17

THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
The respiratory system (RS) is Tesponsible for carrying oxygen from the air to. the bloodstream and for eliminating the waste product carbon dioxide.
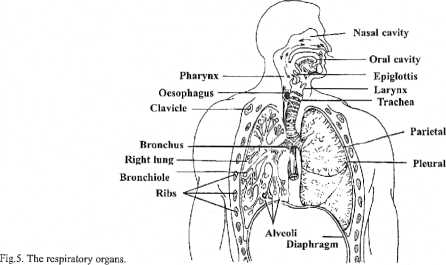
The respiratory system consists of the nose, pharyrix, larynx, trachea, main bronchi, bronchioles and the alveoli of the lungs, called sometimes air sacs.
The initial part of the respiratory system is the nose. It is divided by the ijasal septum into two nasal cavities. The nasal cavities are connccted posteriorly with the pharynx.
The pharynx (or throat), which is a muscular tubę, is divided into nasopharynx behind the nasal cavities, oropharynx behind the mouth and laryngopharynx which opens into the larynx. The tonsils are located in the oropharynx. Both the larynx and trachea are kept open by cartilages in the shape of rings. The larynx contains the vocal cords, by vibrations of which the voice is produced.
The trachea (or windpipe) is a long tubę which runs down through the neck to the thorax. The trachea divides into two bronchi below the base of the neck. Each bronchus enters each lung and then divides and subdivides into thin-walled tubes called bronchioles. Each bronchiole fmally enters the alveoli or the air sacs which form the terminal part of the respiratory tract. There are millions of al veoli in the human lung. The thin walls of the alveoli permit easy passage for the carbon dioxide and oxygen entering and leaving the blood when it circulates in capiiiaries of the alveoli.
The lungs are the essential organs of respiration. They are cone-shaped organs situated in the thoracic cavity on either side of the heart. The base of each lung rests on the diaphragm. Each lung is divided into lobes. The right lung consists of three lobcs: upper, middle and lower. The left lung has two lobes: upper and lower.
Each lung is lined with a double serous membranę, called the pleura. The portion of the pleura that covers the surface of the lung is called the visceral pleura, whilethe portion that lines the chest wali is called the parietal pleura. The space between these membranes is called intrapleural space.
EXERCISE A. Answer the following ąuestions.
1. What are the functions of the respiratory system?
2. What are the main parts of the respiratory system?
3. Ho w are the larynx and trachea kept open?
4. Where are the vocal cords located?
5. What are the lungs composed of?
6. Where are the lungs located?
7. How many lobes does the right lung consist of?
E. Donesch-Jeżo - English for Medical Students and Doctors - 1
Word List
• alveoli (pl.) ['aelvialai], (sing.) alvcolus - pęcherzyki płucne
• attach [o'taetJ] - przyłączyć
• base [bcis] — podstawa
• bronchi (pl.) ['bropkai], (sing.) bronchus - oskrzela
• bronchiole ['bropkiaul]
- oskrzelik
• cone [kaun] - stożek
• faclor ['fsktaj - czynnik
• hoarseness ['ho:snis]
- chrypka
• hurt [łi9:t] - zranienie;
zranić, boleć
• laryngopharynx [l9,ripgo'ficripks]
- krtaniowa część gardła
• linc [lain] - linia; wyścielić
• lobe [laubl - płat
• lung [Up] - płuco
• nasopharynx [,ncizo'faeripks]
- część nosowa gardła
■ oropharynx [3uro'fćeripks]
- część ustna gardła
• parietal [pa Taili] - ścienny
• pleura fplusra] - opłucna « respiration [,respi'rcijbn]
- oddychanie
• respiratory system ['respiratari 'sistom]
- układ oddechowy
• sac [stek] - pęcherzyk
• tonsil ['tonsil] - migdałck
• trachea [lra'ki3] - tchawica
• visceral fvis3ral] - trzewny
• vocal cords (pl.)
['vauk3l rko:dz] - struny
głosowe
17
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
CSG078 Unit 7The Futurę and the ConditionalThe Futurę Tense The futurę tense is used to indicate act
system 33 33 advantageous for runners, quick walkcrs, and jumpers to haye strong muscles round the w
IMG&54 [Briefing crew and passe nge rs I. Make thc following announcemcnl (on the PA • system): 2. T
UNIT 6THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system provides a framework for the body and protects the vit
00039 ?0994c0b89c0edd69cbdfecf717cc9b 38 Molnau OPS5 (Official Production System, Version 5) is a w
11836 system 18 They were proud of what was very much to their disgrace. The pores of their skin wer
7. Integration of weaponized unmanned aircraft into the air-to-ground system / Dav
Philips406 3 System Contro! Keys. F. łprostoauto.holm.ru l. OPEN Push thc bulton to fold down the fr
O Google implementation of DFS (cf. The Google File System - whitepaper) O Distributed FS 3 For dist
Domain Name System DNS is a hierarchical client/serverbased distributed database management system.
Nie można wyświetlić tej strony Zabezpieczenia systemu Windows The server 192.168.18.235 is asking f
więcej podobnych podstron