
Employee Management
Managing an employee means:
• Recruitment
• Performance
• Development
• Retention

Competencies and Performance
• “Distinctive Competencies are sets of unique capabilities and values
possessed by certain organisations
.”
Selznick, 1949
• “Distinctive Competencies .... each organisation should identify and
exploit those resources, skills and organisation characteristics that
give it a comparative advantage over its competitors
.”
Hayes and
Wheelwright 1979
Once an organisation knows what these are and harnesses them, it
begins to measure them. Yet:
“As soon as an performance measures are used as a means of control,
the people being measured begin to manage the measures rather than
performance” (Neely, 1998)

Why People are Important
As product life cycles shorten and skill
development life cycles lengthen .....
then the resource base must therefore
be actively managed as the mainstay of
competitive strategy
(Klein, Edge and Kass 1991)

Identifying Resource
o
What it is
-
An activity and or process that is
capable of utilisation
by the organisation
o
What it does
-
An activity or component within an organisation that
adds
value
to the Organisation
o
How it does it
-
Provides functionality
to the organisation
o
Definition
-
Resources are those aspects of an organisation which constitute
order-Qualifying
and
order winning
capabilities
(where recognised)
Tangible resource
–
Machines - skills - location - use of existing technology - adaptability - information
transfer
Non tangible resource
–
Good will - knowledge - willingness to adapt - future technological capability - ability
to learn - match of organisation culture - communication

Managing People
Most organisations develop systems and
procedures to manage their human assets
• Appraisal schemes
• Career planning
• Compensation system
(Understanding Organisations, Charles Handy, 1993:225)
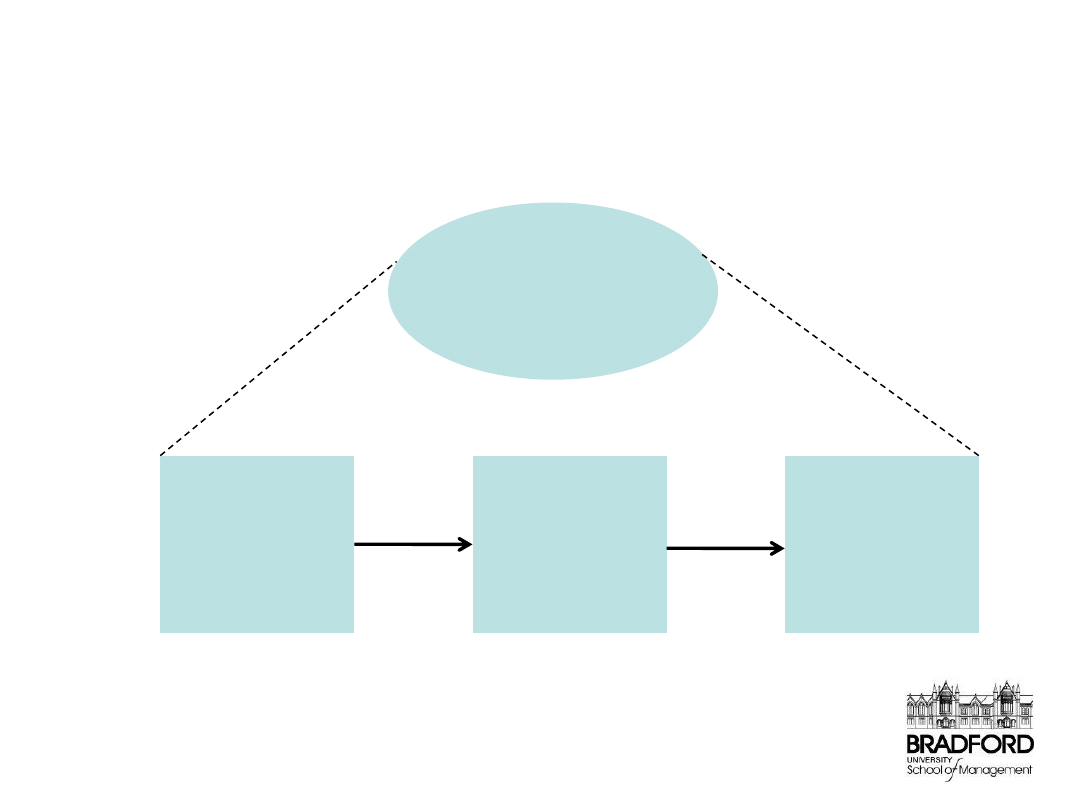
Performance-driven Behaviour
De Waal, 2007:211
Design a
Performance-driven
Behavioural Model
Foster
organisational
performance-
driven
behaviour
Foster
individual
perofrmance-
driven
behaviour
Align personal
with
organisational
objectives

