netter22
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
Cerebellum: Afferent Pathways
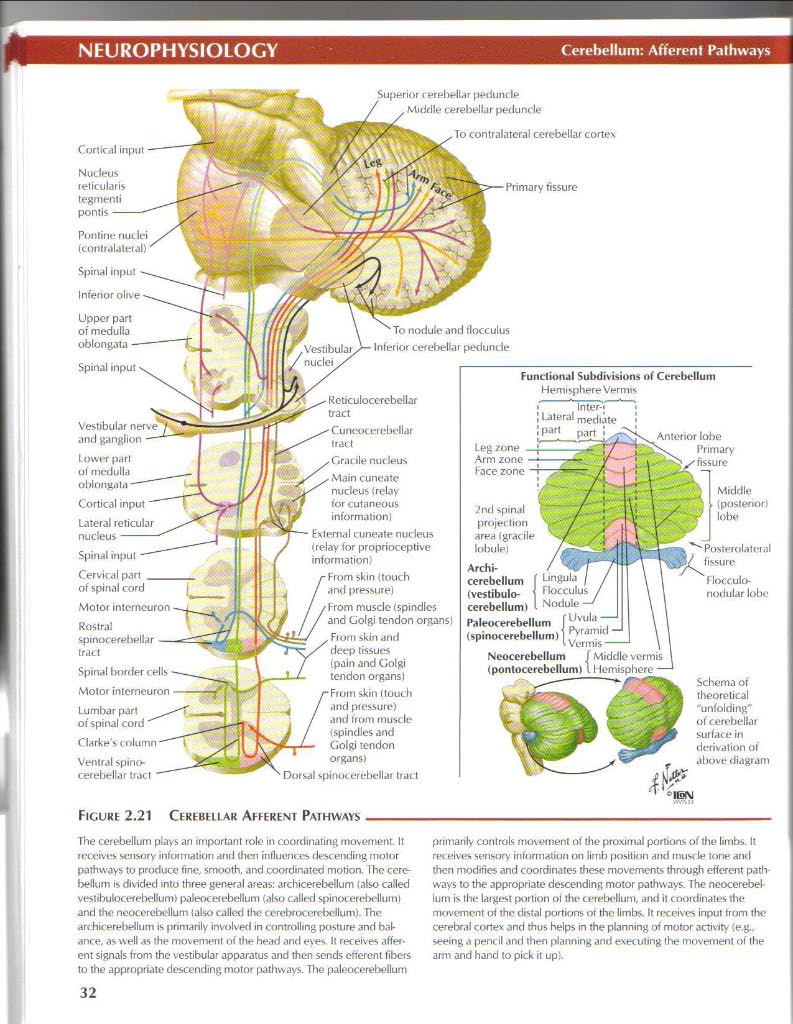
Cortical input
uperior cerebellar peduncłe
Midrłle cerebellar peduncłe
Cortical input
Spinał bortter cells
Lumbar part
ot spinał cord
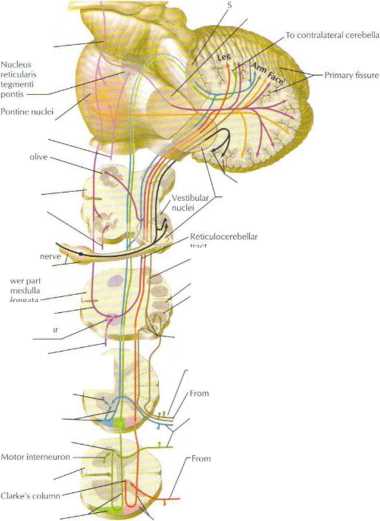
Functional Subdivisions of Cerebelluni
Hemisphere Ve
ungula / /
Flocculus / Nodule —'
«. JlI,uUrr
im)|Pyram'd-
Ventral spino
Leg /one Arm zonę Face zonę
2nd spinał
prnjpc tmn
igranie
Spinał input Interior
Upper part ot medulla oblongata
Vestibular and ganglion
Spinał input Cervical parł of spinał cord |
Motor intcrneuron Rost rai
spinocerebellar traci
To nodule and tlocculus Interior cefebellar peduncłe
Cuncocerebellar traci
Gracile nurteus Matn cuncatc nudeus (relay tor cutaneous intormation)
External runeate nucleus {relay ter proprioceptive information)
From skin (touch and pressure)
musde (spindlcs and Golgi tcndon organs) From skin and tleep tissues (pain and Golgi tcndon organs) skin (toucłi and pressure) and from muscłe ispindles and Golgi tcndon organs)
Dorsal spinocerebellar traci
Archi-ccrcbellum (vestibulo-cercbcllum)
Paleocerebellum (spinocerebellum)
Antcrior lobe
Primary
Ncoccrcbcllun
(pontoccrebcllum) l Hemisphere
"unfoldine"
above diagram
Figurę 2.21 Cerebeuar Aeeeremt Pathways
The ccrcbellum plays an important role in coordinating n>ovcmenL It rcceivcs sensory intormation and then influenr.es descending motor pathways to produce fine, smooth. and coordinated motion. Ihc ccrcbellum is divided mto three generał areas: archicerebełlum latso called vestibulocerebeBum) paleocerebellum (also called spinocerebefium) and ihc neocerel>ellum talso called the cerebrocerebdlum). The ar< hi< ereł>ellum is primarily involved in controlling posturę and bal-ance, as well as the movpment ot the head and eyes. It receives affer-ent signals from the vcstibular apparatus and then sends cnercnt tibers to the appropriate descending motor pathways. The paleocerebellum pnmańly Controls movement of the proximal portions of the limbs. It ret eives sensory information on limb posilion and muscłe tonę and then modities and coordinates these rrtovements through efferent pathways to the appropriate descending motor pathways. The neocerebel lum is the latgesl portion ol the c erebelluni, and it coordinates the movement oi the distal portions ot the limbs. It receives input trom the cerebral corte* and thus helps in the planning of motor activity (e.g. seeing a pencil and then planning and execuling the movement of the arm and hand to pick it up).
32
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
netter30 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Sensory Pathways: I Spinothałamic iract lower part of medulla
netter32 NEUROPHYSIOLOCY Sensory Pathways: III Schematic demarcation of dermatomes shown as distinct
netter29 Proprioceptiiid Reflex Pathways: IVNEUROPHYSIOLOGY B. Stretch refie* (reciprocal inhibition
netter36 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Audilory System: Pathways temporal lobe cortex Medial geniculate body High
netter40 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYGustatory (Taste) System: Pathways Sensory cortex łjust below face area) Lat
netter26 NEUROPHYSIOLOCYProprioception and Reflex Pathways: I Spinał Effector Mechanisms Schcmalic r
więcej podobnych podstron