Performance Management and
Suppliers
What are
the right
targets?
What are the
strengths/weaknesses?
What does the
order cost?
What do we
have to
concentrate
on?
In which points are
we better/worse than
our competitors?
Why do we
have quality
problems?
What can be
outsourced?
Why
doesn’t it
go faster?
2

Supplier Management
Managing a supplier means:
• Selection
• Development
• Performance
• Retention
3

Outsourcing as a Form of Selection
• Strategic reasons
– improve business focus
– gain access to world-class capabilities
– accelerate re-engineering benefits
– share risks
– free resources for other purposes
• Tactical reasons
– reduces or controls operating costs
– makes capital funds available and provides cash infusion
– compensates for lack of internal resources
– improves management of difficult/out-of-control processes
• Empirical evidence
4
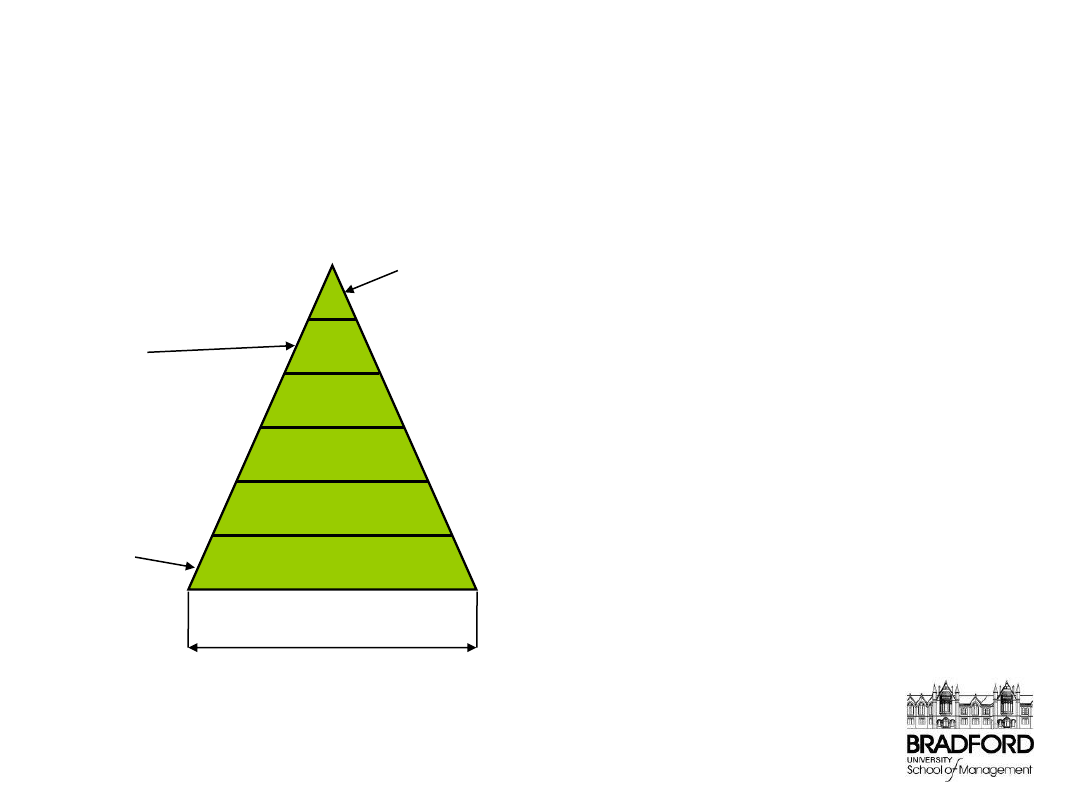
Industry level changes
•
Japanese companies
–
high proportion of outsourced products
–
multiple layered supplier pyramid
•
Pyramid structures
–
stable but agile
–
flexible
–
innovative
–
efficient in cost and administration
•
Adoption of JIT techniques
–
drastically reduces inventory
–
increases vulnerability to uncertainty
–
increases dependence on supplier quality
•
Time and product variety
–
simultaneous engineering & product development teams
–
increased outsourcing - PDT members include suppliers
–
product design reflects suppliers capabilities
Finished
product
First tier
supplier
Last tier
supplier
Number of units supplied
5
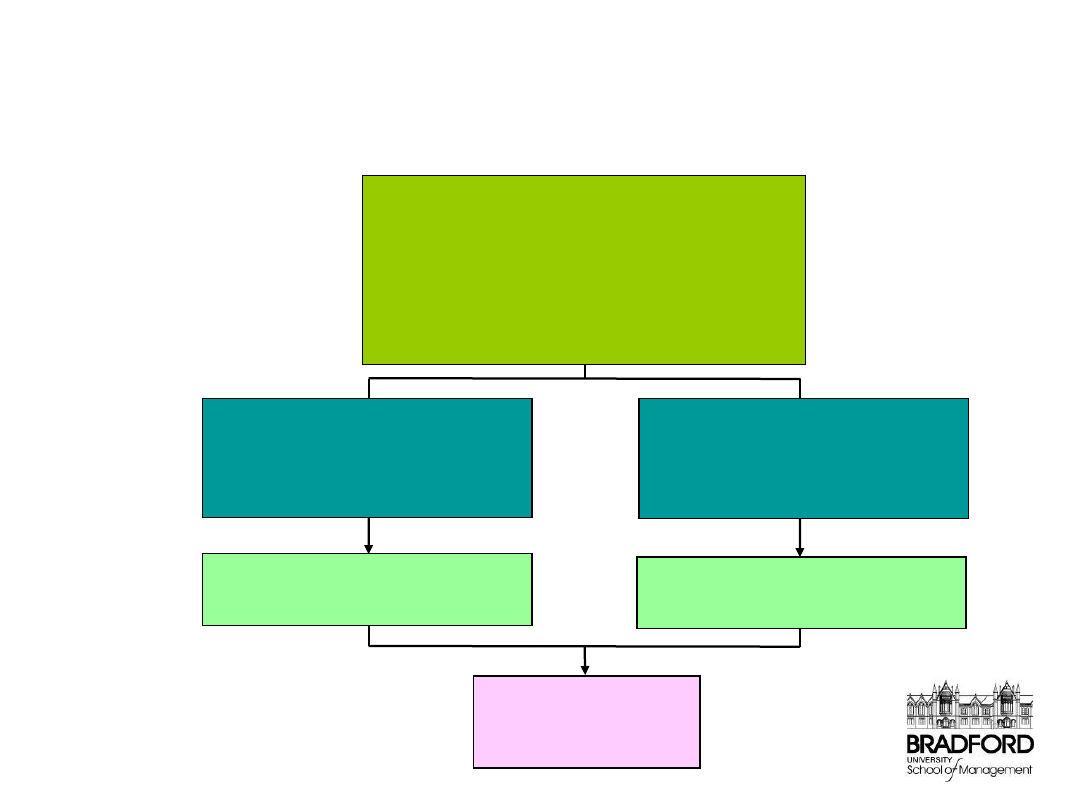
Company level changes
Multiple Criteria
•
low cost
•
high quality
•
high flexibility (volume, product variations)
•
high service
•
continues improvement and innovation
System Sourcing
•
increased value of purchase
•
reduced number of vendors
•
tiered structure of supply-chain
Collaborative Programs
•
product design and development
•
quality upgrades
•
continuous improvements
Increased value of purchase
per vendor
Long-term relationship with
vendor
Benefits due to:
•
economies of scale
•
learning curve
6
7
Strategic Importance & Criticality matrix
