Proxy Server Status Explained
What does each proxy status mean?
There is no 100% anonymity as such on the Internet. Any proxy server by design provides some degree of cloaking. Different server types can counter specific attacks.
Alive - provides basic anonymity - your IP won't show up in default web server logs.
(Alive) - same as previous but supports SSL connections. In cases where SSL (https://) connection it will behave as an Anonymous server.
Anonymous - proxy server doesn't include your IP in the extra headers. These headers by default are not logged.
(Anonymous) - same as previous, but supports SSL connections.
Elite-Anonymous - this server doesn't send any additional headers at all. Can be countered by use of Java.
Socks v4/v5 - Same as Elite-Anonymous.
Private - server is password protected (access was denied).
How many high-anonymous and elite servers are there?
It's hard to give an exact number. For public lists, the rough estimate is that only 5-10% of alive servers are actually high anonymous. Private lists usually have more. That's why it's important for Proxy Switcher to check for actual state of the servers (registered version only).
Availability of High Anonymous & Elite servers
How many high-anonymous and elite servers are there?
It's hard to give an exact number. For public lists, the rough estimate is that only 5-10% of alive servers are actually high anonymous. Private lists usually have more. That's why it's important for Proxy Switcher to check for actual state of the servers (registered version only).
Configuring
Mozilla Firefox for increased privacy:
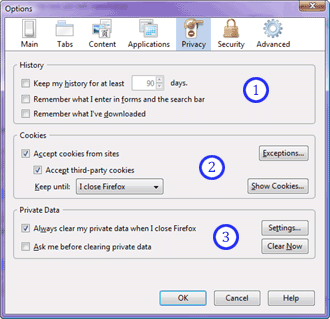
Privacy Settings
Table of contents:
Summary:
This
article describes what private information Mozilla Firefox stores on
your system and how to reconfigure it to reduce it's amount.
While
using a proxy server will give you a certain level of protection
aginst the detection of your IP address, the browser will store
plenty of information about sites you visit. Although Firefox has
built-in feature to clear history and temporary files, but that might
not be enough to really clear it.
The reason is that it's pretty hard toactually
remove any
files from the Windows file systems. There are a lot of forensic
tools that can restore deleted files or even restore whole drive
contents even after drive format. So the question is, what to do. The
answer is a preventive measure are more effective than trying to
remove data that's already written to the disk. One of preventive
measures is to configure browser to not store any private data
(history, passwords, cache, etc.) in the first place. Since if no
data is actually stored it's not needed to delete it. While this
maybe sometimes might be inconvenient it's usually not a big
issue.
As
a target browser we will be using Mozilla Firefox 3. There
are following components that need the reconfiguration:
First
thing that has to be corrected is Firefox browsing history settings.
These settings are located in the Privacy tabsheet of the
Tools->Options... menu. You need to uncheck boxes that enable
logging of browsing history and user entered strings.
The
obvious dangers of the stored browsing history is that the
address of each and every web page you have visited is
recorded.
Of course there are plenty of forensic tools that will extract and
trace all the sites you have visited.
Cookies
are used by websites to store little data snippets in your browser.
Almost all the sites leave some kind of cookie in your browser.
Luckily Firefox has an option to remove cookies when it's exited.
Altho it's possible to not accept cookies at all, but that often can
cause problems since some sites actually need to have cookies enabled
to for navigation to work.
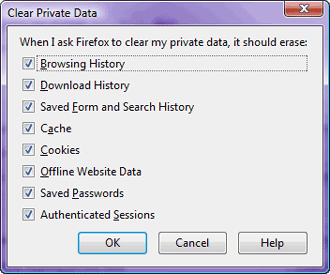 The
dangers of cookies are that each of them contains a record of the web
site's address it was sent from. So it works as an evidence that a
particular web site was visited. To see currently stored cookies you
can click the "Show Cookies..." button. It's a very good
idea to get rid of them as soon as possible.
The
dangers of cookies are that each of them contains a record of the web
site's address it was sent from. So it works as an evidence that a
particular web site was visited. To see currently stored cookies you
can click the "Show Cookies..." button. It's a very good
idea to get rid of them as soon as possible.
