netter161

Overview of Hormone Action
ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY
Steroid Hnrmones Thyroid Hormones Vitamin D
O
Peptide and Catecholamine Hormones
Si gnał generator
Celi membranę
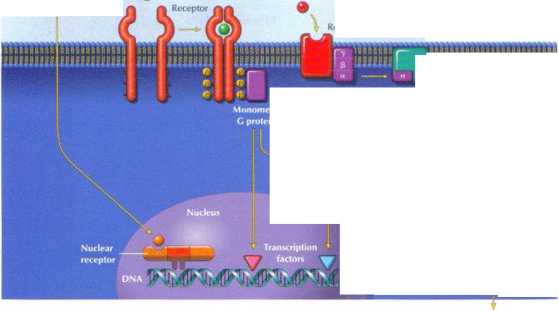
Heterotnmeric C protein
Sccond messengers
----► fcAMP, rCMP, Ca2*,
Tymsine Unasf |p„ diacylglyrerol) actiytty
Rcgulation of mctahnlic pathways, celi growth, etc.
Regulalion of adivitY and ■- mRNA —* conccntration of eniymci and othcr protein*
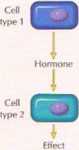
Autocrine

Effect
Paracrine
Endocrine
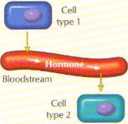
Effect
Neurocrine
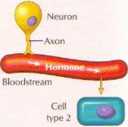
Effect J. Perkins °I®N
Figurę 8.1 Overview oi Hormone Action_
I lormones are invołved in the process of cell-tocell signaling. Hor-mnnes interact with their targel celi*. via specific hormone-receptor interactiun*. (see Chart 1.2). The receptor may be in the plasma membranę or inside the celi (cyloplasmic or nudcar). The hormone-recep-tor interaction may generale second messengers or regulate gene expression. The effect of the hormone on the r ell may be the result of altered metabolit, pathways (i.e., changes in enzyme acthnty r>r concentrations of enzymes) or changes in celi struciure and growth The lower panel illustrates the diłferent modes of cełMo-cell commu nication.
180
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter162 Regulatinn of Hormone Secretion ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Negative Fccdback Hypolhalamus V Targ
netter55 Slructure of the HeartCARDIOYASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Mitral valve Poslerior cusp- Ascending aort
netter70 Monitoring of Blond PressureCARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Low-Pressure Baroreceptors ANP releas
netter70 Monitoring of Blond PressureCARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Low-Pressure Baroreceptors ANP releas
12897 netter104 Anatomy of Ihc Kidf»RENAL PHYSIOLOGY A. Antcrior surfacc of right kidney Superior ox
netter67 Control of Artcriolar TonęCARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Yasopressin (AI)H) J. Pcrkins MS, MfA I
netter156 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Overvievv of Cii Trać! Fluid and Electrolyte Transport Ingest
netter170 Thyroid Gland: Hormone ActionENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOCY T4® t co3 f Ventilation f Cardiac output
netter53 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Overview of thc Cardiovascular System Pulmonary
więcej podobnych podstron