• Strategic value of part
– value of part in isolation in
market
– technological complexity,
proprietary nature of
technology, fit with PLC
• Criticality of part to assembly
– contribution to functional
performance of final
assembly
– % value of part to final
product, extent to which
quality/reliability of final
product depends on part
Novelty
(outsource or
in-house)
Proprietary
(in-house)
Commodity
(outsource)
Utility
(outsource)
High
High
Low
Low
Criticality of part
Strategic
value of
part
9
Supplier Selection Criteria Can Change
• Novelty
– functionality, quality, service
• Commodity
– price
• Utility
– Cooperation, service
Novelty
(outsource or
in-house)
Proprietary
(in-house)
Commodity
(outsource)
Utility
(outsource)
High
High
Low
Low
Criticality of part
Strategic
value of
part
Do
Nothing
Do
Everything
The character of internal operations activity
Virtual
Spot
Trading
Traditional
Market
Supply
Resource Scope
Long-term
Virtual
Operation
‘Partnership’
Supply
Relationships
Vertical
Integration
T
y
pe
of
int
er
-firm
con
tact
T
ran
sacti
o
n
a
l
–
M
an
y
su
p
p
li
ers
C
lo
se
–
F
ew
su
p
p
li
er
s
Slack and Lewis (2002)
Types of supply relationships
10
11
Purchase portfolio analysis
Supplier market index
(number of available suppliers)
Company index
(buyer strength)
1
11
6
0
100
1
10
0.1
Bottleneck
items
Strategic
items
Non-critical
items
Leverage
items
Company index =
% supplier’s total sales
% buyer’s total purchase
Syson’s (1992) model (See Harrison & van Hoek, 2004)
Low
High
Cost of changing suppliers
When are pure market mechanisms appropriate?
Market
mechanisms
inappropriate
Resource Dimension
Market
mechanisms
appropriate
Leverage
needs
uncertainty
Leverage
market
uncertainty
Num
ber
of
sup
ply
alternati
v
es
Few
Many
Slack and Lewis (2002)
12
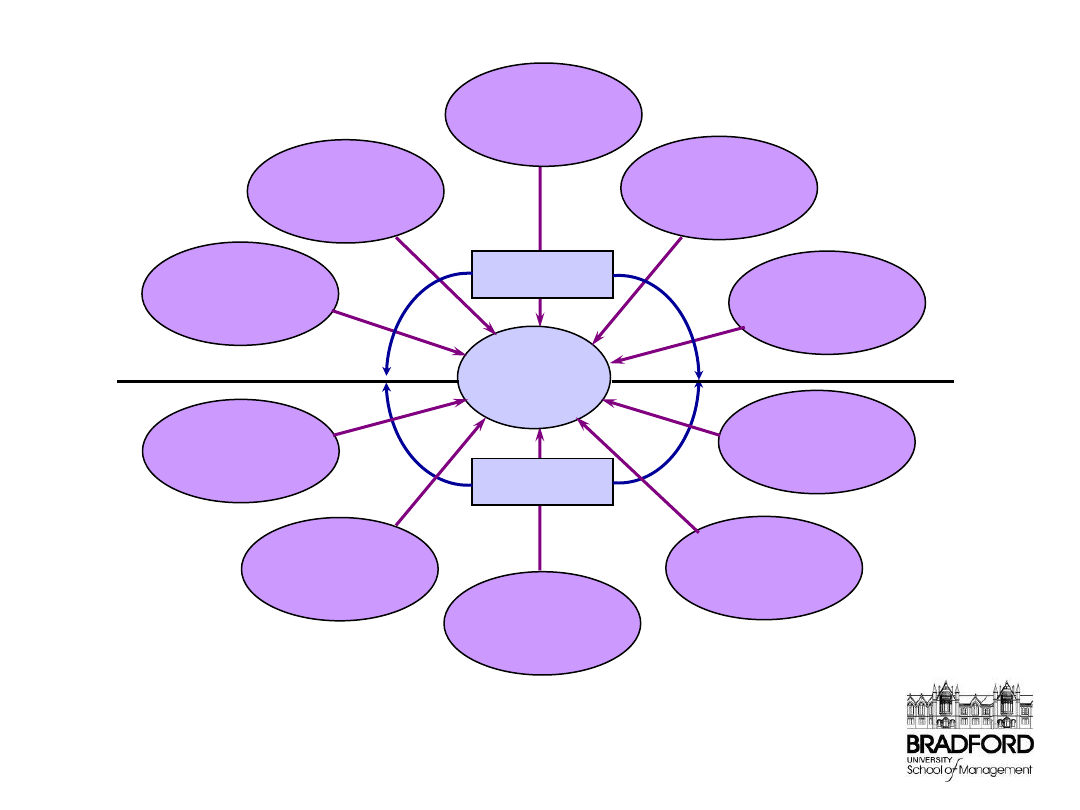
Joint
learning
Joint co-
ordination of
activities
Multiple
points of
contact
Trust
Sharing
success
Few
relationships
Information
transparency
Dedicated
assets
Joint
problem
solving
Long-term
expectations
Attitudes
Actions
Closeness of
relationship
Elements of partnership relationships
Slack and Lewis (2002)
13

