netter172
Adrenai Cland: Histology
ENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY
Capsule Zona glomerulosa
Capsular plexus
Capsule
Cortical capillaries Fasciculata
Medullary capillaries
Normal human suprarenal gland
Humań suprarenal gland after administration of crude ACTH
Schemalic stereogram of intrinsic suprarenal circulation
Suprarenal artery (one of many)
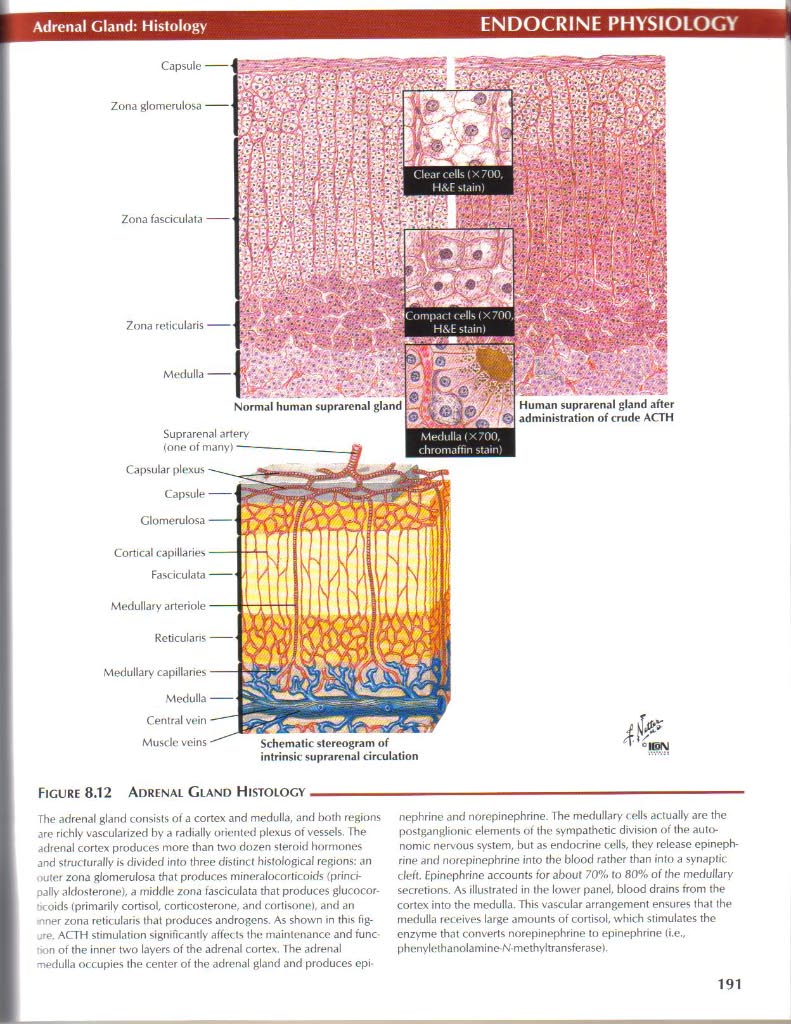
Figurę 8.12 Adrenal Gland Histology-
The adrenal gland consiSlS of a cortex and medulla, and both regions are richly vascularized by a radially oriented plexus of ves5els. The adrenal cortex produces morę than two dozen steroid hormones and sfrucfurally is divided into three distinct hislological regions: an miler zona glomerulosa that produces mineralocorticoids {princi-paUy aldosterone), a mtddle zona fasciculata that produces glucocor-ócoids (primarily cortisol. corticosterone, and cortisone), and an -nner zona rełicularis that produces androgens. As shown in this fig-ACTH stimulation significantly affects the mainlenance and func •>on of the inner two layers of the adrenal cortex. The adrenal medulla occupies the center of the adrenal gland and produces epi-nepbrine and norepinophrine. The medullary < dis ar.tually are the postganglionic elements of the sympathetic division of the autonomie nervous system, but as endocrine cells, they rclcasc epineph-rine and norepinephrine into the blood rather than into a synaptic cleft. Epinephrine accounts for about 70% to 80% of fhe medullary secretions. As illustrated in the lower panel, blood drains trom the cortex into the medulla. This vascular arrangement enstires that the medulla receives large amounts of cortisol, which stimulates the enzyme that converts norepinephrine to epinephnne (i.e., phcnylethanolamine-N-methyłtransferasef.
191
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Nadnercza (glandulae adrenalis)m Kora nadnerczy warstwa kłębkowata (zona glomerulosa) 5-10% warstwa
netter109 Renal Clearance: IIRENAL PHYSIOLOGY PRINCIPIE OF TUBULAR SECRETION LIMITATION (Tm) USINC P
netter135 Gastric Secretion: IGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Neurocrine Regulalion of Acid
netter136 Gaslric Secretion: IIGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Secrelions of gastric acid (H* ) by parie
netter141 Smali Intestine MotiiityGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Rhythmic sepmentation Intraluminal
netter152 Intrahepatii Biliary SystemGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Noto. The figurę shows bile canalic
netter163 Hypothalamus and PituitaryENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Ihalamus Hypothalamic sulcus Hypothalamic a
netter180 Actions of InsulinENDOCRINE PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 8.20 Actions of Insulin- Insulin is a fueł-s
netter190 Whcn words alone won t do, think NetterNetter s Atlas of Humań PhysiologyJohn T. Hansen, P
netter49 I I Cardiac Mustlt*: StructureMUSCLE PHYSIOLOGYFlCURF 3.7 SCHEMA OF STRUCFURt OF CARDIAC MU
netter52 Fxcitation-Conlraclion CouplingMUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY HART 3.1 COMPARISION OF MUSCLE STRUCTURE A
netter78 Airway Structure: EpithcliumRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Mucus- Goblet (mucous)
netter93 O, and CO_. ExchangrRESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 5.19 02 and CO, Exchange As blood flows I
16523 netter73 Rrsponse to txeras»CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Anticipation of exercise stimulates
netter125 fntpric Nervous SystemGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY WW Myenteric plexus (cross section; bema
więcej podobnych podstron