12897 netter104
Anatomy of Ihc Kidf»
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
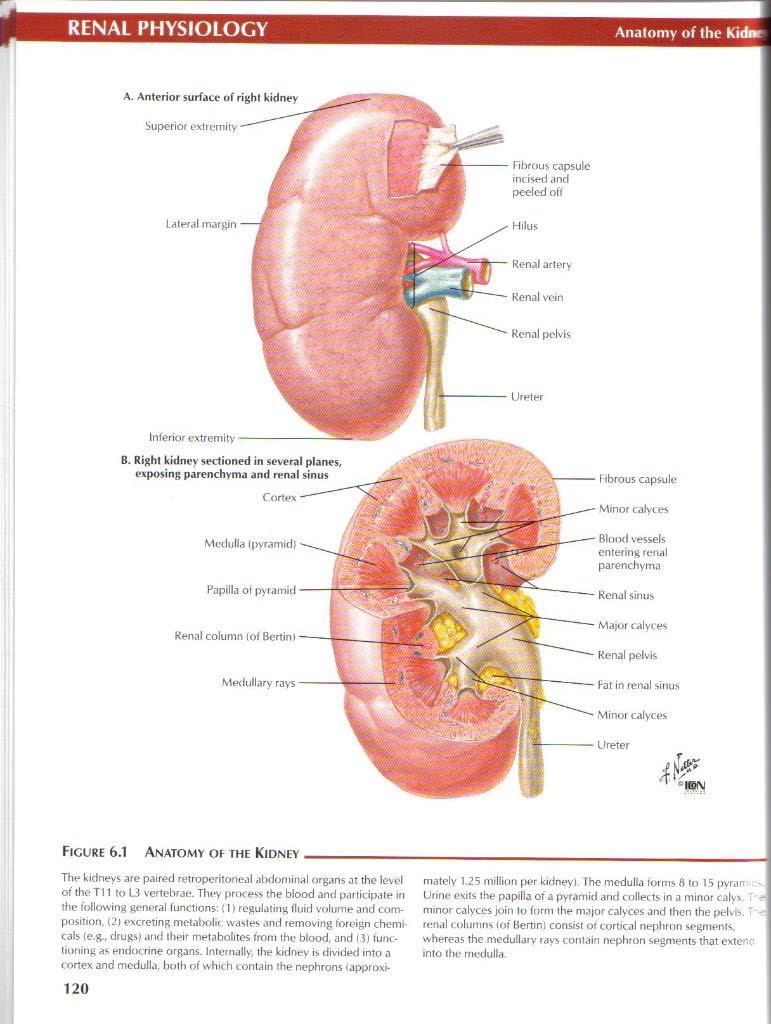
A. Antcrior surfacc of right kidney
Superior oxtremity
Hilus
Lateral margin
Inferior extremity •
B. Righ! kidney sectioned in several planes, exposing parenchyma and renal sinus
Pnpilla ol pyramid Renal column tof Bertin) Medullary rays
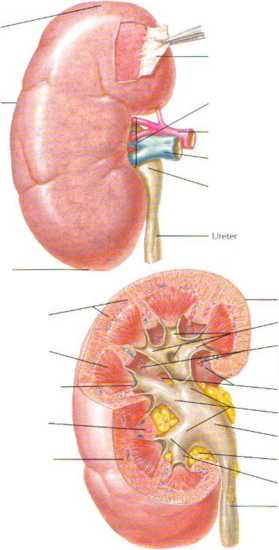
Medulla (pyramid)
Rbrous capsule incised and pecled od
Renal artery Renal vein Renal pelvis
Hibrous capsulc
Minor calyces
Blood vessels entering renal parenchyma
Renal sinus
Major calyces
Renal pelvis
Pat in renal sinus
Minor calyces
Ureter
Ficure 6.1 Anatomy oe the Kidney
The kidneys are paired retroperitoneal abdominal organs at the level of the T11 to 13 vertebrae. They prtFcess the blood and partidpate in the following generał functions: (I) regulating fluid volume and com-position, (2j excreting metabolit, wastes and removing foreign Chemicals (e.g.. drugs) and their metabolites from the blood, and (3) lunc-tioning as endocrine organs. Intemally, the kidney is divide<l into a cortex and medulla, both of which contain the nephrons łapproxi-mately 1.25 million per kidney). The medulla torms 8 to 15 pyrarn Urine exits the papilla of a pyramid and < ollects in a minor calyv I -minor calyces join to form the major calyces and then the pelvis. i renal columns (ot Bertinl consist of cortical nephron segments, whereas the medullary rays contain nephron segments that exlenc into tłu.* medulla.
120
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
26834 netter121 Anatomy of the Kidney: The Nephron RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Cortical nephrons dilute the uri
skanuj0015 (279) Neuroanatomy 10. Sectional Anatomy of the Brain -landtudinal Mrafcsure ■PHlfillilll
88514 skanuj0015 (279) Neuroanatomy 10. Sectional Anatomy of the Brain -landtudinal Mrafcsure ■PHlfi
netter161 Overview of Hormone ActionENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Steroid Hnrmones Thyroid Hormones Vita
netter162 Regulatinn of Hormone Secretion ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Negative Fccdback Hypolhalamus V Targ
netter180 Actions of InsulinENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 8.20 Actions of Insulin- Insulin is a fueł-s
netter190 Whcn words alone won t do, think NetterNetter s Atlas of Humań PhysiologyJohn T. Hansen, P
netter55 Slructure of the HeartCARDIOYASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Mitral valve Poslerior cusp- Ascending aort
netter70 Monitoring of Blond PressureCARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Low-Pressure Baroreceptors ANP releas
netter82 Nłedianics of Respiration: Elastic Properties IRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY During a slow expirat
więcej podobnych podstron