netter80
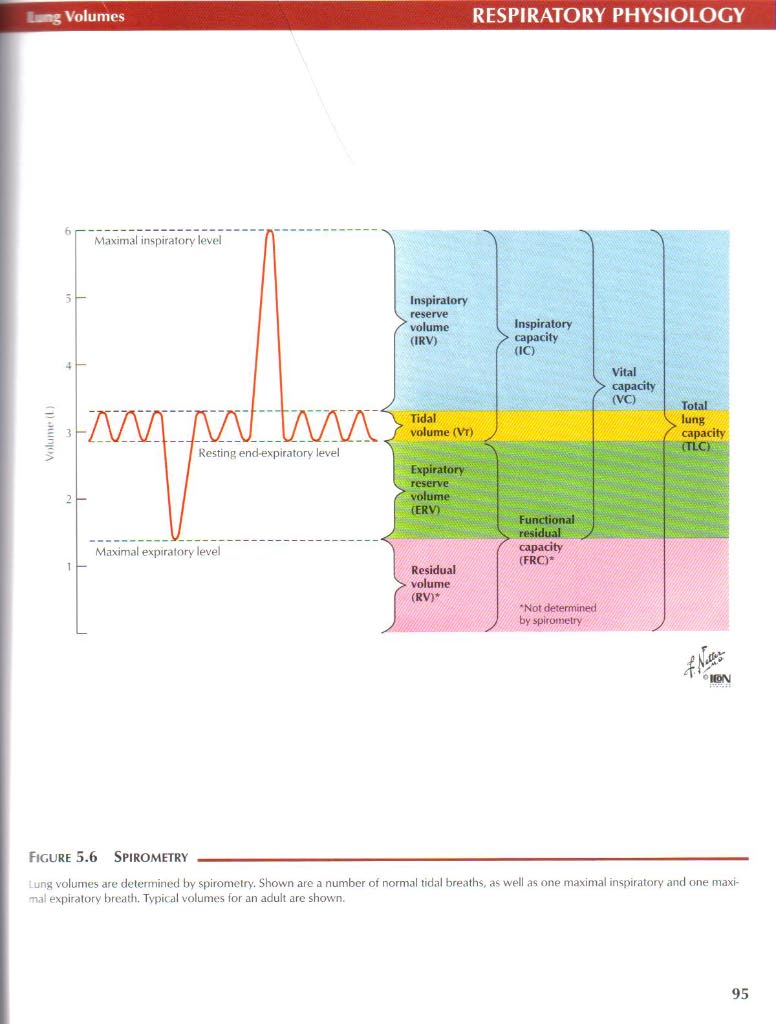
Mt% Yolumps
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY
|
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) |
Inspiratory > capacity (IC) |
Vital y> capacity [ (VC) |
Total |
|
Tidal volume (Vt) ) |
v ■<">* f capacity | ||
|
-> |
(TLC) | ||
|
Expiratory reservc volume (ERV) 'V |
. sr j | ||
|
Rcsidual volume (RV)* |
' capacity (FRC)* •Notdetermmed by spirometry | ||
Figurę 5.6 Spirometry -
. ung volumes are determined by spirometry. Shown are a number of normal tidnl breaths, as well as onp maximal inspiratory and one maxi-•nal expiralory brcath. Typical volumes for an adult are shown.
95
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
57087 netter79 Respiratory MusclesRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Muscles of Inspiration_A Muscles of
netter86 . et tianics of Rcspiration: Flow-VolumeRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY V high lung vołumes, ratę of
netter113 Urine DilutiorRENAL PHYSIOLOGY h2o Na Cl" h2o 375 —*t- Urea Notę: Figurcs given are e
netter126 Autonomie lnnervationGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 7.5 Aijtonomic Innervation The inn
netter127 Autonomie lnnervationGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY m generał sympathetics decrease peristals
netter134 Castric DigestionGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 7.12 Gastric Digestiye Function The st
netter58 Bectrocardiogram: ICARDIOYASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Normal $cqucncc ot Cardiac Depolarization and
netter60 Electrocardiogram: IIICARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Norm.il Sequence of Cardiac Depolarization
netter61 Cardiac CycleCARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 4.9 Cardiac Cycle The cardiac cycle represent
netter90 Yenlilalion/PerfusionRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY A. Conditions with Iow ventilation/perfusion ra
więcej podobnych podstron