People and Knowledge
Knowledge is information with process
applied to give it “value added”
Liebowitz, 1999
“Knowledge is information combined
with experience, context, interpretation,
and reflection. It is a high value form of
information that is ready to apply to
decisions and actions”.
Davenport et al., 1998

Performance and Knowledge
Two distinctions can be observed from the
definitions of knowledge. These are:
• The data-information-knowledge
progression
• The human/social element which
encompasses beliefs, skills and
experiences

Identifying Knowledge
Swan et al., 1999
Social Knowledge
• Knowledge for innovation is socially
constructed and based on experience.
• Knowledge can be tacit and is
transferred through participation in
social networks including occupational
groups and teams
• The primary function of knowledge
management is to encourage
knowledge sharing through networking
• The critical success factor is trust and
collaboration
Cognitive Knowledge
• Knowledge for innovation is equal to
objectively defined concepts and
facts
• Knowledge can be codified and
transferred through text: information
systems have a crucial role
• The primary function of knowledge
management is to codify and capture
knowledge
• The critical success factor is
technology

What does knowledge do?
Knowledge…………
• Is the driving force behind operational processes and tasks
• Enables the smooth running of processes that transform inputs into
outputs
• Allows each process to be broken down so that requirements for
performing the tasks can be identified
There fore, knowledge is………….
“ the know what, know why and know how to manage organisational processes
and procedures in the facilitation of input transformation to produce goods
and/or services and is embodied in the successful execution of processes,
