutathione transferase
glutathione peroxidase
NADPH oxidase
13
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
0656PWsrT Rysunek 02 03
02 03
GIge zal 06 02 03 Przekroj geo inz
Neuropsychologia kliniczna PRZYBORSKA W5A afazje cd 02 03 15 do pdf odblokowany
DGP 2014 02 03 rachunkowosc i a Nieznany
higiena 02.03.2007, HIGIENA - WYKłADY NA PWSZ
02 03 2012 wiedza o państwie i prawie
Lecture 01 02 03 Computer Unix
3. Mikrobiologia 02.03.2012r. - OUN
Spotkanie weekendowe z KSM 29.02-02.03.2008, „Spotkanie weekendowe z KSM'em”
N B T 02 03 2014
07 gestalt - kognitywizm 23.02.2007 - 02.03.2007, JĘZYKOZNAWSTWO, Notatki
ćw.02.03.06 - Ścieki, Ścieki:
ćw.02.03.06 - Ścieki, Ścieki:
bd 02 03 Hurtownie danych Ix
Wypalenie zawodowe GB 02 03 281
2008 02 03 17 51 mapa konturowa polski rzeki i miasta A4
sedymentologia3 sko 02.03, Geologia GZMiW UAM 2010-2013, II rok, Sedymentologia, Wykłady, wykłady 1-
więcej podobnych podstron