Firefox
has a built-in private data cleaning utility. It can clean up any
remaining traces of data (which should small to non-existant). The
best option is to enable it to clear data whenever you close the
brower. This way you can be fairly certain not to forget to run it.
Only problem is that if you crash or power down without proper
shutdown this procedure won't be executed, so keep that in mind.
If
you click the "Settings..." button you can see what private
data can be removed. Also check that all the options in this
window are enabled.
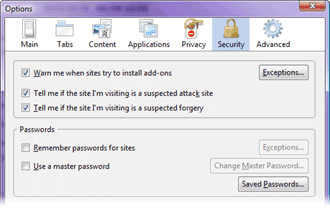 Saved
passwords are a particularly dangerous feature. Only recently Firefox
started use of encrypted saved passwords. The ramifications for the
stolen saved passwords are immense. There have been numerous
reports of passwords stolen from
compromised machines (say good-bye to your Paypal account
for example). The best way is not to save passwords in the browser.
If youreally need
to save passwords, consider using some good 3rd-party utility
designed exactly for a safe password storage.
Saved
passwords are a particularly dangerous feature. Only recently Firefox
started use of encrypted saved passwords. The ramifications for the
stolen saved passwords are immense. There have been numerous
reports of passwords stolen from
compromised machines (say good-bye to your Paypal account
for example). The best way is not to save passwords in the browser.
If youreally need
to save passwords, consider using some good 3rd-party utility
designed exactly for a safe password storage.
N.B. If you fill the login form on some website by default Firefox will ask you - "Do you want to save password for this site?" - in case you answer "not for this site" - it's name will end up inside Firefox's exception list which is readable to anyone. Same goes for all the exceptions lists in the browser! So you need to answer "No" in such cases.
Table of contents:
Caching
in FireFox consists of online and offline content caching. To disable
caching and thus reduce the amount of private information stored we
need to reconfigure following things:
Firefox internal settings - about:config
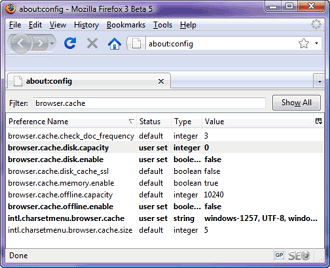 Some
of the browser's settings aren't directly accessible from the options
window. What we want to change is the browser's content caching
settings. To access them you need to type "about:config"
in the address bar. This will load up list of Firefox internal
settings. Next to filter out interesting settings, write
"browser.cache"
into the filter edit box.
Some
of the browser's settings aren't directly accessible from the options
window. What we want to change is the browser's content caching
settings. To access them you need to type "about:config"
in the address bar. This will load up list of Firefox internal
settings. Next to filter out interesting settings, write
"browser.cache"
into the filter edit box.
Settings of particular interest
arebrowser.cache.disk.enable,
browser.cache.disk.capacityand browser.cache.offline.enable.
Set disk cache and offline cache enabled flags to false and the
capacity to zero.
The risks of caching on disk are obvious
- content of the pages you load are stored on your disk ready for
somebody else to view and analyze.
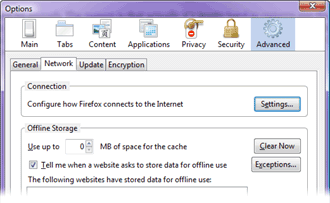 This
is a fairly new feature that some websites use to try to store data
for offline use. They usually store code and documents so they
could be used when Firefox is switched to "Work
offline"
mode. As any cache it can contain sensitive information that you
might not want to see recovered. So uness you got an appication you
really want to use with this particular feature it's a good idea to
disable this as well.
This
is a fairly new feature that some websites use to try to store data
for offline use. They usually store code and documents so they
could be used when Firefox is switched to "Work
offline"
mode. As any cache it can contain sensitive information that you
might not want to see recovered. So uness you got an appication you
really want to use with this particular feature it's a good idea to
disable this as well.
For the sake of completness I'll mention bookmarks. It's simple - if you bookmark some page, that bookmark can be viewed by anybody else that has access to your computer. Athough you have to keep in mind that some sites can forcefully add bookmarks. So keep your eyes open and naturally don't add sites to bookmarks you don't want to be traced to.
