skanuj0018 (241)
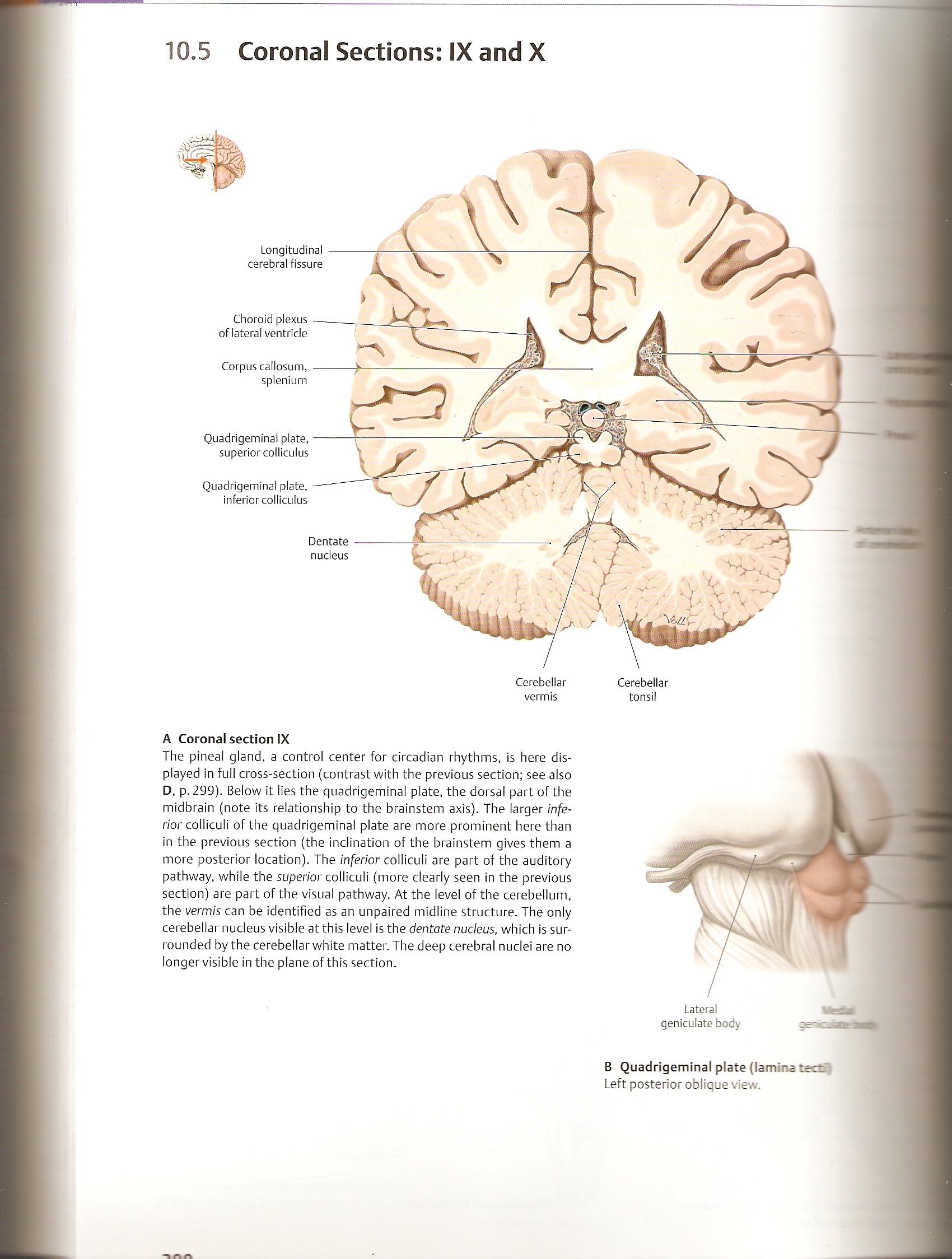
10.5 Coronal Sections: IX and X
Quadrigeminal piąte, superior colliculus
Quadrigeminal piąte, inferior colliculus
Longitudinal cerebral fissure
Choroid plexus of lateral ventride
Corpus callosum, splenium
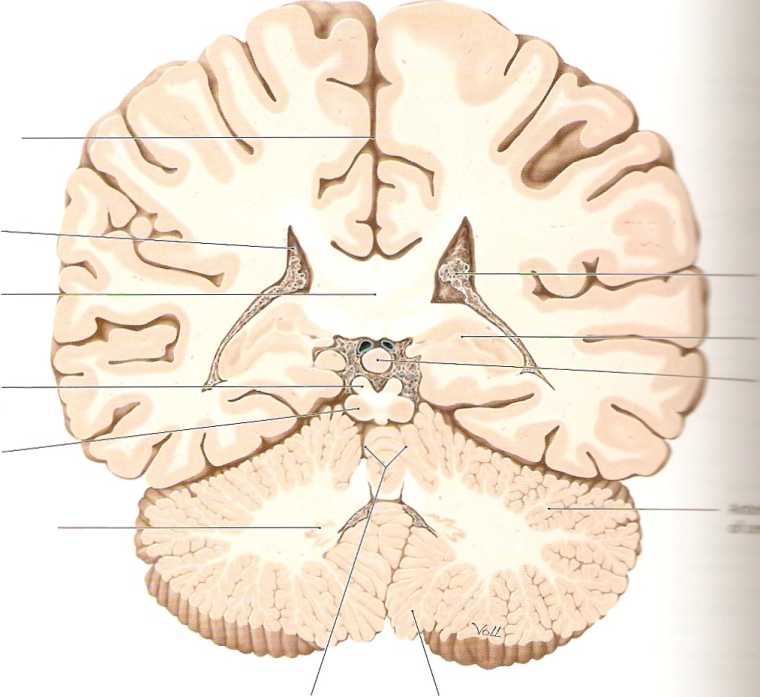
Cerebellar
vermis
Cerebellar
tonsil
Dentate
nudeus
A Coronal section IX
The pineal gland, a control center for circadian rhythms, is here dis-played in fuli cross-section (contrast with the previous section; see also D, p. 299). Below it lies the quadrigeminal piąte, the dorsal part of the midbrain (notę its relationship to the brainstem axis). The larger inferior colliculi of the quadrigeminal piąte are morę prominent here than in the previous section (the inclination of the brainstem gives them a morę posterior location). The inferior colliculi are part of the auditory pathway, while the superior colliculi (morę clearly seen in the previous section) are part of the visual pathway. At the level of the cerebellum, the vermis can be identified as an unpaired midline structure. The only cerebellar nucleus visible at this level is the dentate nudeus, which is sur-rounded by the cerebellar white matter. The deep cerebral nuclei are no longer visible in the piane of this section.
