1
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
Measure mass of molecule
How?
2
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
Measure the degree of deflection
Light molecule
Large deflection
Heavy molecule
Small deflection
Measure mass of molecule
3
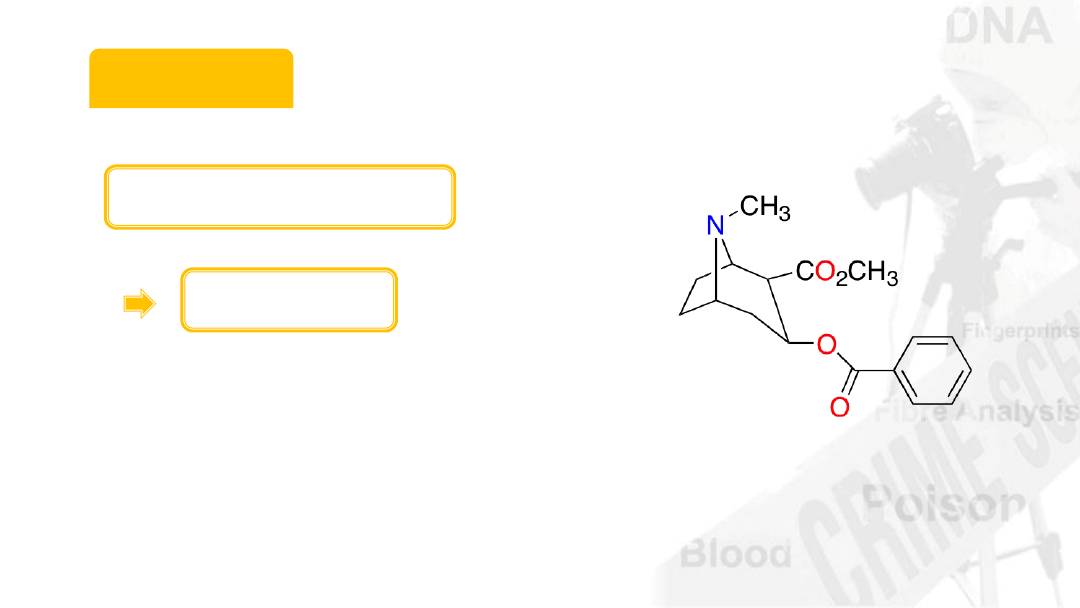
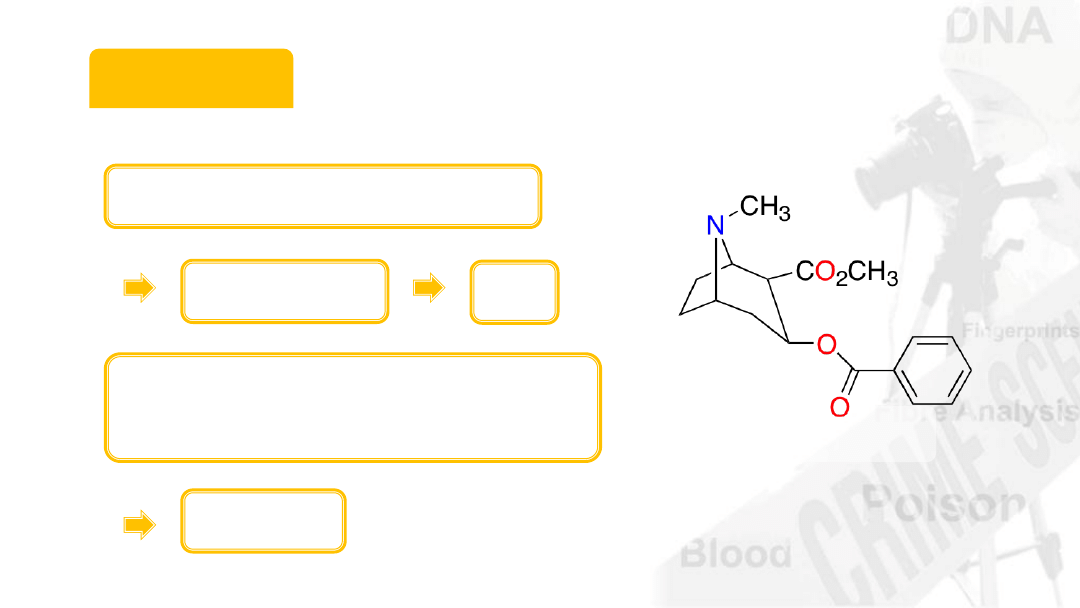