Table of contents:
Mozilla
Firefox is a very modular browser it support active content like Java
and Javascript, ActiveX, 3rd party extensions and plugins. This gives
a lot of flexibility, but at the same time increases risks of losing
your privacy. Here we'll cover configuration options which help to
reduce this risk.
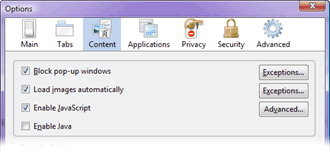 Java
and Javascript are languages fairly often used in the web
environment. The trouble with them is that they can easily be used to
obtain your personal or private data and send it back to the
website.
Java
and Javascript are languages fairly often used in the web
environment. The trouble with them is that they can easily be used to
obtain your personal or private data and send it back to the
website.
Usually you can disable Java, for the most of the
time, since there aren't a lot of sites that require it. Javascript
is more problematic since a lot of sites use it for navigation and
other things.
Obiously the safest way would be to disable
both, but that will cause problems with browsing. So one of the
reasonable options is to leave Javascript enabled and
use NoScript extension
for Firefox (available at the Mozilla plugin's site).
 ActiveX
plugins (for an example adobe flash player, windows media video (wmv)
player and others) are actually full fledged programs, they can
potentially do anything they want with your computer. There are even
reports of some Firefox extensions being used as a deployment for a
trojan programs. The safest way would be to disable all of them
completely. Sadly, yet again, this might not be an option. So the
reasonable solution is toonly
allow the plugins you trust and really need.
ActiveX
plugins (for an example adobe flash player, windows media video (wmv)
player and others) are actually full fledged programs, they can
potentially do anything they want with your computer. There are even
reports of some Firefox extensions being used as a deployment for a
trojan programs. The safest way would be to disable all of them
completely. Sadly, yet again, this might not be an option. So the
reasonable solution is toonly
allow the plugins you trust and really need.
As
a personal opinion I suggest to disable flash plugins, they might be
pretty, but the problem is there were multiple exploits found in the
flash player. Which would mean that in case your system is unpatched,
or there is an unknown vulnerability a simple flash banner could
potentially compromise your whole system.
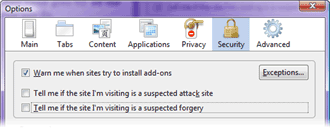 While
the idea that browser checks site against online blacklists
in-general is good and welcome addition. The problem is that to
do so browser needs to submit the page address you are viewing to the
checker's site (hopefully nothing else). Which is counterproductive
if you want extra privacy. So it's a risk vs risk, it's up to you to
choose which you want - disable suspected
attack siteand suspected
forgery site
checks or not.
While
the idea that browser checks site against online blacklists
in-general is good and welcome addition. The problem is that to
do so browser needs to submit the page address you are viewing to the
checker's site (hopefully nothing else). Which is counterproductive
if you want extra privacy. So it's a risk vs risk, it's up to you to
choose which you want - disable suspected
attack siteand suspected
forgery site
checks or not.
Lets take a look at probably the most popular toolbar. While the Google toolbar itself is fairly harmless, the problem with it is that it submits the site addresses you visit to the Google. They are supposedly using them to find new pages to index. But objectively that is a pretty large security problem. So it's better to disable it if you have it installed.
While Firefox has a marvelous extensions out there you have keep in mind additional risks associated with their usage. Main privacy problems with addons are:
Might be storing your browsing history.
In severe cases might be leaking it to some 3rd party.
Installations might be purposely infected by viruses or trojan programs - consider using only signed extensions.
Particular addons are sending information to 3rd party sites.
Some examples - if you use popular AdBlock Plus program and manually add some extra blocks then their addresses will be stored inside browser and might be an unpleasant surprise later.
It is possible to reconfigure Firefox in a such way it leaves fairly minimal browsing traces on the user's system. The problem with it is that a browser configured in a such way is not very user friendly. Only solution to this in, my opinion, is to use two browsers - one configured in a secure manner, other one unsecure. So then by default you use the secure one, while switching to unsecure one for sites that refuse to work otherwise.
