25428 skanuj0014 (281)
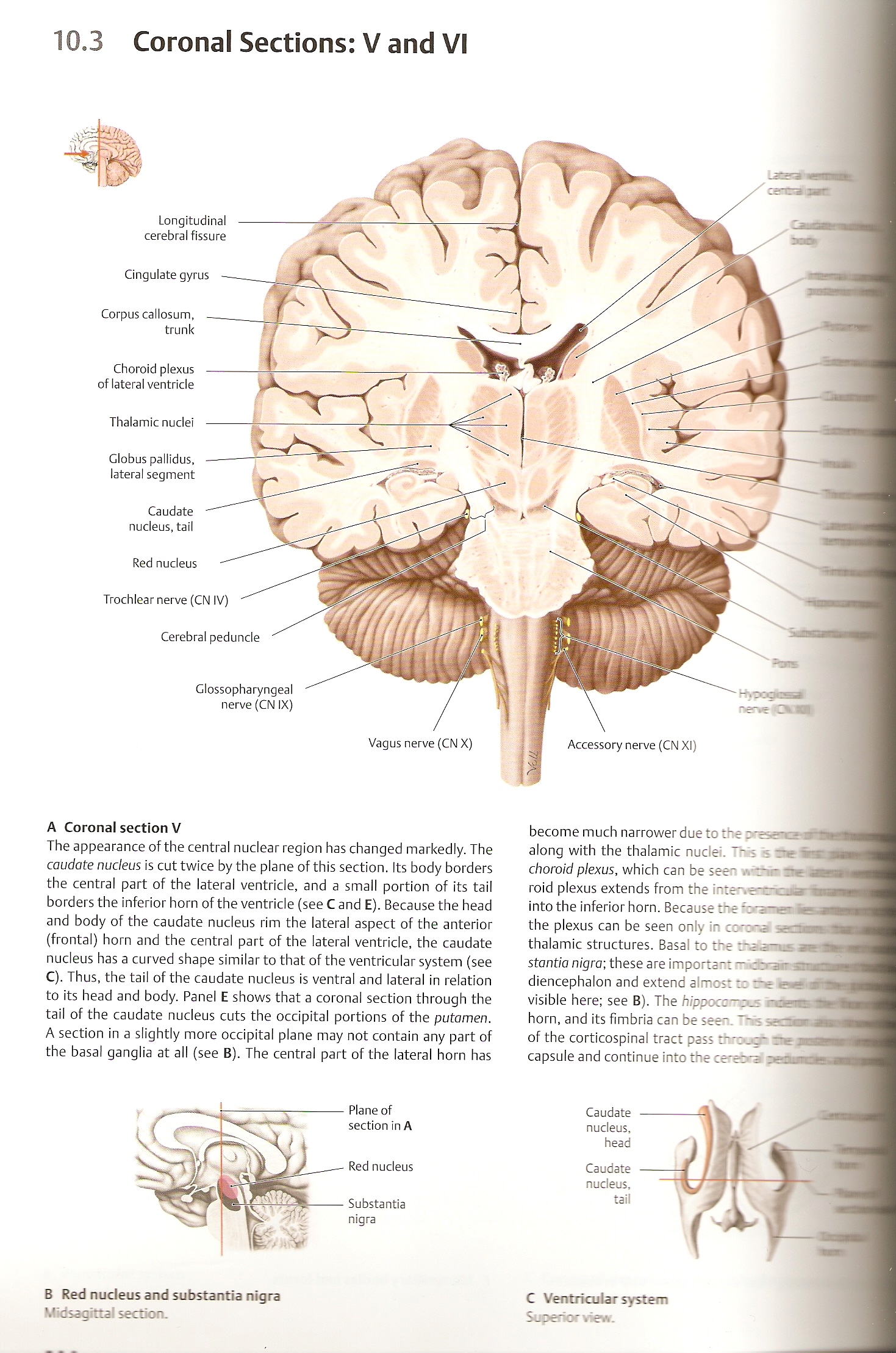
10.3 Coronal Sections: V and VI
Cingulate gyrus
Corpus callosum, trunk
Choroid plexus of lateral ventride
Thalamic nudei
Globus pallidus, lateral segment
Caudate nudeus, taił
Red nudeus
Trochlear nerve (CNIV)
Cerebral pedunde
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Vagus nerve (CN X)
Accessory nerve (CN XI)
Longitudinal cerebral fissure
A Coronal section V
The appearance of the central nuclear region has changed markedly. The caudate nudeus is cut twice by the piane of this section. Its body borders the central part of the lateral ventricle, and a smali portion of its taił borders the inferior horn of the ventricle (see C and E). Because the head and body of the caudate nucleus rim the lateral aspect of the anterior (frontal) horn and the central part of the lateral ventricle, the caudate nucleus has a curved shape similar to that of the ventricular system (see C). Thus, the taił of the caudate nucleus is ventral and lateral in relation to its head and body. Panel E shows that a coronal section through the taił of the caudate nucleus cuts the occipital portions of the putamen. A section in a slightly morę occipital piane may not contain any part of the basal ganglia at all (see B). The central part of the lateral horn has
become much narrower due to the along with the thalamic nuclei. This s AeftM choroid plexus, which can be seen re aa roid plexus extends from the inter.e^cichtafli into the inferior horn. Because the foraneBMH the plexus can be seen only in colona sofl thalamic structures. Basal to the raawfll stantia nigra; these are important midtrat smm diencephalon and extend almost to ~e e«e »l visible here; see B). The hippocar~OLS nrioaffl horn, and its fimbria can be seen. This ssiM of the corticospinal tract pass thro-cr 'mejafli capsule and continue into the cerecra r^ainom
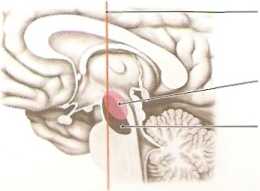
Piane of section in A
Red nudeus
Substantia
nigra
Caudate
nudeus,
head
Caudate
nudeus,
taił

B Red nucleus and substantia nigra Midsagittal section.
C Ventricular system Superior view.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
skanuj0018 (241) 10.5 Coronal Sections: IX and X Quadrigeminal piąte, superior colliculus Quadrigemi
skanuj0022 (192) 10.6 Coronal Sections: XI and XII (Occipital) Longitudinal cerebral fissure Calcari
12753 skanuj0017 (249) Posterior lobe of cerebellum Pineal Hippocampus Choroid plexus of lateral ven
skanuj0003 (409) 10 ANDRZEJ KOWALCZYK 2005). It may be presumed that in many parts of the world the
skanuj0016 (266) Neuroanatomy 10. Sectional Anatomy of the Brain10.4 Coronal Sections: VII and VIII
skanuj0016 (266) Neuroanatomy 10. Sectional Anatomy of the Brain10.4 Coronal Sections: VII and VIII
12442 skanuj0001 (37) W .10. 2oXo,.P, %oAOu< V* Up/iol hvvM»- °W. ^ciui/cwŁ^
więcej podobnych podstron