Cocaine
Molecular formula
C
17
H
21
NO
4
4
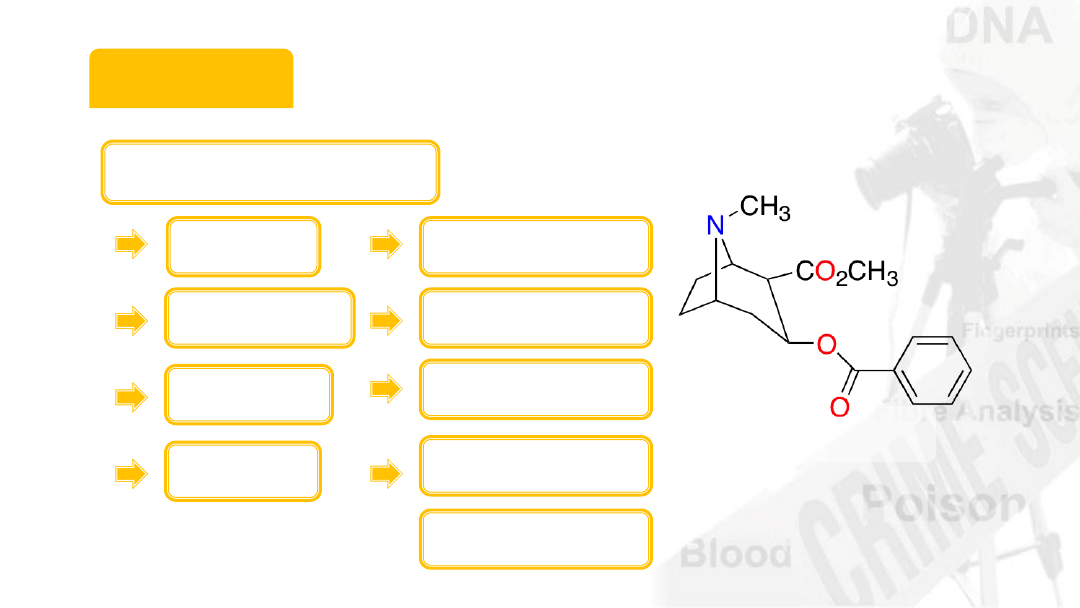
Cocaine
Molecular weight
12 x 17 = 204
1 x 21 = 21
14 x 1 = 14
16 x 4 = 64
Total = 303
Carbon
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Oxygen
C
17
H
21
NO
4
5
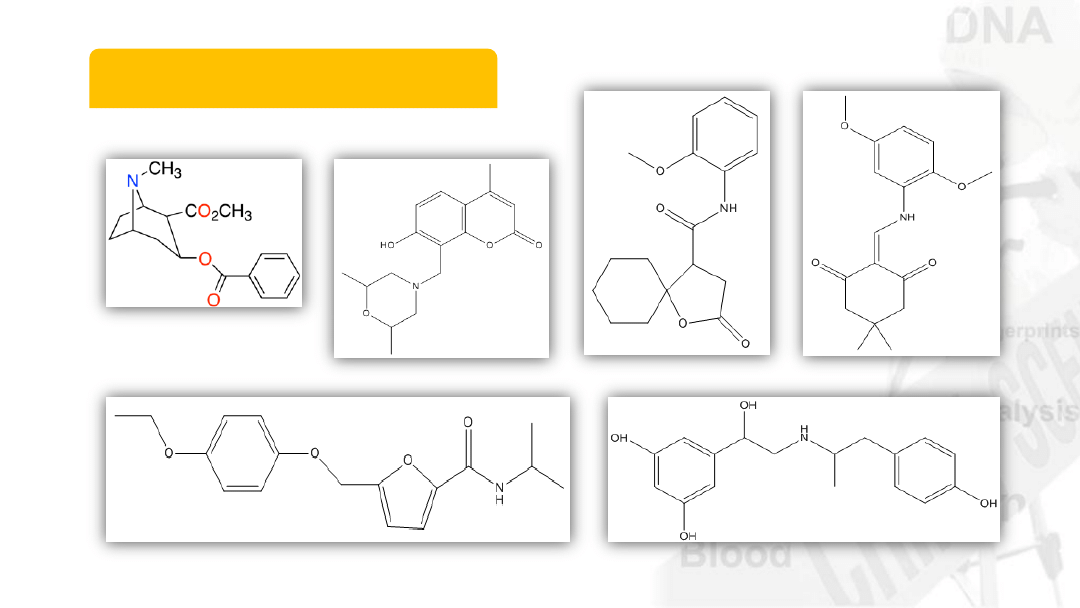
Cocaine
Molecular weight = 303
Cocaine?