ProxySwitcher's
proxy scanner:
Maximizing Scanning Speed
|
Disclaimer of responsibility - since this article involves changing of internal behaviour of the Windows operating system author cannot take any responsibility for the results these actions might cause. Proceed at your own risk.
Currently this article applies to following operating systems: Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 2 Microsoft Windows XP Service Pack 3 Microsoft Windows Vista Microsoft Windows Vista Service Pack 1
How Proxy Switcher operates Now
on to understanding what Proxy Switcher does to find
working/anonymous/elite servers. First thing that gets done is
fetching list of web site addresses that contain public
proxy lists. Then this list is used to download and parse actual
proxy lists from all the listed web servers. Now comes in the
actual scanning - Proxy Switcher has to go over all the
proxy addresses that were retrieved and actually try to use
them to determine are they any good. Removing speed limit Code that controls the connection speed is hidden inside driver named tcpip.sys. The only way to disable these limitations is to patch this annoying driver. 32 bit Windows
Windows Vista x64 If
you are using Windows Vista x64 SP2 then there is no need to
change anything - limitation has been removed by Microsoft itself.
As for pre-SP2 this is hardest of all, since Microsoft has made it
mandatory for all the drivers to be signed to be loaded. So best
solution is to install service pack 2 or newer. However if that is
not possible there is a way to patch the driver. This must be done
in two steps - first need to to disable driver signature checking,
then to actually patch the tcpip.sys driver.
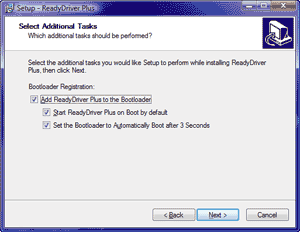
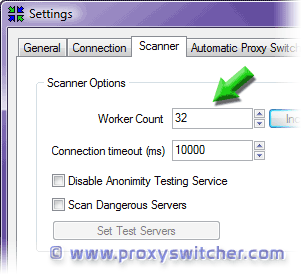
Disabling signature checking Currently (SP1) the only legitimate way to disable driver signature checking is to select "Disable driver signature checking" option each time Windows is booted. Clearly that is far from being convenient. This problem is solved by theSetupReadyDriverPlus utility - it automates selection of this option. Patching tcpip.sys Then we can proceed to patching tcpip.sys driver. This can be done by applying search for version specific patches. So the best solution is to install SP2 or later service pack. Changing Scanner Options
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Anonymous Browsing Using Socks servers
What are Socks servers
Socket servers work at lower level (socket level) compared to HTTP servers. In case of HTTP proxy browser pretty much tells it - "Hey, go fetch that page for me!". As in case of socks servers - it can ask only to establish a connection to some server, rest is done by the browser (or in this case by Proxy Switcher).
There are certain benefits to using socks servers:
Socks usually works faster than HTTP proxy servers.
Socks servers inherently qualify as Elite-SSL.
Socks & Proxy Switcher Pro
Proxy Switcher PRO version since release 5.0.0 supports socks servers. If you switch to socks server Proxy Switcher will emulate it as HTTP proxy server. So it will work same way as you use regular HTTP servers.
Internet Explorer and socks servers
Here is an observation I made. Internet Explorer doesn't seem to play nice with socks servers. The issue is it says proxy is unreachable most of the time. Looks like problem is that IE is made to work with servers with very low latency (that are on LAN). So you make sure your Proxy Switcher has preferences Internet Explorer Control set to auto.
Wrap-up
Things required to use socks servers through Proxy Switcher:
Registered version of Proxy Switcher Pro version 5.0.0 or newer
If you have had version older than 5.0.0 installed on your machine: check that Internet Explorer Control in preferences is set to auto
That's it - use them same way as regular servers
How to force programs to use Proxy Switcher.
At the moment this article applies only to 32 bit programs (it does work under x64 OS). For it to work you need Proxy Switcher Pro version 5.3.0 or newer.
