netter26
NEUROPHYSIOLOCY
Proprioception and Reflex Pathways: I
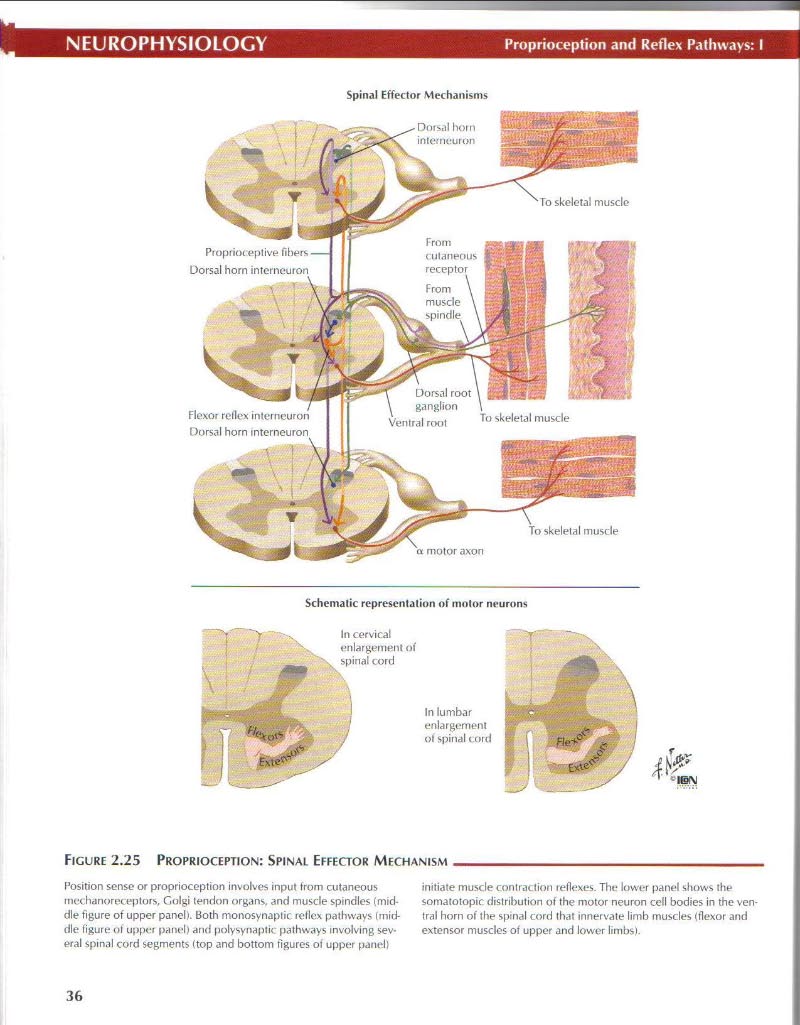
Spinał Effector Mechanisms
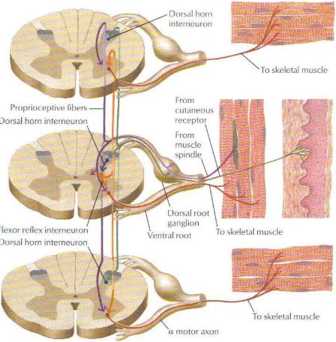
Schcmalic rcpresentation of motor neurons
Figurę 2.25 Proprioception: Spinae Effector Mechanism
Position sense or proprioception invohres input from cutaneous me< hanoreceplors. Cdgi tendon organs, and muscle spindles (mid-dle figurę of upper panel). Both monosynaptic rcflcx pathways (mid-dle figurę ot upper panel) and polysynaptic pathways invołving sev-eral spinał cord segments (top and bottom tigures of upper panel) initiate muscle contraction reflexes. The lower panel slłows the somatotopic distribution of the motor neuron celi bodies in the ven-tral horn of the spinał cord that innervate limb muscles (flexor and extensor muscles of upper and lower limbs).
36
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
56944 netter28 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYProprioception and Reflex Palhways: III Ib fi bers Extrafusul musde fi
netter36 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Audilory System: Pathways temporal lobe cortex Medial geniculate body High
netter40 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYGustatory (Taste) System: Pathways Sensory cortex łjust below face area) Lat
50914 netter27 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY A(3 fibers from paciniform corpuscles and Rufiini temiinalsPropr
netter14 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYSpinał Cord: Membranes and Nerve Rools Posterior view Ventral ramus ot spina
netter10 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYSynaptic Tr.insmission: Temporal and Spatial Summation C. Icmporal exritator
netter11 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYCerebrospinal Fluid (CSF): Brain Ventricles and CSF Composition Frontal (ant
netter20 NEUROPHYSIOLOGYThe Cerebral Cortex Sm!,} Spn4,,,v Sensory Promotor; orientation, eye and
netter29 Proprioceptiiid Reflex Pathways: IVNEUROPHYSIOLOGY B. Stretch refie* (reciprocal inhibition
netter30 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Sensory Pathways: I Spinothałamic iract lower part of medulla
więcej podobnych podstron