netter58
Bectrocardiogram: I
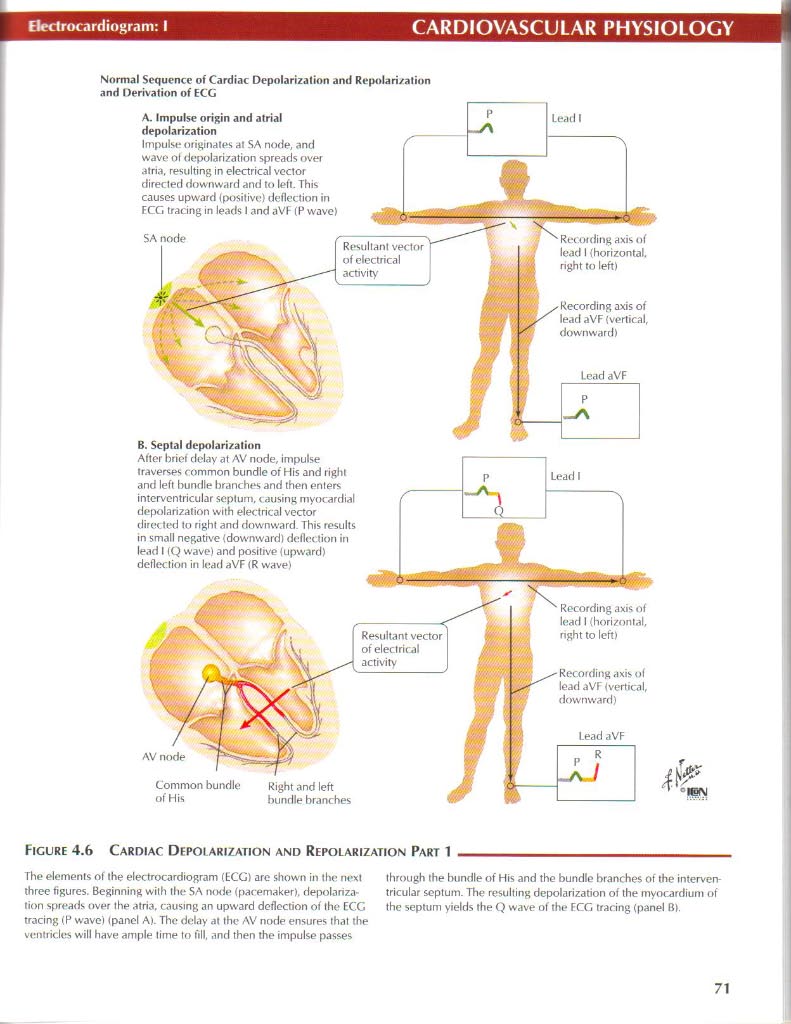
Normal $cqucncc ot Cardiac Depolarization and Repolari/ation and l)erivation of ECG
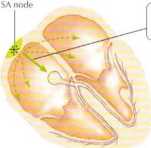
A. Impulse origin and atrial depolarization
Impulse nriginates at SA norie, and wave ol depolarization spreads over atria. resulting in electrical vector directed downward and to left. This causes upward (po$itive) deflection in ECG tracing in leads I and aVF (P wave)
ReCOfding axis uf lead I {horizontal. right to leń)
Recording axis of lead I {horizontal, nght to leń)
Recording axis ol lead aVF {vertical downward)
Common bundle Right and left
of His bundle brancbes
Resultant of electrical activity
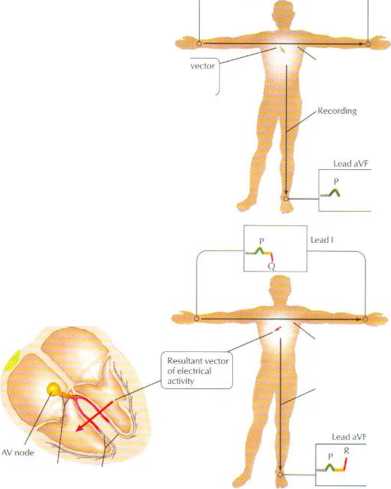
B. Septal depolari/atinn
After brief delay at AV node, impulse traverses common bundle of His and right and left bundle branches and then enters interventricular septum, < ausing myocardial depolarization with electrical vector directed to right and downward. This results in smali negathre {downward) deflection in lead I (Q wave) and positive (upward) deflection in lead aVF (R vvave)
Figurę 4.6 Cardiac Depoi arization and Repolarization Part 1
axis of lead aVF Wertical, downward)
The elements of the electrocardiogram (ECG) are shown in the next three figures. Beginning with the SA imhIh (pacemaker), depolarization spreads over the atria, causing an upward deflection of the ECG tracing (P wave) (panel A). The delay at the AV node ensures that the ventricle$ will have ample time to fili, and then the impulse passes
through the bundle of His and the bundle branches of the interven tricular septum. The resulting depolarization of the myocardium of the septum yields the Q wave of the ECG tracing (panel B).
71
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter60 Electrocardiogram: IIICARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Norm.il Sequence of Cardiac Depolarization
netter126 Autonomie lnnervationGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 7.5 Aijtonomic Innervation The inn
netter170 Thyroid Gland: Hormone ActionENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOCY T4® t co3 f Ventilation f Cardiac output
netter94 O, and CO; Exchange and TransportRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Normal Venlilalion &nbs
57225 netter117 Potassium ExcretionRENAL PHYSIOLOGY Low K’ Diet Normal and High K*
netter106 Glomerular FiltratinnRENAL PHYSIOLOGY Colloid osmotic pressure of plasma (Uln) U
netter113 Urine DilutiorRENAL PHYSIOLOGY h2o Na Cl" h2o 375 —*t- Urea Notę: Figurcs given are e
netter127 Autonomie lnnervationGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY m generał sympathetics decrease peristals
netter134 Castric DigestionGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 7.12 Gastric Digestiye Function The st
netter145 DetecationGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Certam physiologic. events, as arising (orthocołir r
netter156 GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Overvievv of Cii Trać! Fluid and Electrolyte Transport Ingest
więcej podobnych podstron