netter125
fntpric Nervous System
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY
WW
Myenteric plexus (cross section; bematoxylin-eosin, x 200)
Sultserous plexus
Longitudinal
intramuscul;
plexus
Myenteric
(Auerbach‘s)
plexus
Myenteric plexus (parallel section; methylene bluo, X 200}
Submucosal ploxus (longitudinal section: hematoxylin-eosin, X200)
Lumen

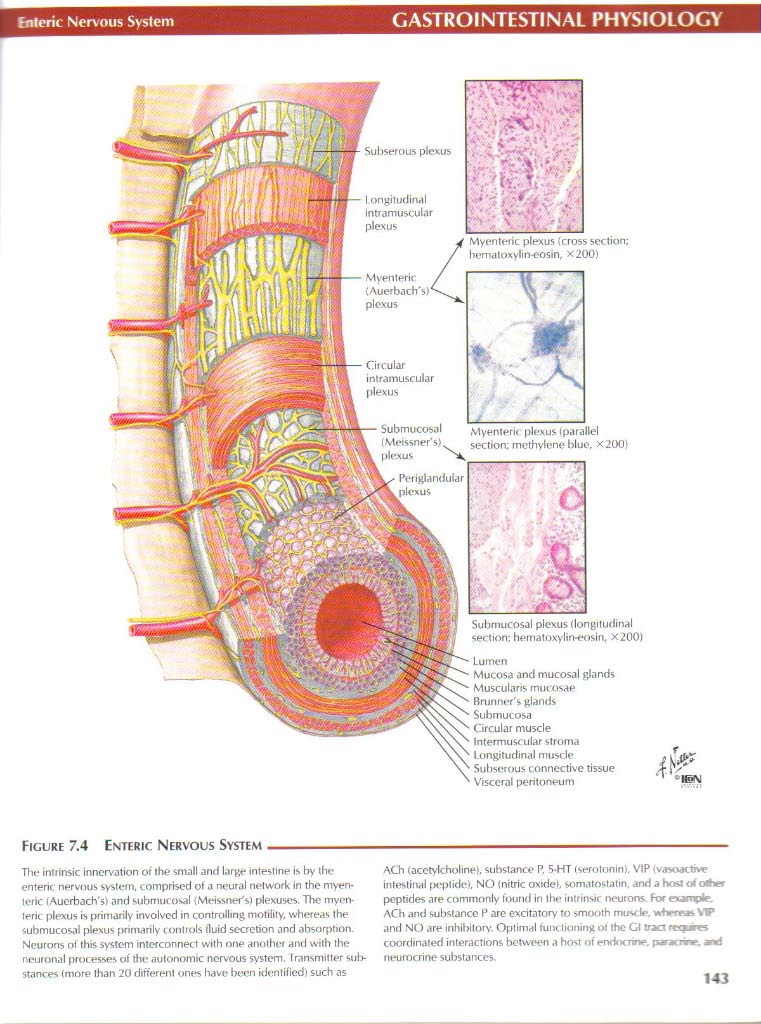
Mucosa and mucosal glands Musculans mucosae Brunner's glands Submucosa Circular muscle Intermuscular stroma Longitudinal muscle Subserous connectiye tissue Visceral peritoneum
Figurę 7.4 Enteric Nervous System-
The intrinsic innervation ot the smali and large intestine is by the enteric nervous system, comprised ot a neural nelwork in the myen-teric. (Auerbach's> and submucosal (MeissnePs) plexuses. Tlie myenteric plexus is primarily involved in controlling motility, whereas the submucosal plexus primarily Controls tluid secretion and absorptión. Neurons of this system interconnect with one another and with the neurónal processes ot the autonomie nervous system. Iransmitter sul>-stances (morę than 20 differenl ones have becn identified) such as
ACh (acetylcholine), suhstance P. S-HT (serotonin), VIP <vasoactive intestinal peptide), NO (nitric oxidel, SomałOStatin, and a host o< other peptides are commonly found in the intrinsic neurons. For exampie. ACh and substance P are excitatory to smooth mu** W*, wherras V7P and NO are inhibitory. Optimal tum tioning ot the Gl tract rcqurw coordinated interactions between a host ot endocrine. paraem*. and neurocrine substances.
143
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter125 fntpric Nervous SystemGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY WW Myenteric plexus (cross section; bema
24728 netter125 fntpric Nervous SystemGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY WW Myenteric plexus (cross section
netter152 Intrahepatii Biliary SystemGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Noto. The figurę shows bile canalic
56281 netter15 Peripheral Nervous SystemNEUROPHYSIOLOGY Postorior horn Dotsal root ganglion Sensory
netter16 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYAutonomie Nervous System: Schema Intracranial wssels Facial nenie (VII >
netter172 Adrenai Cland: HistologyENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Capsule Zona glomerulosa Capsular plexus Caps
netter109 Renal Clearance: IIRENAL PHYSIOLOGY PRINCIPIE OF TUBULAR SECRETION LIMITATION (Tm) USINC P
netter135 Gastric Secretion: IGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Neurocrine Regulalion of Acid
netter136 Gaslric Secretion: IIGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Secrelions of gastric acid (H* ) by parie
netter141 Smali Intestine MotiiityGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Rhythmic sepmentation Intraluminal
netter163 Hypothalamus and PituitaryENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Ihalamus Hypothalamic sulcus Hypothalamic a
netter180 Actions of InsulinENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 8.20 Actions of Insulin- Insulin is a fueł-s
więcej podobnych podstron