No
C
17
H
21
NO
4
Isomers
Same atoms can be
arranged in different ways
6
C
17
H
21
NO
4
Isomers
Cocaine

7
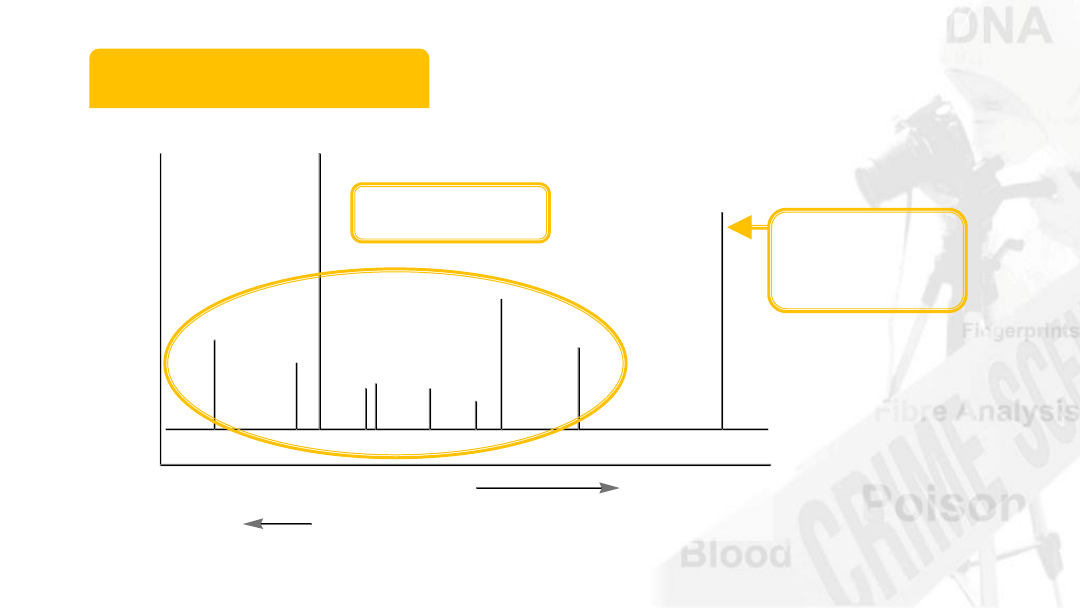
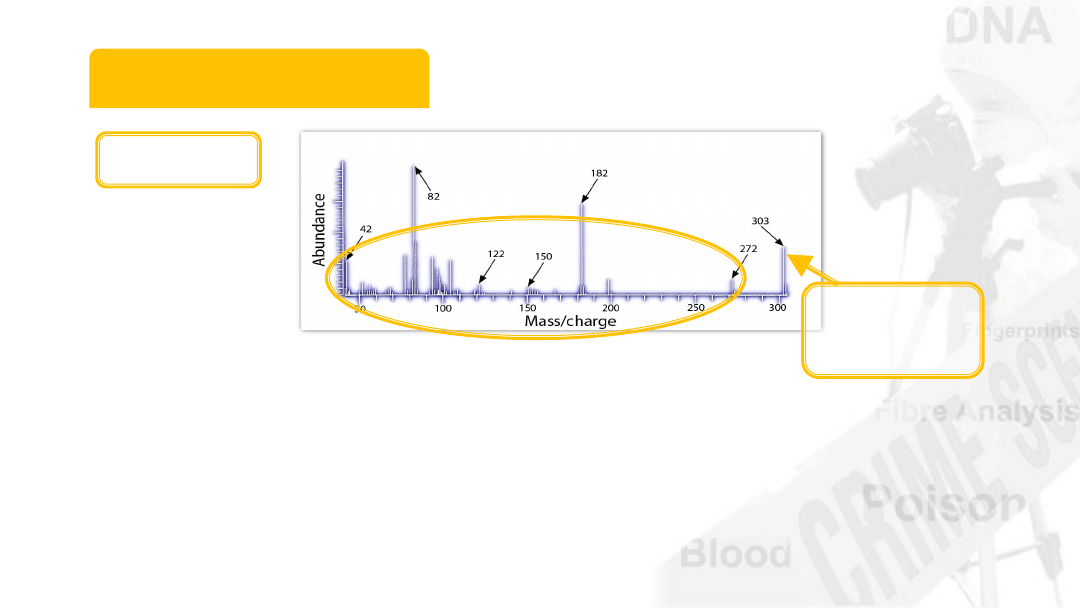
Mass Spectrum
Pattern of fragments at detector
8
Mass Spectrum
mass
