21 (956)

the relatively larger mass of the hips. In the example above, this means that dorsal flexion will be retained caudal to the treated segment. Theoretically, specific treatments, with locking both caudal and cranial to the segment treated, can be conducted by placing the entire vertebral column in dorsal flexion and lateral flexion to the right (so it locks) and inducing left lateral flexion in the treated segment. But in practice this is impossible to induce. Therefore, flexion is changed in both the frontal and the sagittal planes. In the example above, dorsal flexion is retained but lateral flexion changes from left to right to lock caudal to the segment treated, while lateral flexion to the left is retained while sagittal piane flexion changes from dorsal to ventral to lock cranial to the segment treated. As illustrated in Fig. 9, locking both caudal to and cranial to the segment treated can be achieved by changing sagittal piane flexion either caudal to or cranial to the segment treated. The choice between these two approaches is largely a matter of convenience for the therapist and for the patient.
Fig.9.Two alternative double locking methods for a typical specific treatment of lower thoracic spine; segment T11-T12 in physiological position in dorsal flexion, lateral flexion to the left and rotation to the right.
A: Segments caudal to the segment treated are in ventral flexion, lateral flexion and rotation to the left, and thus lock for rotation to the right. Segments cranial to The segment treated are in dorsal flexion, lateral flexion to the right and rotation to the left, and thus lock for rotation to the right.
B: Opposite locking alternative: Segments caudal to the segment treated in dorsal flexion, lateral flexion to the right and rotation to the left, thus locking for rotation to the right. Segments cranial to the segment treated are in ventral flexion, lateral flexion and rotation to the left, and thus lock for rotation to the right.
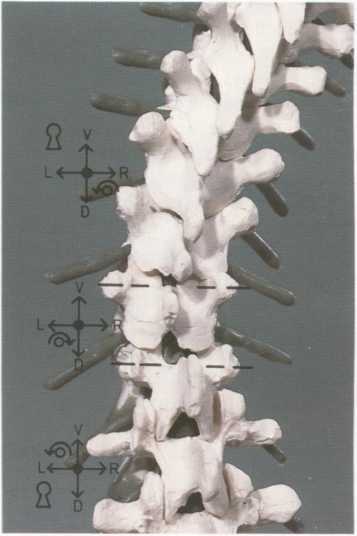
Fig. 9 a.

Fig. 9 b.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
18vcl02 A pointer to the allocated memory Each chunk that you allocate will be contiguous
11 Urszula Tyluś unconscious adverse effect of the family surroundiiig which means that the process
56 (315) 3.5.5C. Non-specific technique for the deep ventral muscles to increase dorsal flexion
57 (308) 3.5.5D. Non-specific techniąue for the deep ventral muscles to increase dorsal flexion
54 (307) 3.5.5A. Non-specific technique for the deep ventral muscles to increase dorsal flexion
55 (318) 3.5.5B. Non-specific technique for the deep ventral muscles to increase dorsal flexion
04 m HPUSBFW WARNING! AlL DATA ON THE Kingston DataTraveler 2.0 PMAP (954 MB) (P:) D£VICE WILL BE LO
36ECONOMIC JPRS-EER-91-053 25 April 1991 product per unit of power is three times higher. This means
61 Figurę 2.2 Relationship between mass and sex independent BMR and the natural rangę of minimal&nbs
step21 part 42 make surę the larger section of part 40 (the seam) is at the bottom!!
of Conscious Intention to Act in Relation to Onset of Cerebral Activity (Readiness-Potential): The U
więcej podobnych podstron