There are programs that simply do not know how to use proxy servers. As an example here will look at SEO keyword software. Issue is that if you use it - quite soon google will block your IP for issuing too many queries over a period of time. Usual solution would be to set program to use Proxy Switcher's internal proxy server and set Proxy Switcher to auto switch between proxy servers. Solution is to trick the program into using a proxy server
Configuring Proxy Switcher
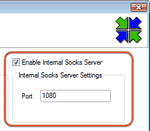 Go
into View->Preferences... click
on Internal
Proxy and
verify that internal socks server is enabled. Click OK to close the
window. If there are no issues (like some other program that has
taken the port already) that's all that's required.
Go
into View->Preferences... click
on Internal
Proxy and
verify that internal socks server is enabled. Click OK to close the
window. If there are no issues (like some other program that has
taken the port already) that's all that's required.
Tricking a program to use Proxy Switcher
To
do this we need a help of additional piece of software that will work
as a loader for the target program. It will intercept TCP/IP requests
and forward them into Proxy Switcher which will route them where you
desire. At the moment
 this
likely will not work for the UDP requests, so don't bet on all games
working via this.
this
likely will not work for the UDP requests, so don't bet on all games
working via this.
The loader software I used is Freecap,
it is a free clone of the more popular sockscap software. Download
links are at the end of the article. I used the "no
installation" version - unzipped it in separate folder and run
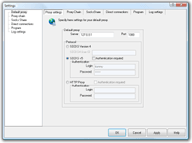
freecap.exe file. So I did following, first went
into File->Settings and
configured proxy settings in following manner: Default
proxy server: 127.0.0.1 port 1080 Protocol SOCKS v5, no
authentication required.
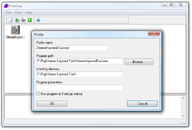
Next
step is to add our target application. Go to File->New
Application click
Browse button and find the target application. In this case I used
Xtreme Keyword Tool v 2.0. Other fields will get filled automatically
- click on picture to the right. Click OK to close the window. After
which double clicking the icon that was created will start the target
program with redirection of it's requests to Proxy Switcher.
Download links
I have mirrored binary and source files on my server:
Standalone
freecap 3.18 (.zip no installer)
Freecap
3.18 installer (.exe)
Source
code of freecap 3.18
Stop Group Policy from overriding your proxy settings.
Group Policy & Proxy settings.
At the moment this does not work with Windows 8 and thus is disabled starting from version 5.3.2 of the Proxy Switcher. In fact running earlier versions with Windows 8 will cause trouble.
If
your machine is a member of domain, then it could be that every 5 to
90 minutes your proxy settings get changed. It happens if domain
controller pushes out group policy settings. But there is a way avoid
such annoying behavior.
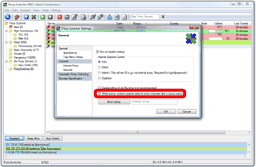
Proxy Switcher can stop proxy changes by group policy settings.
Solution is to go to View->Preferences... from main menu. Then inGeneral tab make sure the checkbox While active, protect against external proxy changes (like a group policy).
How does it work
If you are interested - this is how it works: when GPO is refreshed Windows writes updated proxy settings into registry. Thus the proxy settings get changed. What Proxy Switcher does is goes into registry and keep proxy settings as read-only, for most of the time, to prevent group policy settings from being applied to proxy settings.
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
INSTRUKTAŻ OGÓLNY(1)
wykład 6 instrukcje i informacje zwrotne
Instrumenty rynku kapitałowego VIII
05 Instrukcje warunkoweid 5533 ppt
Instrukcja Konwojowa
instrukta stanowiskowy 3
Instruktaz dla BHP pracownika
2 Instrumenty marketingu mix
Promocja jako instrument marketingowy 1
Instruktaż stanowiskowy 5
Promocja jako instrument marketingowy
Instrumenty muzyczne
Instrukta stanowiskowy
Metodyka Instruktażu stanowiskowego
Instrukcja do zad proj 13 Uklad sterowania schodow ruchom
Instrukca 6 2
instrukcja bhp przy magazynowaniu i stosowaniu chloru w oczyszczalni sciekow i stacji uzdatniania wo
Piec LSL UB Instrukcja obsługi
Budzik Versa wielkość karty kredytowej instrukcja EN
więcej podobnych podstron