amount of deflection
Molecular
ion (M
+
)
Fragments
9
Mass Spectrum
Highest weight
Lower weights
Always the same pattern
Pattern of fragments at detector
Molecular ion
Fragment ions
10
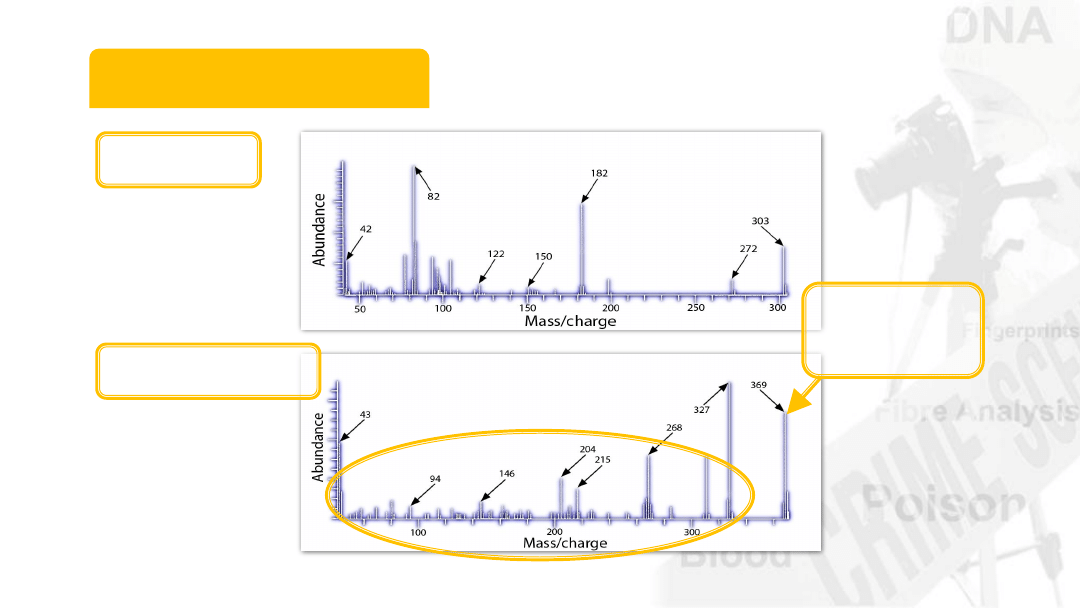
Mass Spectrum
Same
Cocaine?
