Y(s)
Y(s)
X(s)
G
2
(s)
G
1
(s)
G
1
(s)G
2
(s)
G
2
(s)
G
1
(s)
G
2
(s)
G
1
(s) G
2
(s)
1 G
1
(s)G
2
(s)
G
1
(s)
X(s)
Y(s)
X(s)
Y(s)
X(s)
Y(s)
X(s)
Y(s)
G
1
(s)
X(s)
Y
1
(s)
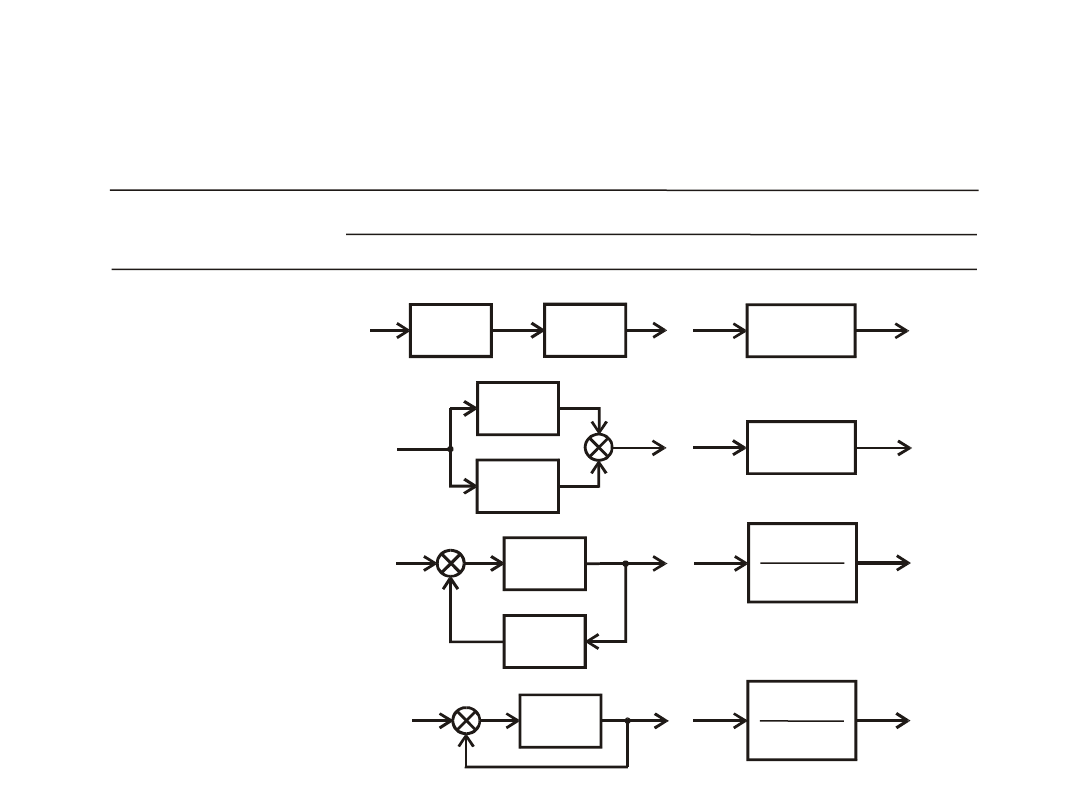
Table 3.1
Equivalent systems
Transformation
type
before transformation
after transformation
1.
Series
connection
2.
Parallel
connection
3.
Connection with
feedback
4.