Degrees of Trust
Slack and Lewis (2002)
14
…trusting you is likely to
give me more benefits
than not trusting you...
…I believe I can trust you
because I think I know
you enough to be
confident you will behave
as I would wish...
…I trust you because I
know that you know that I
wouldn’t let you down and
you know that I know that
you wouldn’t either......
Calculative
trust
Cognitive
trust
Bonding
trust
Based on
knowledge
Based on
feelings
T
ime
Cumulativ
e
po
sitiv
e
ex
perie
nce
s

Key issues in Relationship
Development
• Economic consequences need evaluating
• Supplier relationships differ
• The level of involvement needs managing
• Supplier-buyer interface points must be
identified
• Interdependency must be handled
• Suppliers need motivating
Finally……Contracts must be specified
15

16
Strategic Business Implications
• Buy decisions cannot always be reversed
– reacquiring competences
• Division of labour applies to both supplier and buyer
– effectiveness of process design
• Core competences can be difficult to identify
– competences change with time
• Outsourcing decisions change control boundaries
– access and control of critical resources
• Specialisation affects depth and scope of knowledge
– supplier buyer interaction influences evolution
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Lecture 2 Customer Relationship Management
Lecture 3 Employee Relationship Management v2
CRM - customer relationship management, CRM, czyli skrót od Customer Relationship Management, to okr
McGraw Hill Briefcase Books Customer Relationship Management
Lecture 1 Business Performance Management
Customers Relationship Management
Customer Relationship Management
Advertising, Marketing, Promotions, Public Relations, and Sales Managers
Norbury General relativity and cosmology for undergraduates (Wisconsin lecture notes, 1997)(116s)
(IV)Relative therapeutic efficacy of the Williams and McKenzie protocols in back pain management
Lecture 12 Where Next for Performance Management
Lecture 10 Frameworks for Quality Performance Management
Gardner Differential geometry and relativity (lecture notes, web draft, 2004) (198s) PGr
The Gospel of St John in Relation to the Other Gospels esp that of St Luke A Course of Fourteen Lec
IR Lecture1
uml LECTURE
więcej podobnych podstron