Authentic sample of cocaine
Compare the 2 fragmentation patterns
Cocaine
11
Mass Spectrum
Molecular
ion (M
+
)
Cocaine
12
Mass Spectrum
Cocaine
Diamorphine
Molecular
ion (M
+
)
13
Techniques
Chromatography
Separation of mixtures
1
Spectroscopy and spectrometry
Identification of components
2

14
Techniques
Combining separation and identification
Gas chromatography -
Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
Hyphenated technique
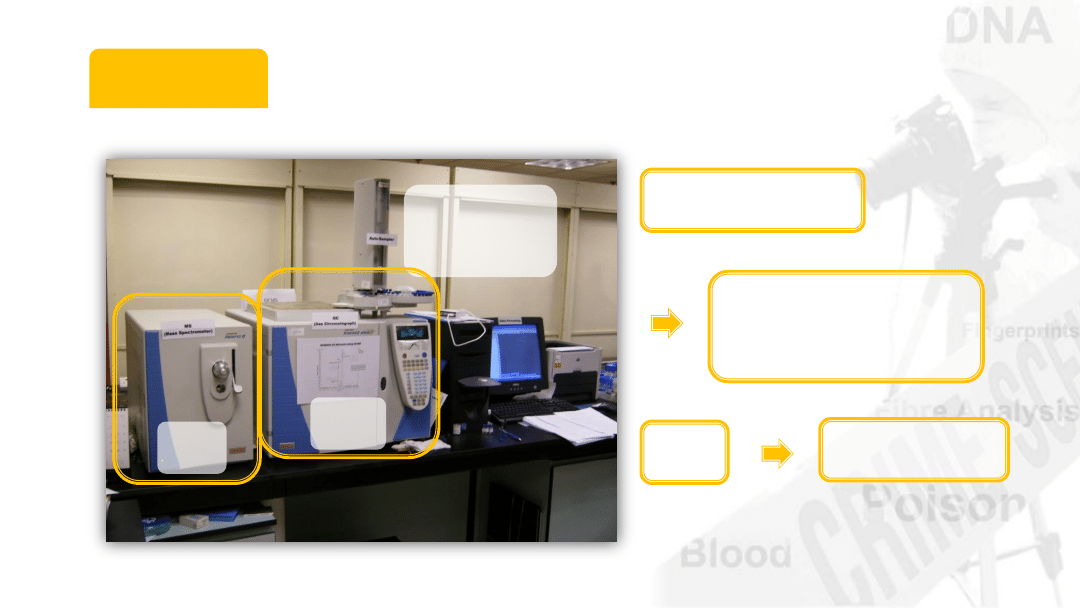
15
GC-MS
GC output
Auto-
sampler
Goes to mass
spectrometer
MS
Detector
MS
GC
16
GC-MS
GC output
Retention time of components
MS output
Identification
Quantify amount
Combines separation and identification
17
Summary
Chromatography
Separation of mixtures
1
TLC, GC and HPLC
18
Summary
Infrared spectroscopy
Identification by molecular vibrations
2
Molecular stretching and bending
Chromatography
1
19
Summary
Mass spectrometry
Identification by fragmentation
3
Infrared spectroscopy
2
Chromatography
1
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Electron ionization time of flight mass spectrometry historical review and current applications
Mass spectroscopy overview
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectroscopy in food aplication
2B 3 Infrared Spectroscopy
Szewczyk, Rafał i inni Rapid method for Mycobacterium tuberculosis identification using electrospra
Amstrad Sinclair Spectrum 2B 3B service manual
2b ANALIZA RYNKU
ćw 2b
BIOCHEMICZNE EFEKTY STRESU (2B)
2b Dieta w ciąży i przed poczęciem
R 4 2b mp
019 Masowe środki przekazu mass media
więcej podobnych podstron