netter144

Colonie Motility
GASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY
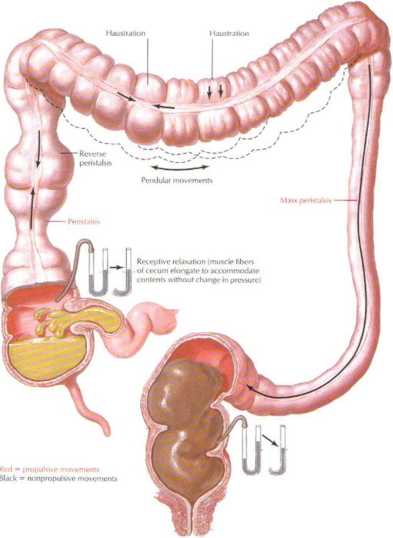
Adaptiw lelłOtation (intralumin.il pressure inereased as contents enter bowel segment; Jater rruy return to normal as musculature relaxes to aCcommodate contents)
Figurę 7.22 Coionic Motility
Motility patterns in the colon include thosc chał propel luminal contents toward the rcctum (i.e., peristalsis and mass peristalsis) and łhose that prolong contact of the luminal contents with the absorp-łive epithelial cells. These Inter patterns allow suttident contact time for maximal absorption of fluid from the feces. Conditions that pro mote the própulsive patterns result in diarrhea.
162
Wyszukiwarka
Podobne podstrony:
27075 netter133 Gastric MotilityGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Factors Afferting Caslric
netter141 Smali Intestine MotiiityGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Rhythmic sepmentation Intraluminal
netter60 Electrocardiogram: IIICARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Norm.il Sequence of Cardiac Depolarization
netter129 MotilityGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY GUT LUMEN MUCOSA Ascending (orał) pathway Excitatory m
70370 netter129 MotilityGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY GUT LUMEN MUCOSA Ascending (orał) pathway Excita
netter106 Glomerular FiltratinnRENAL PHYSIOLOGY Colloid osmotic pressure of plasma (Uln) U
netter113 Urine DilutiorRENAL PHYSIOLOGY h2o Na Cl" h2o 375 —*t- Urea Notę: Figurcs given are e
netter126 Autonomie lnnervationGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 7.5 Aijtonomic Innervation The inn
netter127 Autonomie lnnervationGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY m generał sympathetics decrease peristals
netter134 Castric DigestionGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 7.12 Gastric Digestiye Function The st
netter152 Intrahepatii Biliary SystemGASTROINTESTINAL PHYSIOLOGY Noto. The figurę shows bile canalic
netter58 Bectrocardiogram: ICARDIOYASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Normal $cqucncc ot Cardiac Depolarization and
netter61 Cardiac CycleCARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY Figurę 4.9 Cardiac Cycle The cardiac cycle represent
więcej podobnych podstron