Lateral
geniculate body
B Quadrigeminal piąte (lamina tectfi Left posterior oblique view.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
skanuj0022 (192) 10.6 Coronal Sections: XI and XII (Occipital) Longitudinal cerebral fissure Calcari
25428 skanuj0014 (281) 10.3 Coronal Sections: V and VI Cingulate gyrus Corpus callosum, trunk Choroi
skanuj0016 (266) Neuroanatomy 10. Sectional Anatomy of the Brain10.4 Coronal Sections: VII and VIII
skanuj0016 (266) Neuroanatomy 10. Sectional Anatomy of the Brain10.4 Coronal Sections: VII and VIII
57747 skanuj0289 (2) Rozdział 10. ♦ Podstawy SQL 303 SELECT * FROM Osoba WHERE Id >= 3 AND Id <
10, ) r SECOND SECTION "Laws can, and often are subverted.’* Jennings Having given a very brief
skanuj0047 (6) 2009-10-15Polymers Are Like TV: Both Have Lots and Lots of RepeatsPolimery różni
skanuj0008 (40) kkk >14 . 3 vL 1^ iiX p ? -1 r /K-u 1^ V —.. i,
skanuj0009 ie/j y^ 10 L V C I t /u. spraw przez różne organy stosujące prawo - jeden organ na podsta
więcej podobnych podstron