21 Glikoliza(1)
2ATP
Anaerobic
homolactic
fermentation
2NADH
2NAD
2Lactate
Glycolysis
Glucose
2ADP^ | ^2NAD+ + 2P,
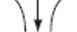
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
2NADH
2Pyruvate
Aerobic oxidation
i
Citric Acid Cycle
2NADH 602
Oxidative
phosphorylation
2NAD+-^4
6C02 + 6H20
Anaerobic
alcoholic
fermentation
2NADH
2NAD
2C02+ 2Ethanol
Figurę 17-1 Glycolysis. Glycolysis convcrts glucose to pyruvate while gcnerating two ATPs. Under anaerobic conditions. alcoholic fermentation of pyruvate occurs in yeast. whereas homolactic fermentation occurs in muscle. Under aerobic conditions. pyruvate is oxidized to H,0 and CO, via the citric acid cycle (Chaptcr 21) and oxidative phosphorylation (Chapter 22).
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
21 Glikoliza Glycolysis Glucose Figurę 17-1 Glycolysis. Glycolysis convcrts glucose to pyruvate whi
skanuj0139 (Kopiowanie) i Gaz wytłaczający 204 Glikokortyfcotteroidy I Glikol hcicsylenowy 21 7, 264
Image096 ftimentacyjmniFermentacje glikolrtyczne - {glikoliza (EMPJ + redukcja za/ Typy fermentacji
Zadanie 21. Kwas określany skrótem GLA to A glikolowy 0 salicylowy 0 hialurorowy □
DSC00243 (2) ggj X ■■■■a* Głównym szlakiem fermentacji glukozy jest glikoliza W wa
Schowek07 Po co im (mikroorganizmom) ta fermentacja? 2(NADH+H*) 2NADPirogronian 2NAD 2(NADH+H*) Ferm
0000043(1) Energetyka glikolizy i fermentacji Katabolizm cukrowców, obok rozkładu tłuszczów, jest po
P1060404 Wykład 9 Metabolizm węglowodanów. Glikoliza, fermentacje, cykl fosforanów pentoz.
21. Podczas fermentacji ATP produkowane jest na skutek (podać 2 przykłady) 22.
Zadanie 21. Kwas określany skrótem GLA to A glikolowy 0 salicylowy Q hialuronowy Q
LastScan5 Glikoliza beztlenowa ~ _ Glukoza + 2Pi+ 2ADP --
2013 10 21 12 44 28 Interpretacja wyników badania uzupełniaiacego: Wtórna fermentacja laktozy /And
DSC00243 (2) ggj X ■■■■a* Głównym szlakiem fermentacji glukozy jest glikoliza W wa
glikoliza? //* ę—o~® C — O"/Z C—O // C —O" H—C—OH ch2o-® 2ADP 2ATP C—OHI
więcej podobnych podstron