microeconomics p19

Microeconomics
Anna Blajer-Goiębiewska M. Sc.
Exercise 13. Building contractor ‘BOB’ has got an order to build few shopping pavilions in a village. Client gives the price of PLN 16 000 for each pavilion which is parameterized due to the contract. The cost of building one pavilion is estimated to be PLN 12 000. Moreover there are other costs that are not directly dependent from the production (for instance accounting Staff salaries, insurance costs, depreciation costs) and these are estimated to amount PLN 48 000. How many pavilions will enable ‘BOB’ company to reach their break even point?
Exercise 14. Fili in the table assuming that the price of the product remains the same, while the level of production in changing. Find the level of production that will maximize the company’s profit.
|
X |
TC |
TVC |
TFC |
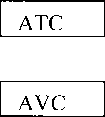
AVC |
AFC |
ATC |
MC |
P |
TR |
MR |
WE |
|
0 |
60 |
0 |
80 | ||||||||
|
1 |
40 | ||||||||||
|
2 |
70 | ||||||||||
|
3 |
120 | ||||||||||
|
4 |
220 | ||||||||||
|
5 |
400 | ||||||||||
|
6 |
630 |
Exercise 15. Assuming that the company is maximizing profit describe the situation, when:
▲
|
a) |
P> ATC |
|
b) |
P = ATC |
|
c) |
ATC > P > AVC |
|
d) |
P = AVC |
|
e) |
AVC > P |
Exercise 16. Fili in the table assuming that there are no fixed costs, the price for the product equals $2 and the price of the only one direct materiał is $7.
|
A |
Pa |
TC |
Px |
TP |
TR |
WE |
Exercise 17. Fili in the table.
|
Cu |
ci |
TC |
VC |
FC |
ATC |
AVC |
AFC |
MC |
X |
P |
TR |
WE |
|
35 |
Min=25 |
10 |
5 |
30 |
Exercise 18. Fili in the table.
|
Cu |
Cj |
TC |
VC |
FC |
ATC |
AVC |
AFC |
MC |
X |
P |
TR |
WE |
|
30 |
45 |
Min= |
20 |
200 |
80 |
Exercise 19. Explain, in what way sunk costs creates our inability to make elear decisions about:
a) US’s involvement in Iraq.
b) going or not watching the basketball gamę with your friend, if there is a big snowstorm and you have already bought tickets (each cost $50). Would you be morę likely to go if the tickets were given to you for free?
c) a cutting-edge digital product, that is not successful in the marketplace, but the costs associated with the product development (in the form of research & development and intellectual property, labor) were significant.
d) choosing commercial partners in the case of an exporter analysing foreign markets.
19
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
skanuj0003 (73) Microeconomics Anna Blajer-Gotębiewska M. Sc. Exercise 8. Consider the fołlowing seą
microeconomics p18 Microeconomics Anna Blajer-Gołębiewska M. Sc. Exercise 9. On the base of profit a
skanuj0002 Microeconomics Anna Blajer-Gołębiewska M. Sc.Exercise 8. Consumer purchases only two type
skanuj0002 Microeconomics Anna Blajer-Gołębiewska M. Sc. Exercise 4. The company produces sophistica
skanuj0003 Microeconomics Anna Blajer-Gołębiewska M. Sc. Exercise 11. Consumer’s income eąuals 12 mo
skanuj0001 Anna Blajer-Goiębiewska M. Sc. Microeconomics7. MARKETS FOR FACTOR INPUTS Exercise 1. The
skanuj0004 Microeconomics Anna Blajer-Gołębiewska M. Sc.COSTS AND COSTS MINIMIZATION Exercise I. Div
skanuj0001 (69) Microeconomics Anna Blajer-Gołębiewska M. Sc.6. IMPERFECT COMPETITION AND STRATEGIC
skanuj0002 (76) Anna Blajer-Gołębiewska M. Sc. Exerci.se 5. There is a duopoly in the market. Compan
skanuj0001 Anna Blajer-Gołębiewska M. Sc. MicroeconomicsCONSUMER BEHAVIOURExercise 1. Match the labę
Anna Blajer-Gołębiewska Małgorzata ZielenkiewiczROZDZIAŁ 8TEORIA GIER JAKO NARZĘDZIE EKONOMII XX I X
86 Anna Bląjer-Golębiewska, Małgorzata Zielenkiewicz • czas podejmowania decyzji
78 Anna Blajer-Golębiewska, Małgorzata Zielenkiewicz Dynamiczny charakter zjawisk wymagał innego
80 Anna Blajer-Golębiewska, Małgorzata Zielenkiewicz własnej użyteczności z wypłat (dlatego też
więcej podobnych podstron