CSG144
133
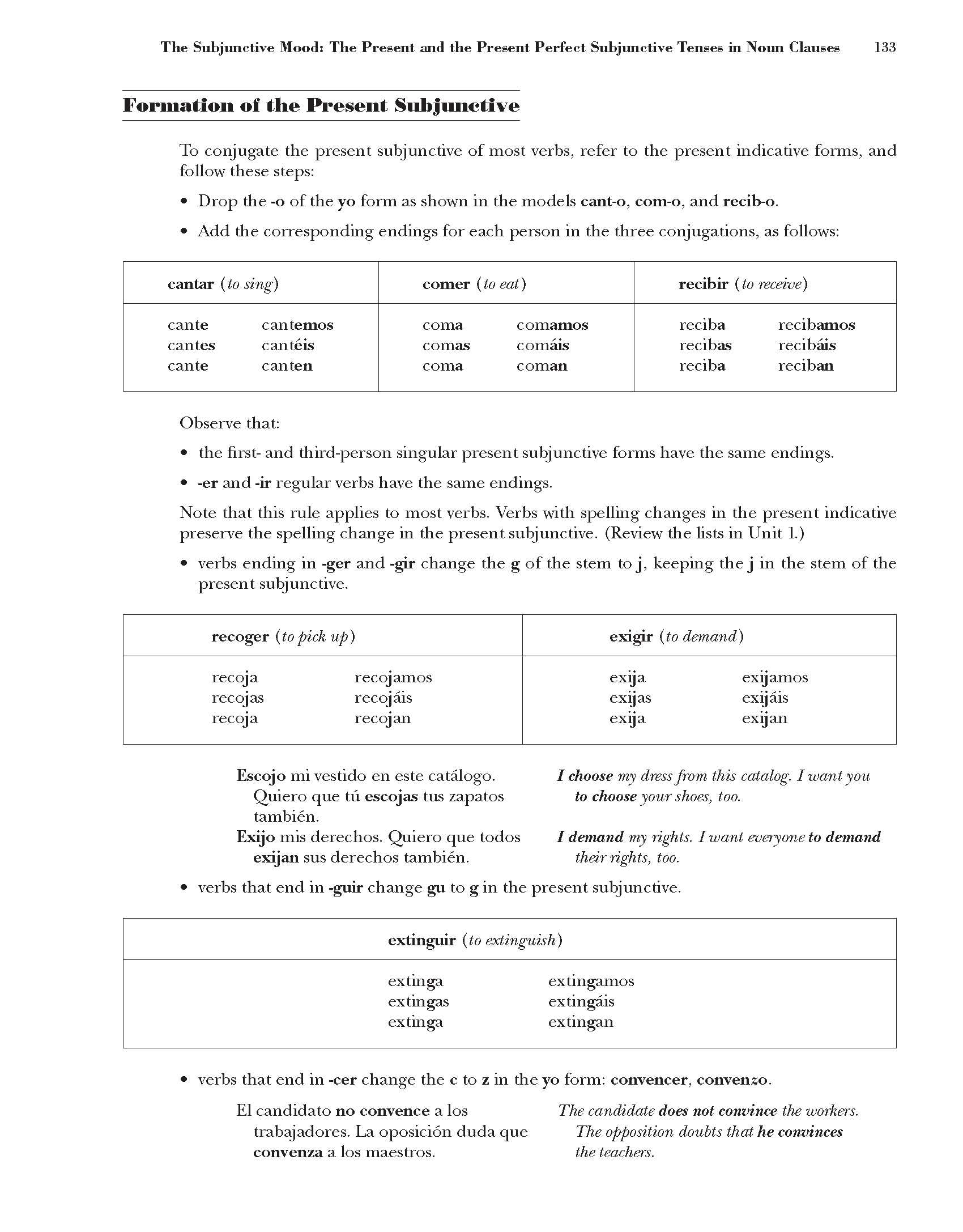
The Subjunctive Mood: The Present and the Present Perfect Subjunctive Tenses in Noun Clauses
Formation of the Present Sub|imctive
To conjugate the present subjunctive of most verbs, refer to the present indicative forms, and follow these steps:
• Drop the -o of the yo form as shown in the models canto, com-o, and recib-o.
• Add the corresponding endings for each person in the three conjugations, as follows:
|
cantar (to sing) |
comer (to eat) |
recibir (to receive) |
|
can te can temos cantes canteis can te can ten |
coma comamos comas comais coma comaii |
reciba recibamos recibas recibais reciba reciban |
Observe that:
• the first- and third-person singular present subjunctive forms have the same endings.
• -er and -ir regular verbs have the same endings.
Notę that this rule applies to most verbs. Yerbs with spelling chan ges in the present indicative preserve the spelling change in the present subjunctive. (Review the lists in Unit 1.)
• verbs ending in -ger and -gir change the g of the stem to j, keeping the j in the stem of the present subjunctive.
Escojo mi vestido en este catalogo. Quiero que tu escojas tus zapatos tambien.
Exijo mis derechos. Quiero que todos exijan sus derechos tambien.
I choose my dress from this catalog. I wantyou to choose your shoes, too.
I demand my ńghts. I want ev ery one to demand theirńghts, too.
|
recoger (to pick up) |
exigir (to demand) |
|
recoja recojamos recojas recojais recoja recojan |
exija exijamos exijas exijais exija exijan |
• verbs that end in -guir change gu to g in the present subjunctive.
extinguir (to extinguish)
extinga
extingas
extinga
extingamos
extingais
extingan
• verbs that end in -cer change the c to z in the yo form: convencer, conyenso.
El candidato no convence a los The candidate does not convince the workers.
trabajadores. La oposición duda que The opposition doubts that he convinces
conyenza a los maestros. the teachers.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
CSG142 Unit 13The 8ubjunotive Mood:The Present and the Present Perfect Subjunctive Tenses in No
CSG146 The Subjunctive Mood: The Present and the Present Perfect Subjunctive Tenses in Noun Clauses
CSG148 137 The Subjimctive Mood: The Present and the Present Perfect Subjunctive Tenses in Noun Clau
CSG150 139 The Subjimctive Mood: The Present and the Present Perfect Subjunctive Tenses in Noun Clau
CSG152 141 The Subjunctive Mood: The Present and the Present Perfect Subjunctive Tenses in Noun Clau
CSG156 The Subjunctive Mood: The Present and the Present Perfect Subjunctive Tenses in Noun Clauses
CSG154 143 The Subjunctive Mood: The Present and the Present Perfect Subjunctive Tenses in Noun
CSG158 The Subjimctive Mood: The Present and the Present Perfect Subjunctive Tenses in Noun
więcej podobnych podstron