Elementary
negative
feedback
X(s)
Y(s)
X(s)
Y(s)
G(s)
1 + G(s)
G(s)
Block diagrams transformation principles - table
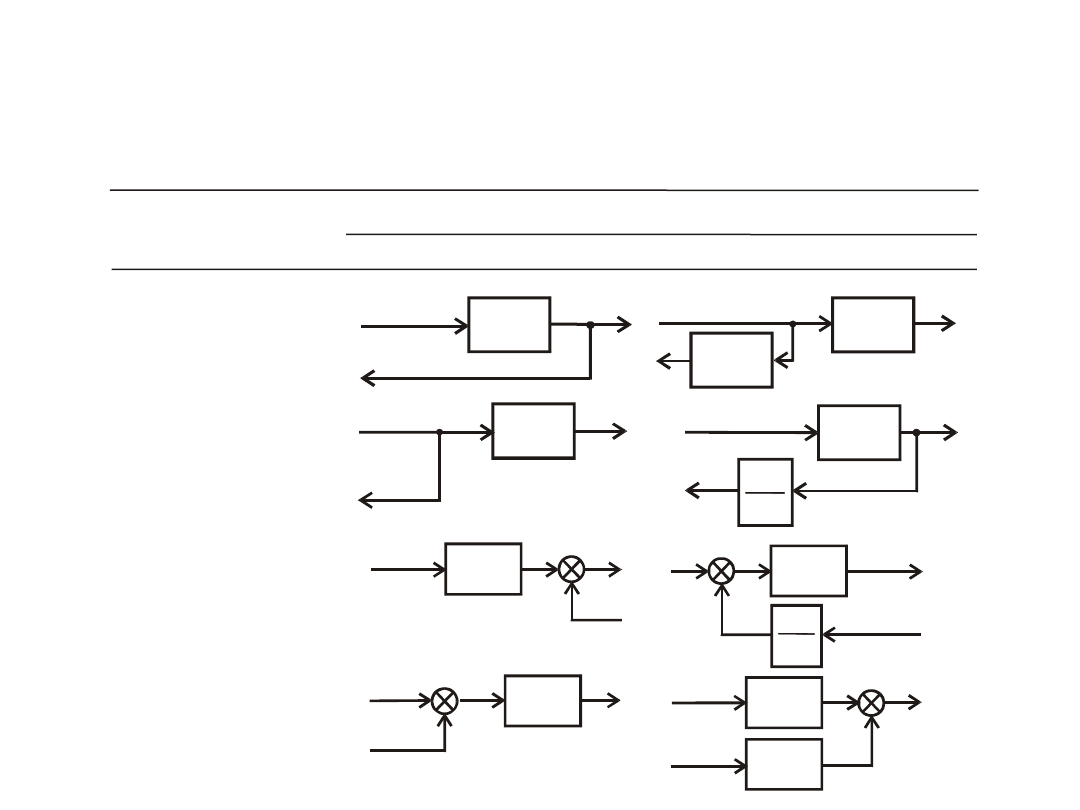
Table 3.1
Equivalent systems
Transformation
type
before transformation
after transformation
X(s)
Y(s)
G(s)
Y(s)
X(s)
X(s)
G(s)
Y(s)
G(s)
Y(s)
G(s)
Y(s)
G(s)
Y(s)
1
G(s)
Y(s)
X(s)
X
1
(s)
X
2
(s)
Y(s)
G(s)
G(s)
X
1
(s)
Y(s)
X
2
(s)
Y(s)
G(s)
G(s)
X
1
(s)
X
2
(s)
Y(s)
G(s)
X
1
(s)
X
2
(s)
6.
Replacing of
connection node after
the element
7.
Replacing of
summation node in
front of element
8.
Replacing of
summation node after
the element
5.
Replacing of
connection node in
front of element
1
G(s)
X(s)
Block diagrams transformation principles - table
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Przekształcenia schematów blokowych
przekształcanie schematów blokowych 1
Przekształcanie schematów blokowych
Przekształcanie schematów blokowych
5 Algorytmy i schematy blokowe
3 Projektowanie układów automatyki (schematy blokowe, charakterystyki)
10 schematy blokowe i grafy (jako zobrazowanie modeli matematycznych)
Schemat blokowy For 1
Schemat blokowy Do While 2
SCHEMAT BLOKOWY
SCHEMAT BLOKOWY RADARU
Algebra schematów blokowych c d
Schemat blokowy If 1
Schemat blokowy For 3
SCHEMATY BLOKOWE ODBIORNIKÓW
06-10, schematy-blokowe
Schemat blokowy While 3
więcej podobnych podstron