netter180
Actions of Insulin
ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY
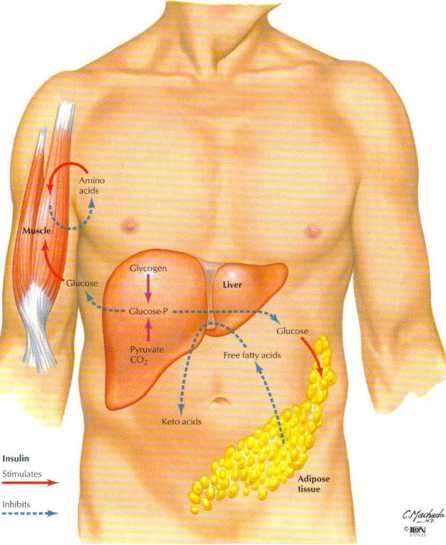
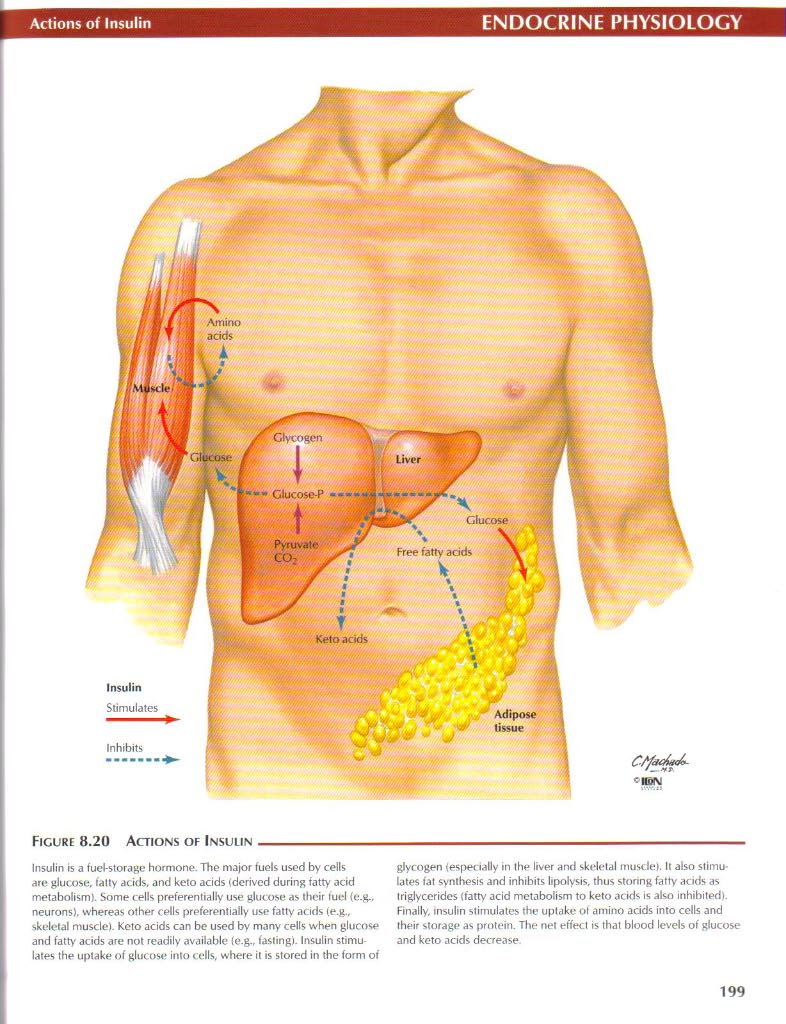
Figurę 8.20 Actions of Insulin-
Insulin is a fueł-storage hormone. The major fuels used by cells are glucose, (alty acids, and keto acids (derived during fatty acid metabolism). Some cells preferentially use glucose as Ibeir lud {e.g.. neurons). whereas other cells preferentially use fatty acids (e.g., skeletal muscle). Keto acids can be used by many cells when glucose and fatty acids are not readily available (e.g., fastingj. Insulin stimu lates the uptake of glucose into cells, where it is stored in the form of glycogen (espedaily in the liver and skelelal muscle). It also stimu-lates fat synthesis and inhibits lipolysis, thus stonng fatty acids as triglycerides (fatty acid metabolism to keto acids is also inhihited). Finally, insulin stimulates the uptake ot amino acids into cells and their storage as protein. The net effect is that blood levels of glucose and keto acids decrease.
199
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter93 O, and CO_. ExchangrRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 5.19 02 and CO, Exchange As blood flows I
64528 netter187 The Mcrtstruaf CycfeENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 8.27 Menstrual Cycle_ The menstruaf
netter161 Overview of Hormone ActionENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Steroid Hnrmones Thyroid Hormones Vita
19314 netter181 Actions of GlucagonENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Ficure 8.21 Actions of Glucagon Glucagon is
netter131 Structure of SłomachCASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 7.9 Structure of THE Stomach_ rhe s
leki nasenne0003 Figurę 20-3. Enhanetd GARA jynapric trans-mission. In ihc presence of GADA, ilic GA
netter109 Renal Clearance: IIRENAL PHYSIOLOGY PRINCIPIE OF TUBULAR SECRETION LIMITATION (Tm) USINC P
netter126 Autonomie lnnervationGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 7.5 Aijtonomic Innervation The inn
więcej podobnych podstron