routines, directives and organisational practices that help to complete the
transformation process”
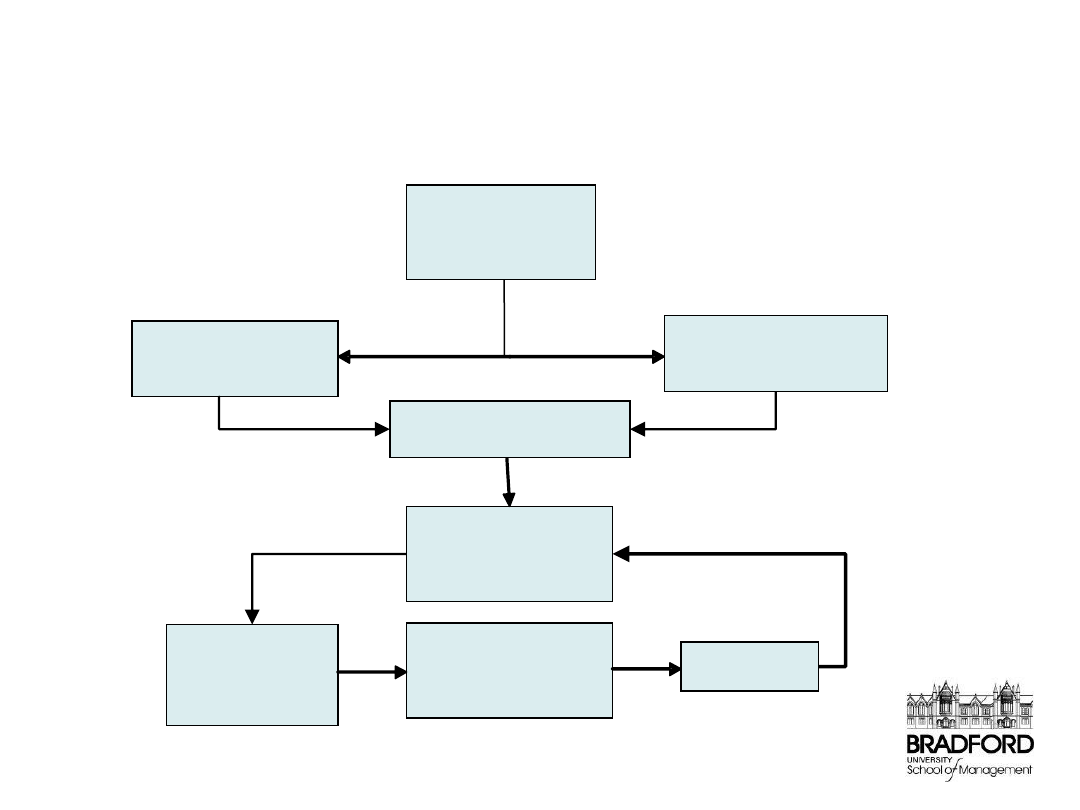
Knowledge Management
Activities
Identify Key
Knowledge and
Competencies
Develop key skills
and Competencies
Access
Knowledge at
the right time
Share Key Knowledge
Integrate new
Knowledge, data
and information
Create Knowledge
for Innovation
Business Process
New and Retained
Knowledge integrated
Output
Feedback
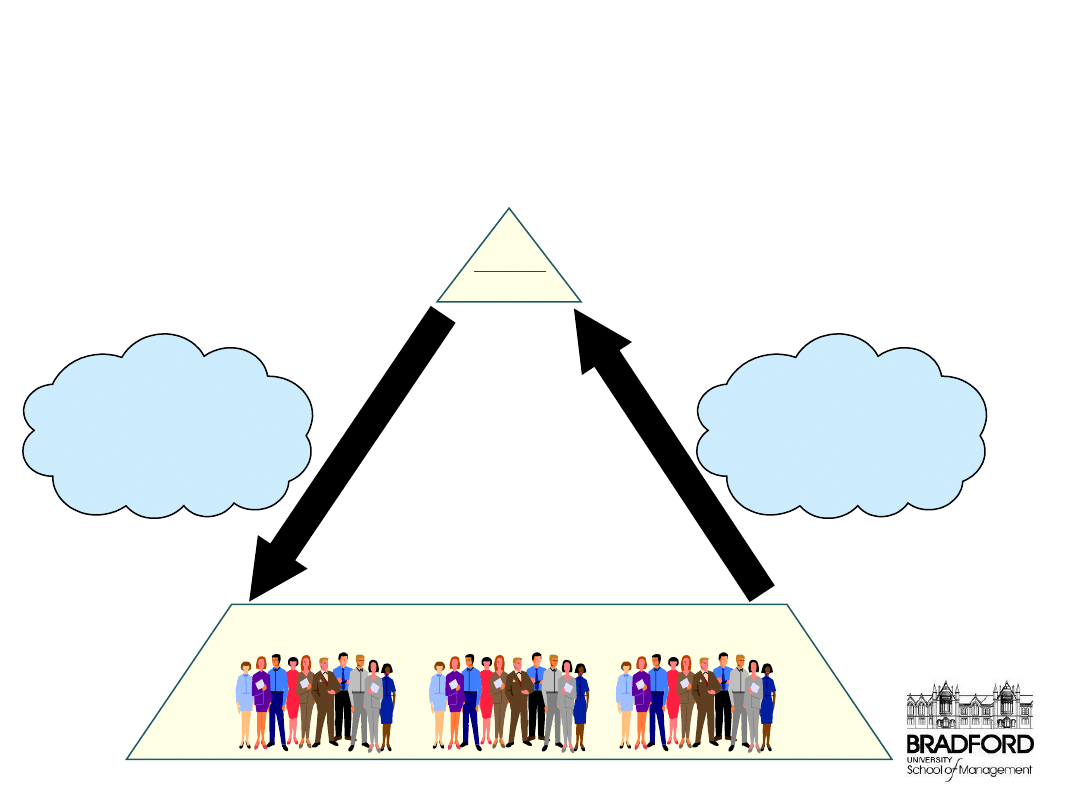
KPIs throughout the organisation
Top-
Down “Bridging
Process” To Share
the Strategy & Align
the Workforce
Bottom-Up Process
to Internalize &
Execute the
Strategy
CORP
SBU
The Strategy Focused Workforce
• EDUCATION
• PERSONAL GOAL
ALIGNMENT
• BALANCED PAYCHECKS
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
Lecture 4 Supplier Relationship Management
Lecture 2 Customer Relationship Management
CRM - customer relationship management, CRM, czyli skrót od Customer Relationship Management, to okr
McGraw Hill Briefcase Books Customer Relationship Management
Yamaha Expansion Manager V2 5 2 for Windows 10 8
Lecture 1 Business Performance Management
Customers Relationship Management
Customer Relationship Management
ZPT 02 Project management processes V2 odblokowany
A Managers Guide To Employment Law
Advertising, Marketing, Promotions, Public Relations, and Sales Managers
How to Persuade and Influence Your Managers Colleagues and Employees
A Managers Guide To Employment Law
Norbury General relativity and cosmology for undergraduates (Wisconsin lecture notes, 1997)(116s)
lecture slides Powerpoint Slides Week1 1 6 Endocrine Assessment & Pathology revised v2
How employers manage absence
(IV)Relative therapeutic efficacy of the Williams and McKenzie protocols in back pain management
więcej podobnych podstron
