F00574 017 f023

[a] Haemodialysis
[Bi Haemofiltration
Dialysate ■
Ultrafiltrate
Haemodialyser
Haemofilter
Blood
Blood
• Typical smali solute clearance 160 mt/min • Typical smali solute clearance (2 litres/hr exchanges)
• Used in both acute and chronic renal failure 33ml/min
• ? Less circulatory instability than haemodialysis
• Used mostly in acute renal failure
• Access to the circulation for haemodialysis or filtration is required. Arleriovenous fistulae. temporary or semi-permanent tunnelled central venous lines or arterio-venous shunts {e.g. Scribner shunt) may be used. The extracorporeal Circuit reguires anticoagulation, typically with heparin
[5] Transplantation
[cl Peritoneal dialysis
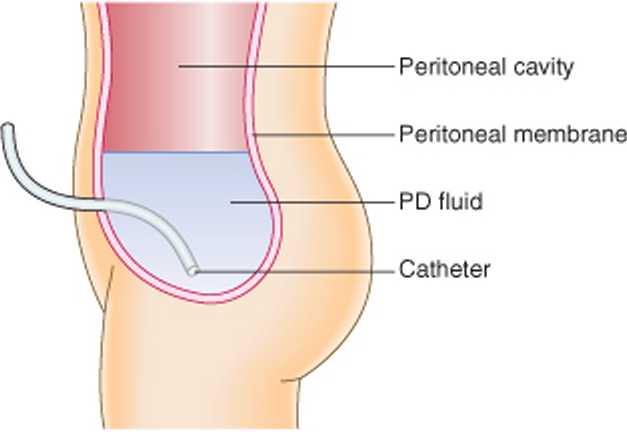
• Access to the peritoneal cavity via Tenckhoff catheter
• Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD): typically 4 exchanges of 2 litres of fluid a day 4-6 hours apart
• Automated peritoneal dialysis (APD): uses a machinę
to perform exchanges overnight (8-10 hours). Used mostly in chronic renal failure

• Successful transplantation extends the life expectancy of patients with end-stage CRF
• Requires long-term use of immunosuppressives with attendant risks
[ę] Conservative management
© Elsevier. Boon et al.: Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine 20e - www.studentconsult.com
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
F00574 017 f001 Vena cava Aorta Renal artery Meau
F00574 017 f002 Renal pelvis Prostatę Ureteric orifice Detrusor muscle Urethra © Elsevier. Boon et a
F00574 017 f003 IN Urea OUT IN Creatinine OUT Reduced excretion •RENAL FAILURE • Competition for
F00574 017 f009 1 1 PRE-RENAL Effects of pre-renal conditions Loss of renal function, e.g. from hypo
F00574 017 f014 Normal Storage micturition cycle Voiding Minimal pressure rise in bladder as it fill
F00574 017 f020 Jugular venous pressure raised in fluid overload or pericardial tamponade Pulsu
F00574 017 f022 Impaircd renal function I P04 excretion Decreased 1,25(OH)2D (diminished corwersion
F00574 017 f030 IgA nephropathy Minimal change nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy Post-streptococcal A
F00574 017 f035a [a] Normal tubular histołogy © Elsevier. Boon et al.: Davidson s Principles and Pra
F00574 017 f035c [Ć] Acute pyelonephritis © Elsevier. Boon et al.: Davidson s Principles and Practic
F00574 017 g001 Fundoscopy Hypertensive changesA Jugular vcnous pressure Elevated in fluid overload
F00574 017 u001 GFR normaJ rangę = 120 ± 25 ml/mia/1.73 m?
F00574 017 u004 CrCI = 186 x (creatinine in umol/l/88.4) ’IM x (Age in yrs)117(0 x (0.742 if female)
F00574 017 f013 Stono in lower urcter ESWL Uteroscopic destruction Dornier basket extraction Stone i
fed 017 a Patent USA 12 czerwca 2001 Strona 12 z 32 US 6246561 BI Fig, 16 B Do ramion rdzenia dostar
skanuj0010 (259) Białystok 3061-1104.6* tonun nirt—nri tuwtn wyanuł RwŁwttrt«» • l«Kyaxdi $a u«wi rj
skanuj0011 (223) K> 1 jpv T~(. i { i BI.TTnH Pi -L- ż 3 r~n< sirif-4 SI J rj_ i 5N*
więcej podobnych podstron